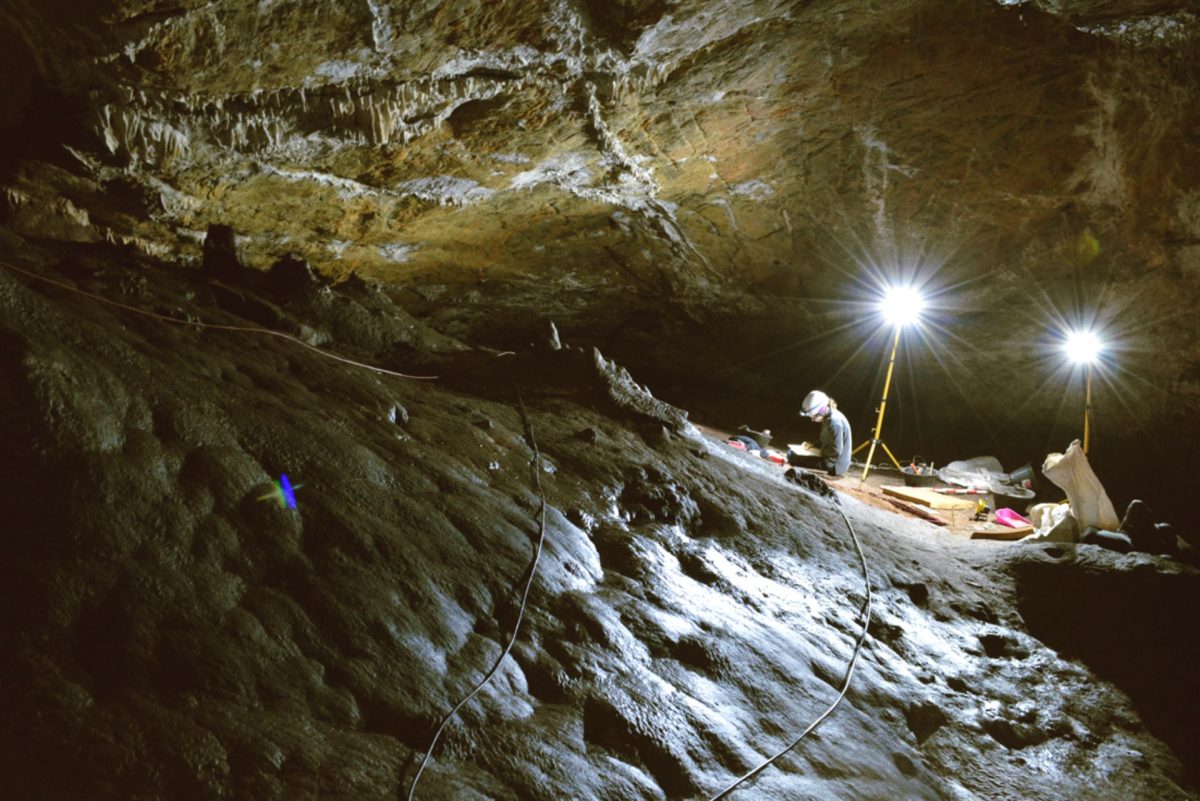
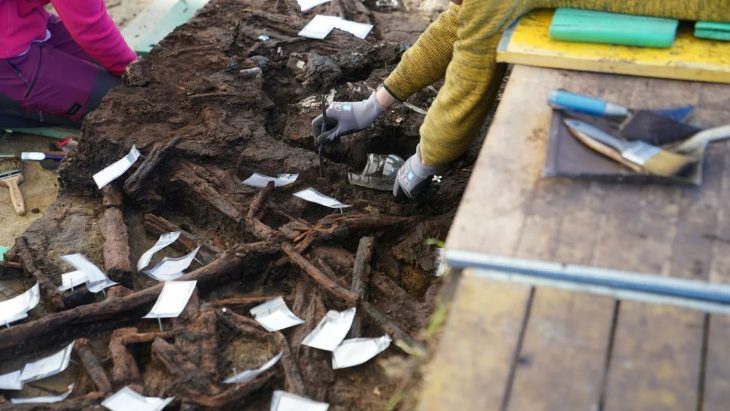
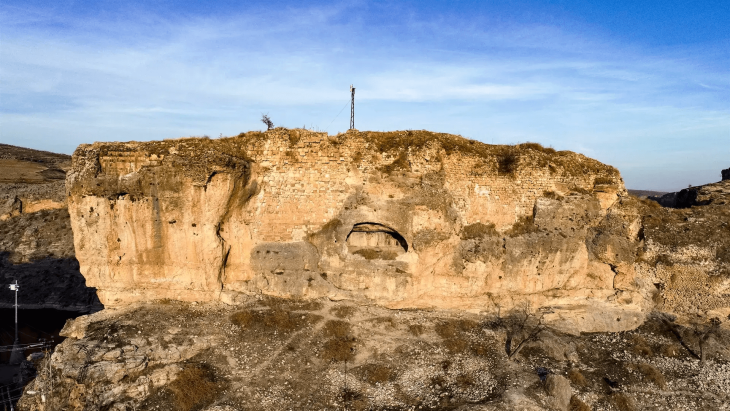
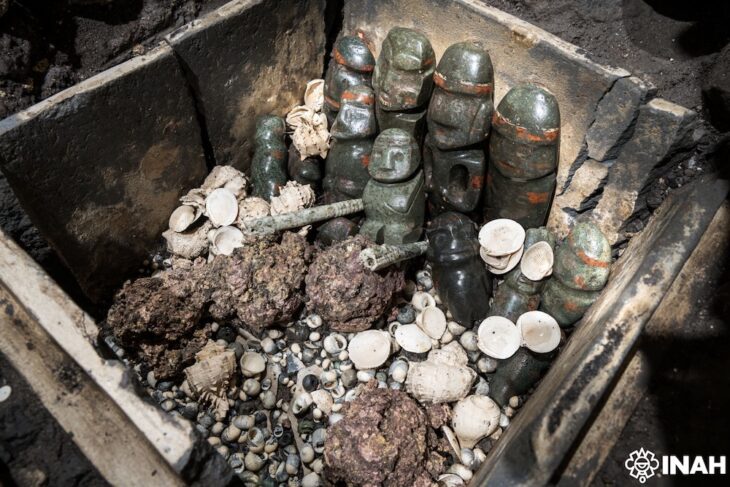
In Malaga’s Cueva de Ardales, up to 13 freshwater and marine shells that were carefully transformed by humans between 25,000 and 30,000 years ago have been discovered.
According to a study published in the environmental scientific journal Environmental Archaeology, the first Homo sapiens wore necklaces and earrings made from seashells from the Bay of Malaga.
This incredible discovery was the result of research conducted in collaboration with the Neanderthal Museum of Colonia, the University of Colonia, and the Cueva de Ardales, according to a press release from the University of Cadiz.
This archaeological enclave is now once more among the most significant in the Iberian Peninsula thanks to the discovery. When it comes to the Paleolithic era, body adornments are a subject of great interest to the scientific community.
According to the scientific article, the shells were “carefully transformed” by humans of the genus Homo sapiens into ornaments and pendants to decorate the bodies of these groups that occupied the Ardales Cave.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
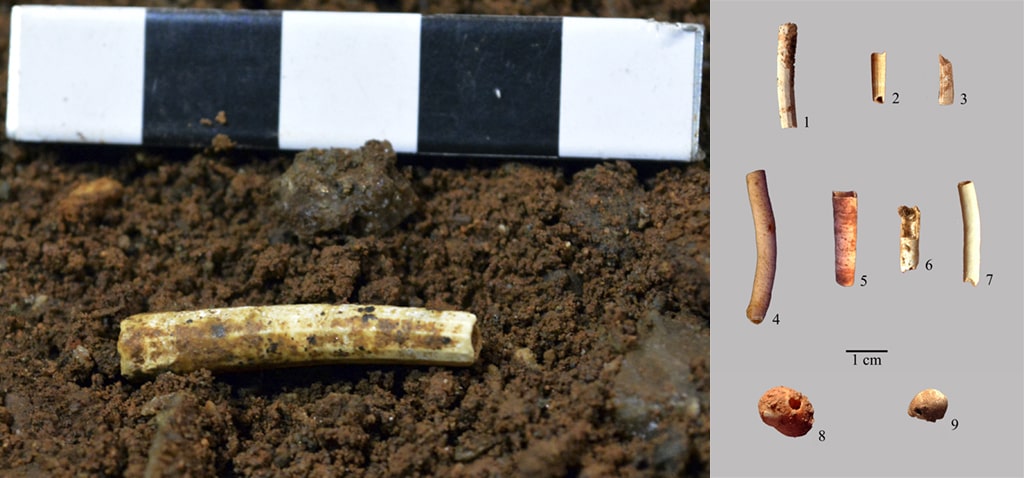

The symbolic value of these natural supports and the distance that human groups occasionally traveled to gather them and turn them into decorative elements represented a significant advancement in the development of cognition.
The analysis of these shells has been headed by UCA professor Juan Jesús Cantillo Duarte. “It is unusual to find this type of marine remains in caves located so far inland and with such an ancient chronology. On the Mediterranean, only a little more than a hundred remains were known, and all of them are located on the coast,” Duarte said.
“ The inhabitants of the Ardales cave, however, had to travel a distance of more than 50 km to collect the shells on the coast”, added Professor José Ramos.
Also noteworthy was: “the presence of vermetids, a kind of tube-shaped snail that is uncommon in the archaeological record”, stressed Cantillo Duarte.
The chronological framework and the association of these ornaments with the rock art and lithic remains documented inside the cave confirm their social dimension.
“The results of the excavations in the Ardales Cave suggest that it was used as a place for specialized symbolic activities during various phases of the Upper Palaeolithic,” said Pedro Cantalejo, research director of the Ardales Cave, for whom the cave still has much to tell.