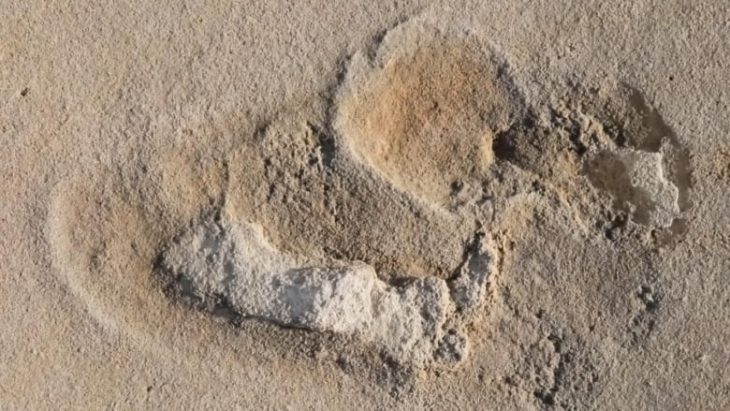
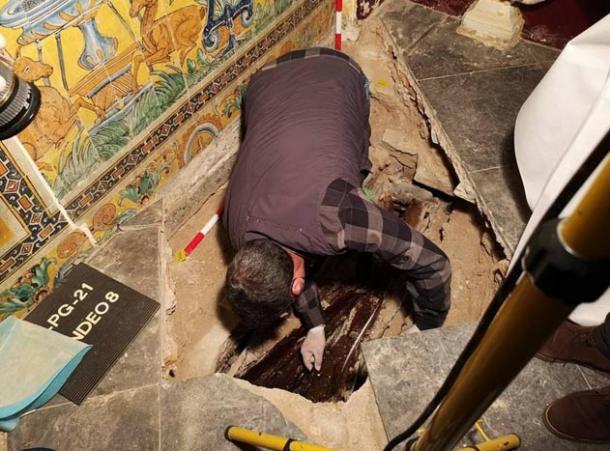
A team of international and South African researchers uncovered the fossil remains of an early hominid kid who died almost 250,000 years ago in a cave in South Africa.
Children’s fossilized remains are uncommon because their bones are too thin and fragile to survive for eons.
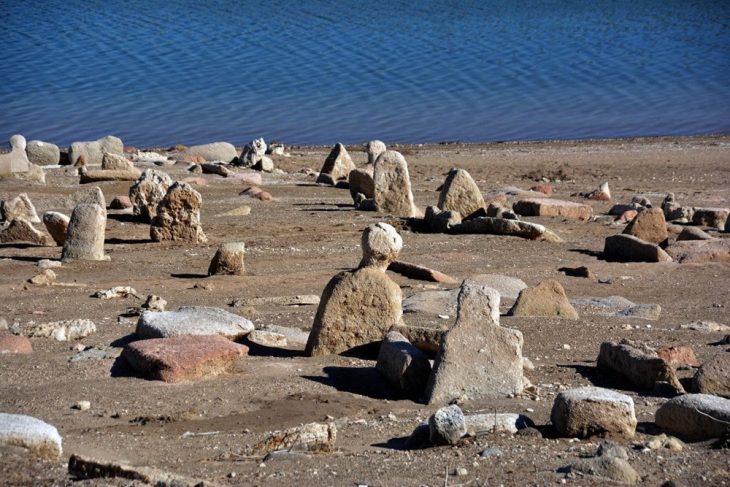
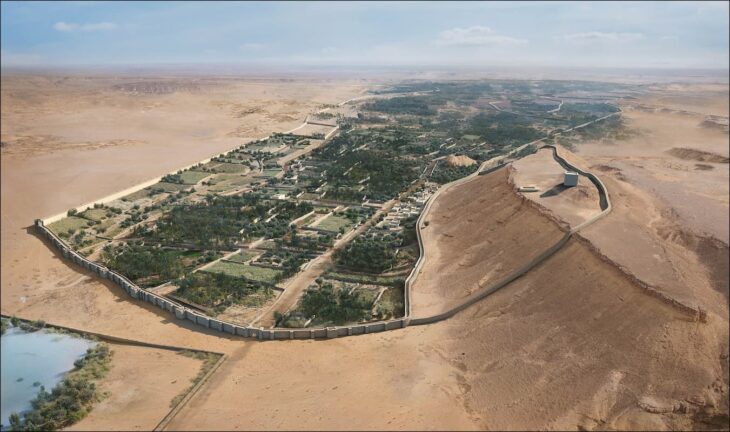
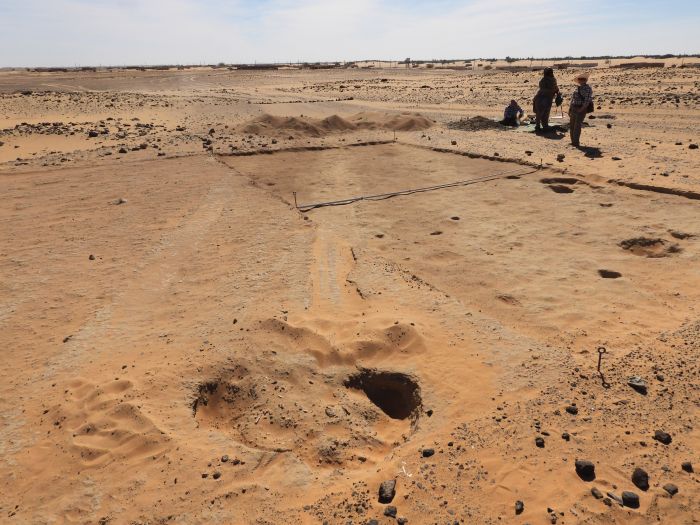
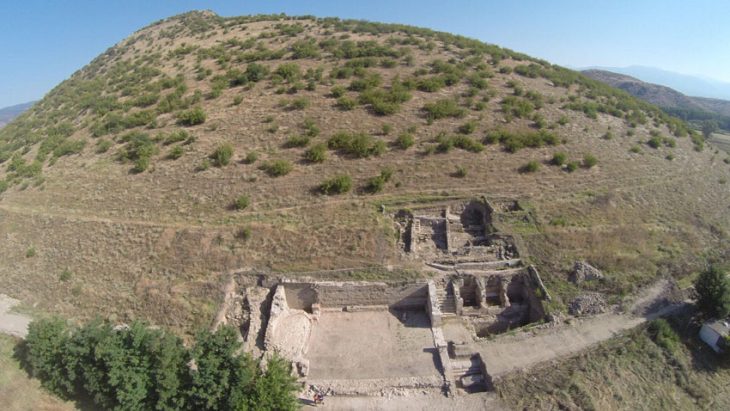
The self-proclaimed Cradle of Humankind, designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1999, is a series of limestone caverns located approximately 50 kilometers (30 miles) northwest of Johannesburg. The most recent discovery was discovered around 30 meters (100 feet) below the earth).
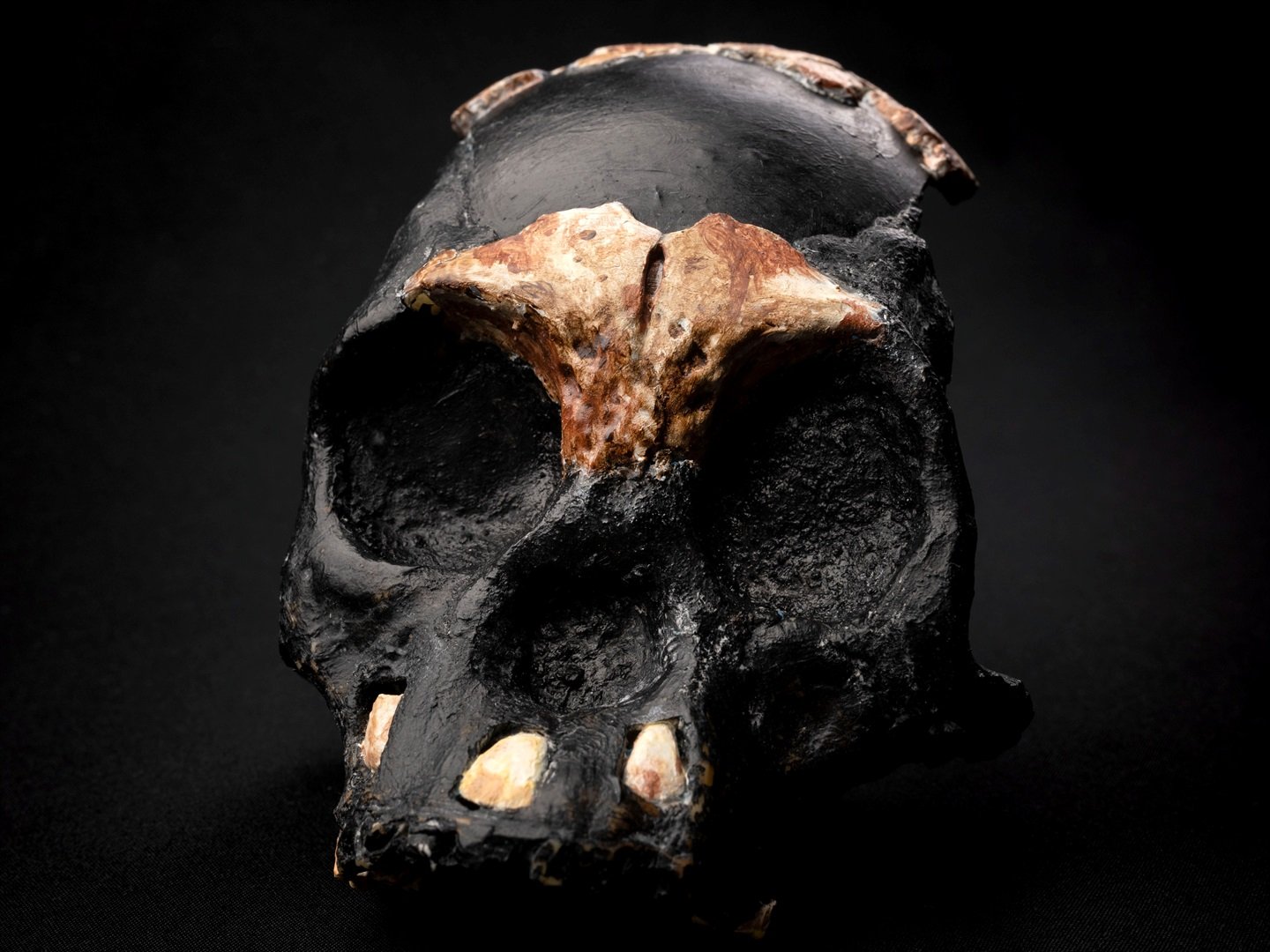
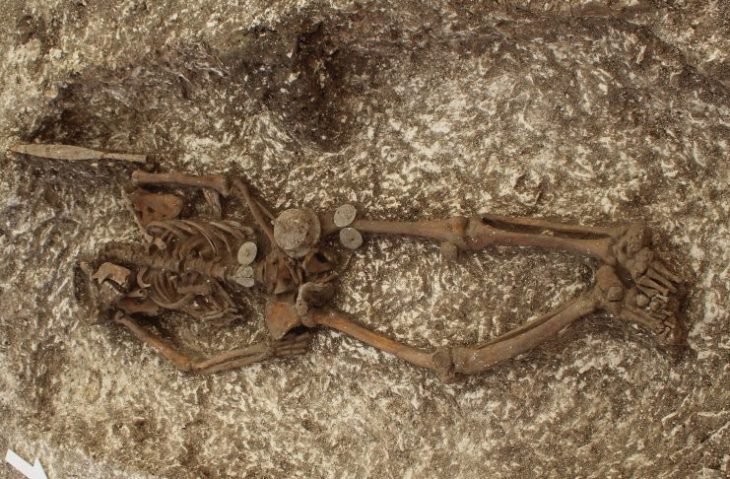
The researchers revealed the finding of a partial skull and teeth of a Homo Naledi kid who died over 250,000 years ago when it was between the ages of four and six. According to the statement made Thursday, the remains were discovered in a secluded portion of the cave, which suggests that the person was deliberately deposited there, maybe as a form of tomb.
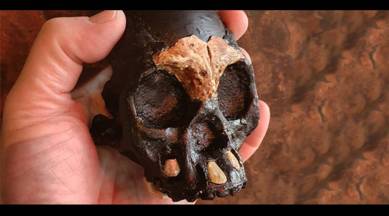
The placement “adds mystery as to how these many remains came to be in these remote, dark spaces of the Rising Star Cave system,” Professor Guy Berger of the University of Witwatersrand in Johannesburg, who led the team said in an announcement Thursday.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“Homo Naledi remains one of the most enigmatic ancient human relatives ever discovered,” said Berger. “It is clearly a primitive species, existing at a time when previously we thought only modern humans were in Africa. Its very presence at that time and in this place complexifies our understanding of who did what first concerning the invention of complex stone tool cultures and even ritual practices.”
Homo Naledi is an archaic human species discovered in the Rising Star Cave, Cradle of Humankind, 30 miles northwest of Johannesburg. Homo Naledi lived between 335,000 and 236,000 years ago, during the Middle Pleistocene epoch. The first finding, made public in 2015, consists of 1,550 specimens representing 737 distinct elements and at least 15 different persons.
The original discovery made public in 2015, complicated our understanding of human development by demonstrating that Homo sapiens most likely coexisted with other species of hominin – the term for hominids that include anatomically modern man.
The new discovery is described in two papers in the journal, PaleoAnthropology.
















