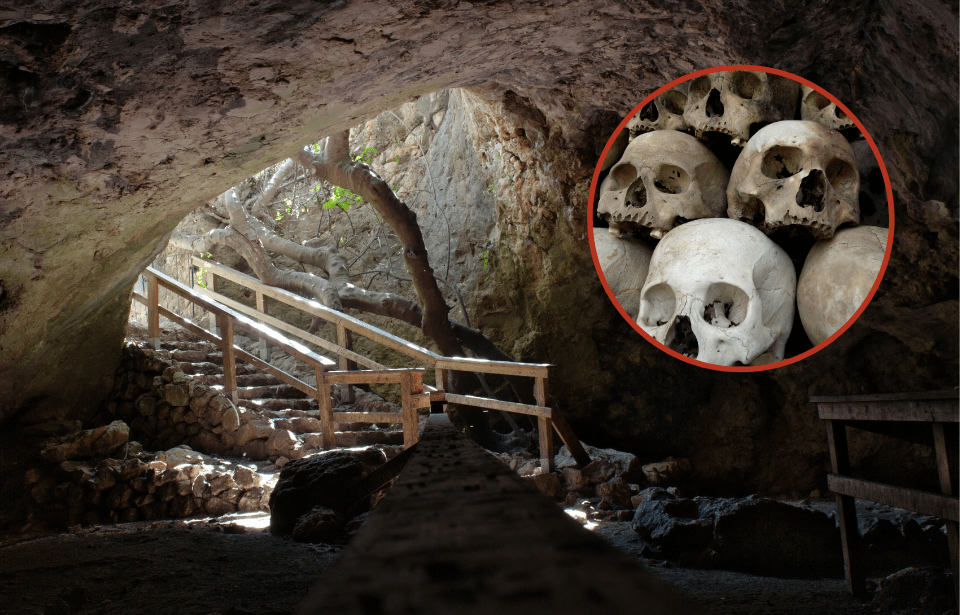
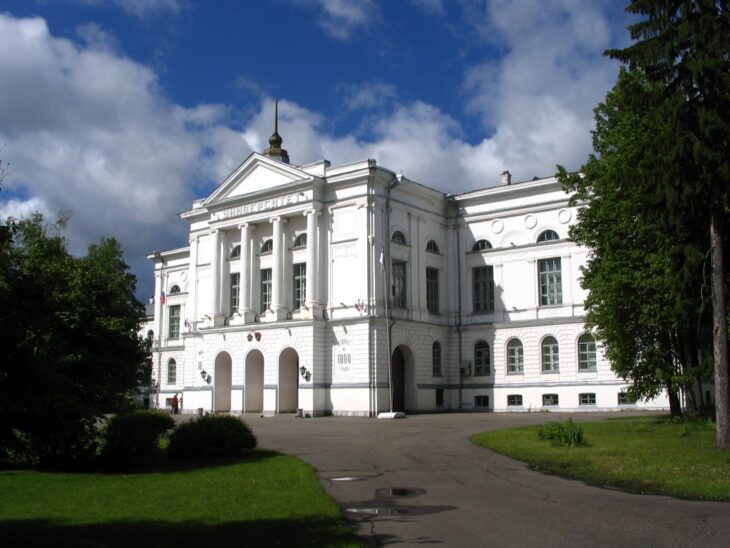
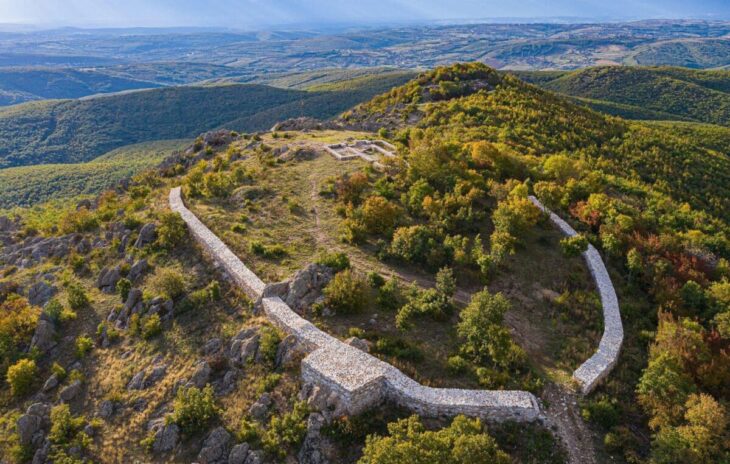
Te’omim Cave in the Jerusalem Hills may once have served as a local oracle where people communed with the dead in the hopes of learning about the future.
In Te’omim Cave, excavations that took place between 2010 and 2016 recovered a huge collection of Roman oil lamps, weapons, pieces of pottery, and actual human skulls hidden inside deep crevices.
This unusual collection of artifacts has persuaded a pair of Israeli archaeologists that an esoteric religious cult existed in the region between the second and fourth centuries AD, or during the Late Roman era.
They believe cult members used Te’omim Cave for ritual ceremonies, some of which included human sacrifices. The cave is described by researchers as a possible “portal to the underworld”.
In a new article appearing in the Harvard Theological Review, archaeologists Eitan Klein from the Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA) and Boaz Zissu from Bar-Ilan University, analyzing the discoveries made at the cave, suggest that Te’omim might have hosted “secret rites.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The use of skulls and other potent objects to pierce the veil of death and enable living people to communicate with the dead was a common form of witchcraft or divination in ancient times.
The researchers state that although these rites frequently occurred inside tombs or burial caves, they occasionally happened in nekyomanteion (or nekromanteion), also known as an “oracle of the dead.” These shrines were generally located found near water sources or in caves that were thought to be potential entrances to the underworld.
Surprisingly, early archaeological descriptions of Te’omim from the nineteenth century reveal that locals still attributed healing powers to the cave’s spring water.
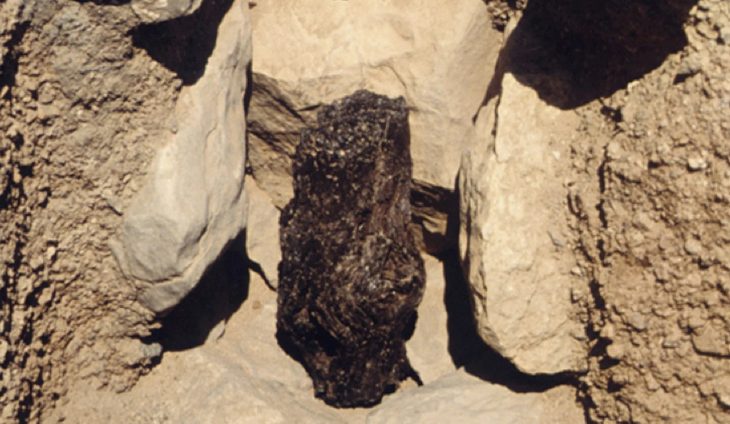
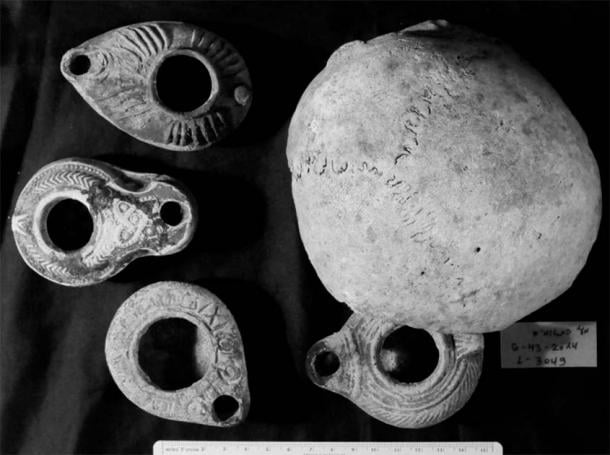
Researchers have uncovered Roman-era items stashed in nooks and crannies within the cave, many of which may have been used to communicate with the dead. One of the main signals for researchers was the discovery of more than 120 preserved oil lamps systematically placed all around the cave system.
“The fact that these lamps had been thrust into and buried deep in these hidden, hard-to-reach crevices suggests that illuminating the dark cave was not their sole purpose,” the authors report in the study. Instead, they believe the lamps were used “as part of a cultic activity.”
“The use of oil lamps for divination … was extremely widespread in the classical periods,” the study said. “The prophetic force behind the lamp was believed to be a spirit or spirits, or in some cases even gods or demons.” Messages would come through the flames of the lamps. “Divination by means of oil lamps was done by watching and interpreting the shapes created by the flame.”
“Some crevices contained groups of oil lamps mixed with weapons and pottery vessels from earlier periods or placed with human skulls,” also write the study authors.
The study explains that weapons were kept close to those who entered the cave for divination. “They served primarily to protect the believer from evil spirits and to ensure that offerings to the specific spirit being conjured up were not seized by other spirits.”
Evil spirits were believed to be afraid of metal, particularly iron and bronze. As such, keeping a metal weapon close by, such as a sword or dagger, would keep you somewhat protected from evil spirits.
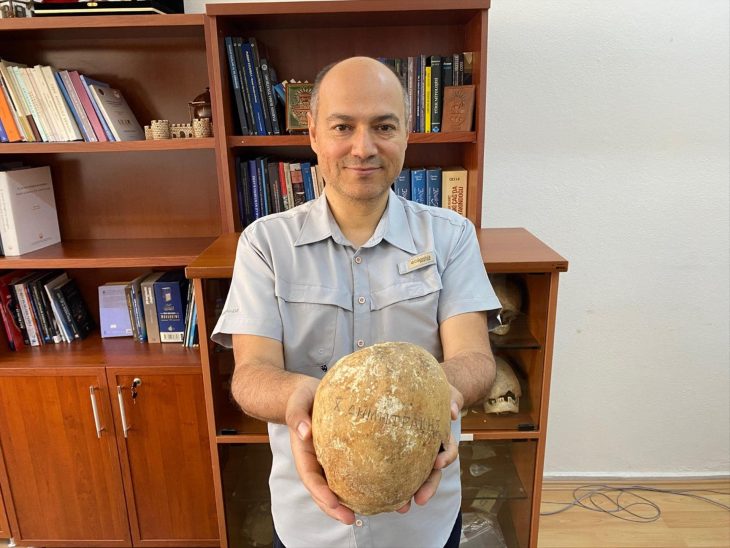
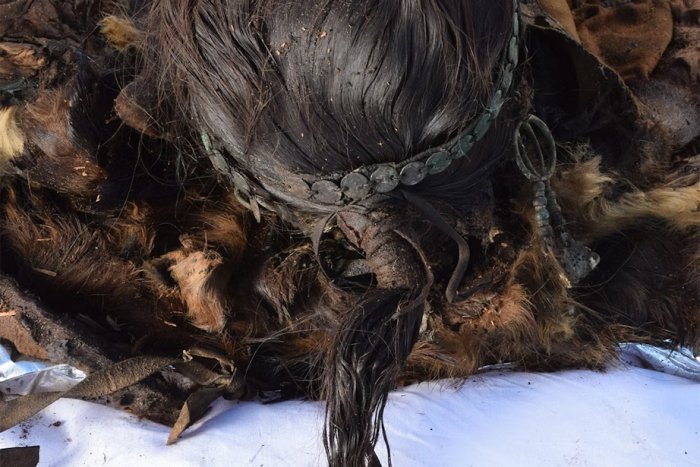
Also found in the cave system were multiple human skulls. The study states, “Due to the archaeological context of the finds and their location inside the cave, we assume that the craniums were placed together with the oil lamps as part of a ritual of magic.”
While it is of course difficult to pinpoint the exact purpose of the human skulls, the study is propose that they were used in a similar fashion to skulls found throughout the former Roman Empire which were employed for “necromancy ceremonies and communication with the dead.”