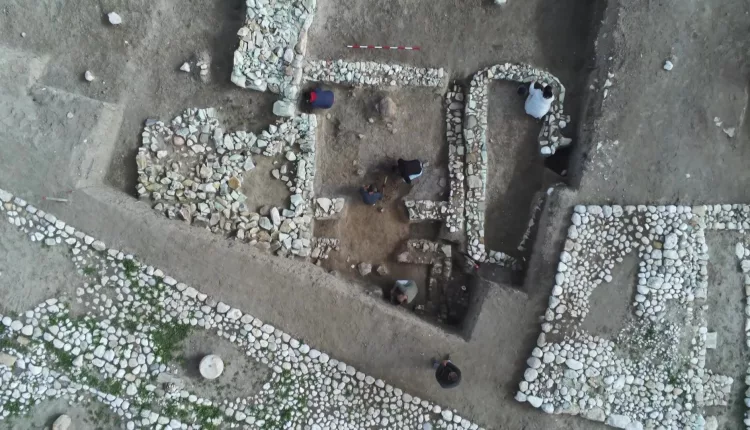
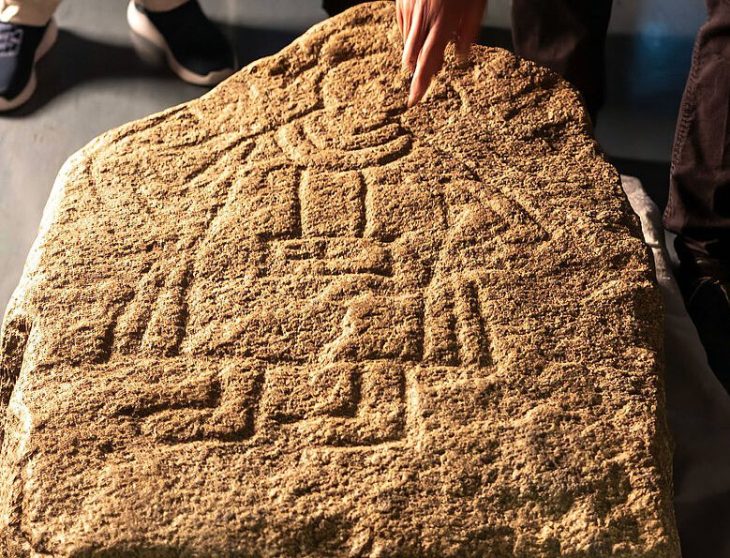
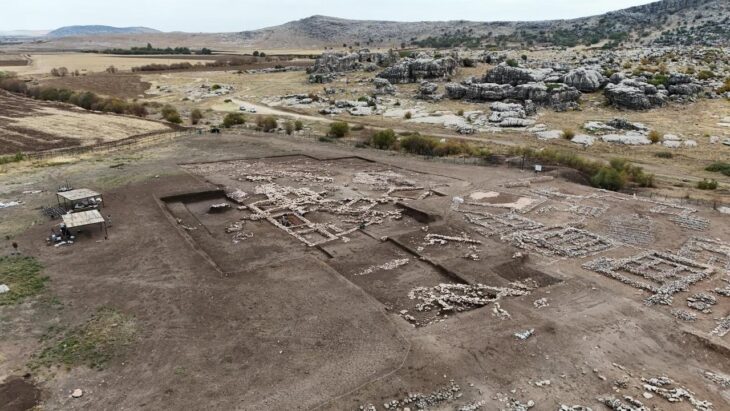
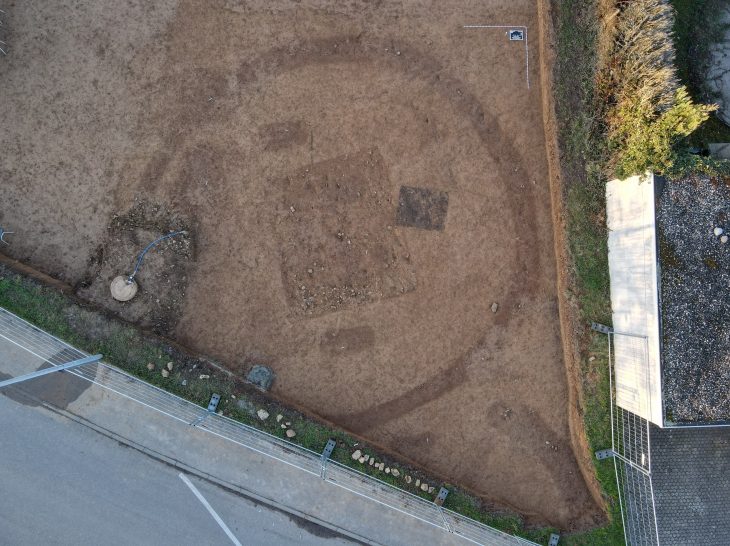
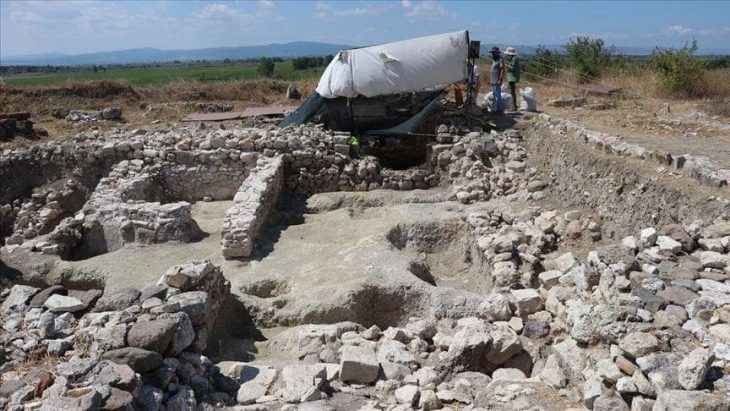
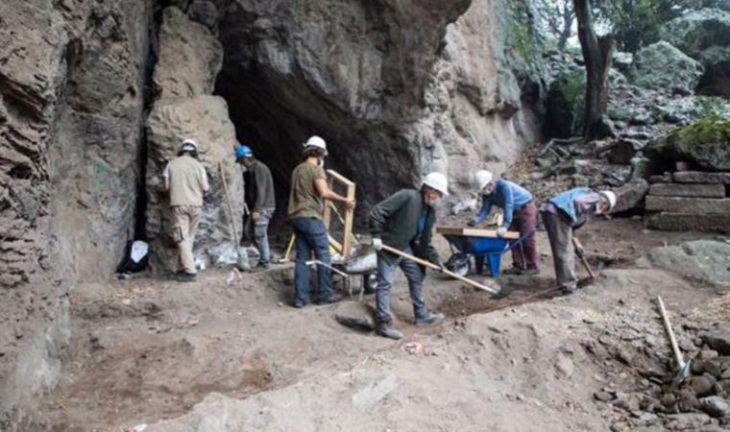
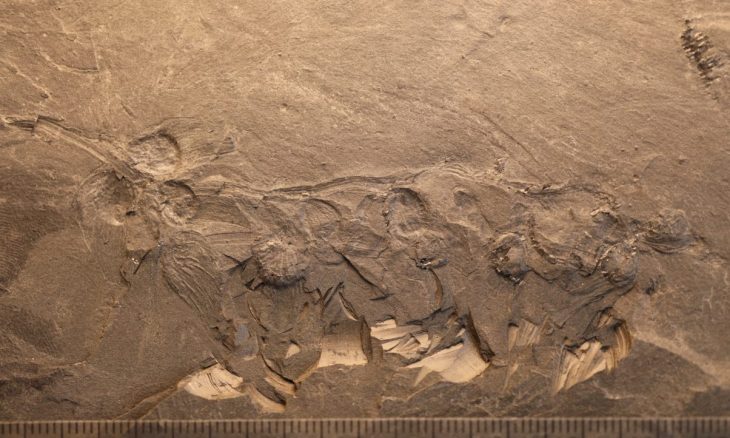
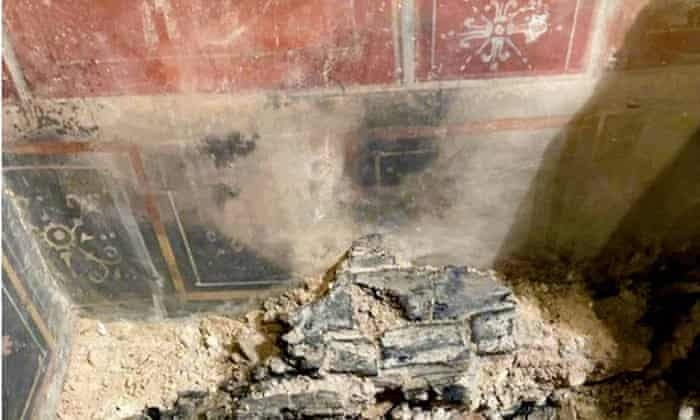
Archaeologists have discovered a sacred room and stone from the Phrygian period, dating back 2,600 years, during excavations at the Oluz Höyük settlement mound in the village of Toklucak in Türkiye’s Black Sea province of Amasya.
Professor Şevket Dönmez, who is an academic at Istanbul University’s Archaeology Department and who leads the excavations described the find as a first in Anatolian archaeology, highlighting the significance of uncovering a sacred stone linked to the goddess Kubaba.
“Discovering a sacred room and its associated sacred stone marks a first-ever occurrence in the field of Anatolian archaeology,” he stated.
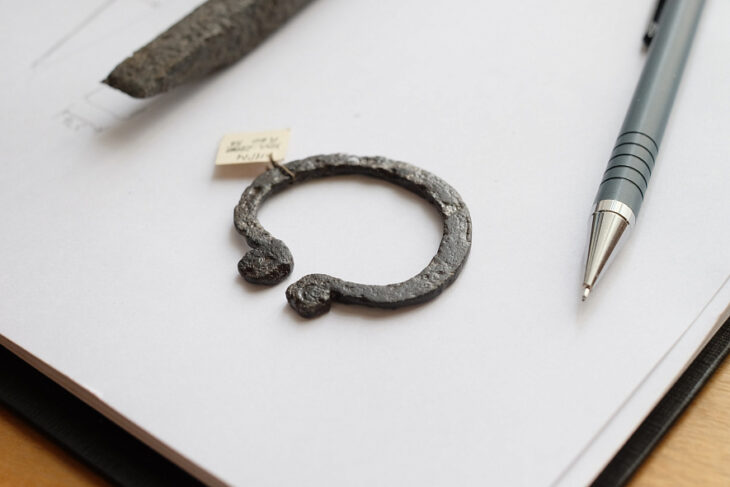
The discovery, including a 20-square-meter structure and altars dedicated to Kubaba, aligns with historical accounts of a black stone representing the goddess.
“Historical texts describe a black stone symbolizing the goddess Kubaba. Finding a sacred stone in a square structure dedicated to her in Central Anatolia is of profound significance in Anatolian archaeology. This discovery brings to life the written sources, providing tangible evidence of the relationship between the sacred stone and the mother goddess. This connection dates back to the 6th century B.C.,” Professor Donmez explained.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
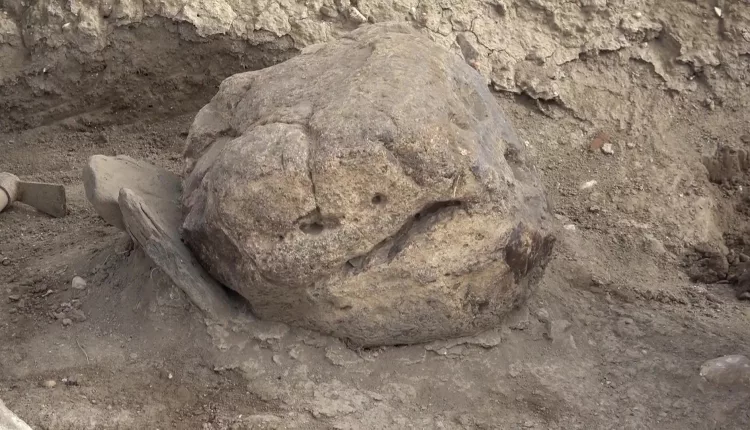

“We believe that more discoveries will emerge from this sacred space. It may even represent a transition to monotheism in Anatolia.”
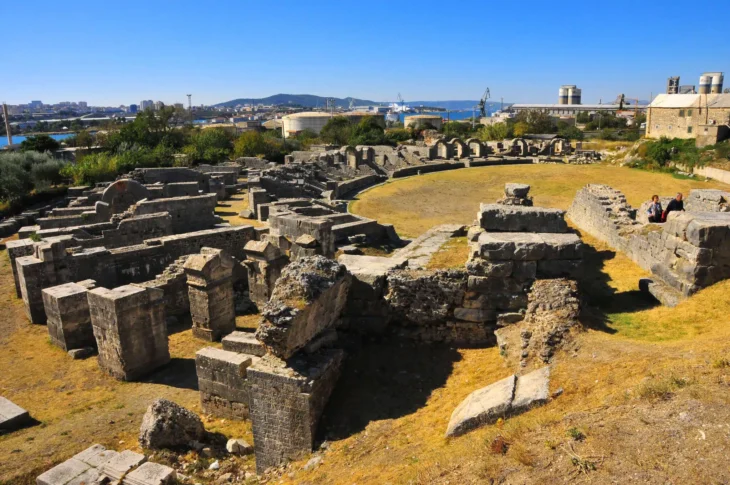
Oluzhöyük the excavations, where they came across a religious complex such as the 2,500-year-old Persian road, the firehouses (Ateşgede) found for the first time in Anatolia, and a multi-column temple, had exciting results every year.
Oluz Höyük made us distinguish some evidence regarding Anatolian Iron Age archaeology and ancient history that we haven’t noticed until today.
Oluz Höyük, located 25 kilometers west of Amasya, is an ancient city that has rich findings of religious structuring. During the excavations that have been going on for 17 years, 10 settlement layers were encountered, and each of them had a religious structure.
You can read our article about the subject: Evidence of the Birth of Archaic Monotheism in Anatolia found at Oluz Höyük, “Havangah prayer at Oluz Höyük”.
The project, supported by Türkiye’s Ministry of Culture and Tourism and local institutions, aims to restore the site and open it to tourism, potentially uncovering more elements of this sacred complex.