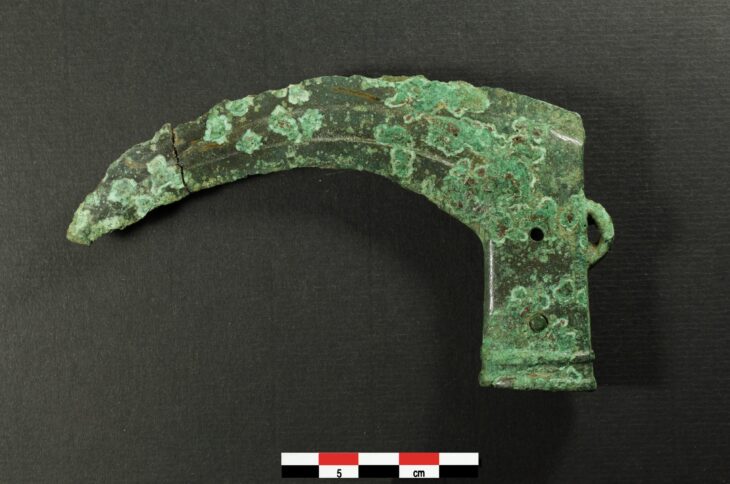
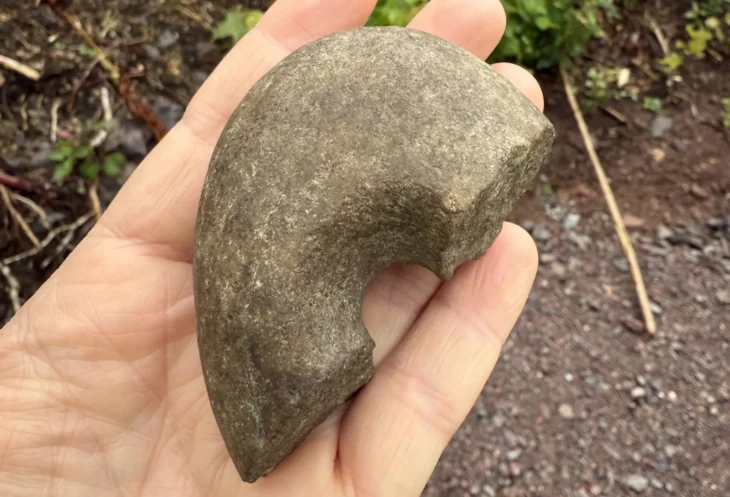
Archaeologists in Wales have made an intriguing discovery near a Roman villa. They have discovered the skeleton of a man buried facedown, adorned with a silver crossbow-style brooch, hobnailed shoes, and a sword. The silver crossbow brooch marks him as a person of high position in military or civil administration, and it is the first of its kind ever discovered in Wales.
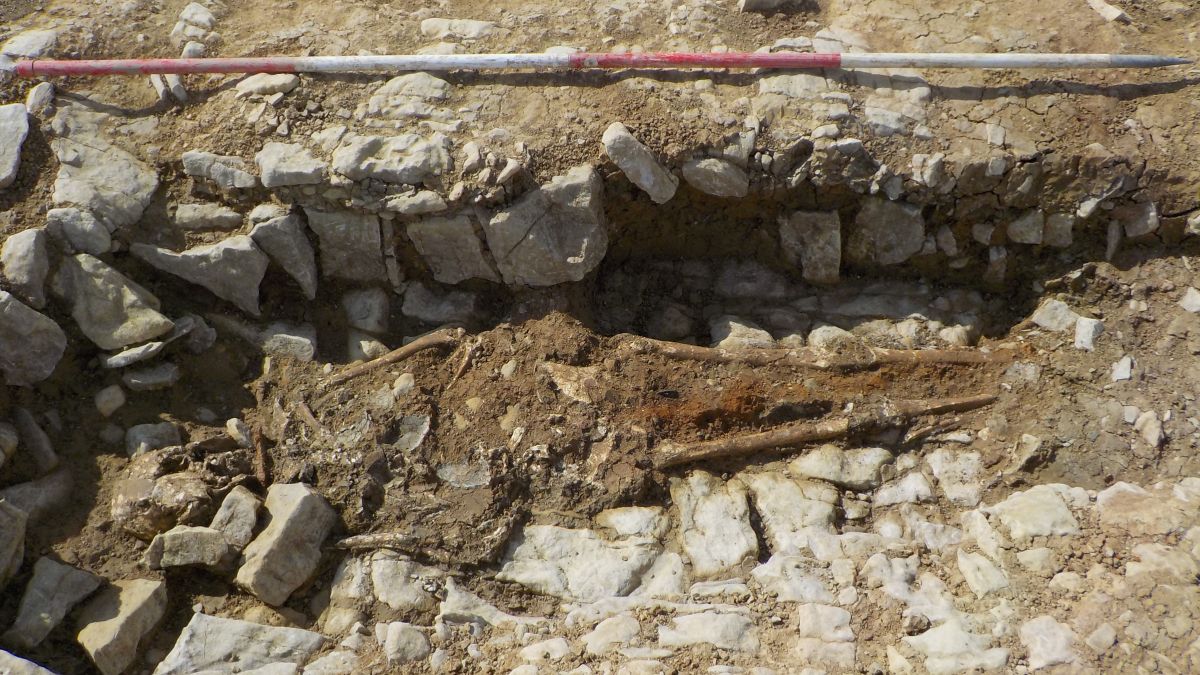
He was found face-down in a prone position, with large nails at the back of his neck, shoulder, and between his feet. This unusual posture and the presence of nails suggest that he was bound in strong restraints before burial.
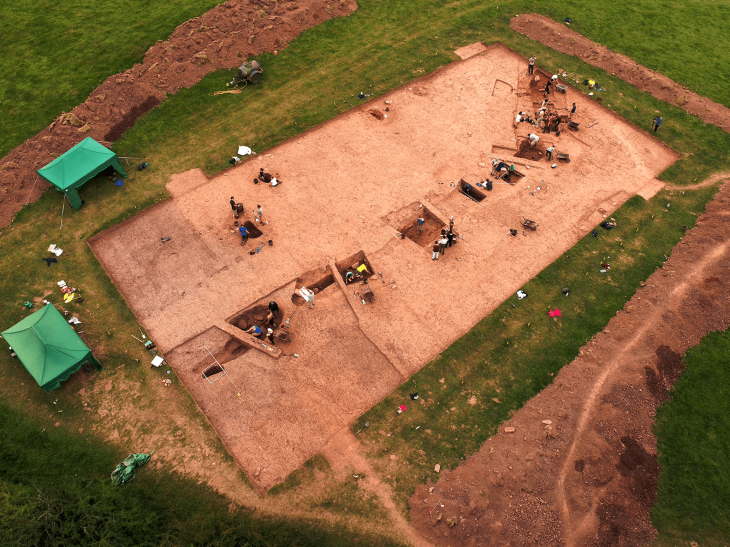
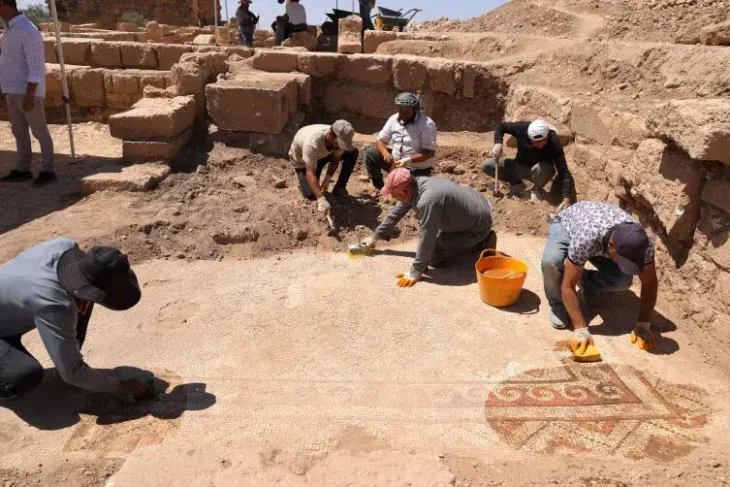
This burial, along with four others dating from the mid-third to late-fourth centuries, was found during a road improvement project near the town of Barry in south Wales. These burials are thought to be related to the Whitton Lodge Roman villa, which was discovered 50 years ago.
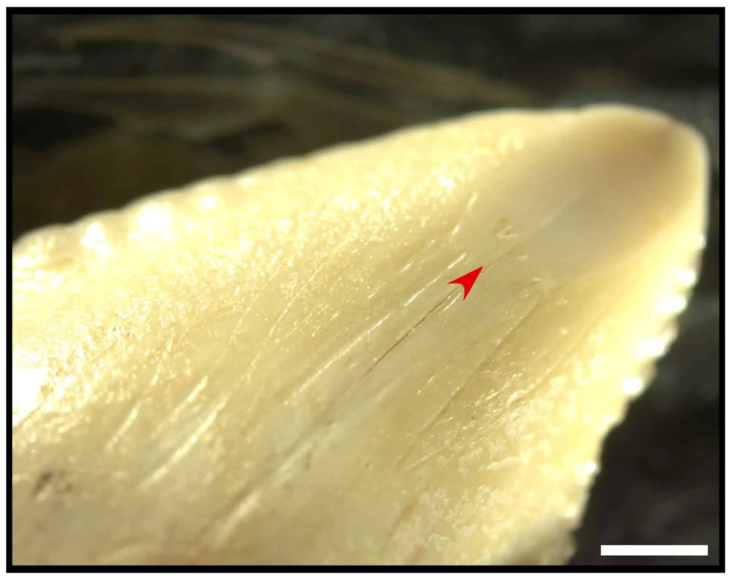
As implied by such a burial position, he was not a slave or a typical criminal. He was placed in a rock-cut grave with a wooden plank border rather than being thrown into a pit. The sword that was discovered between his legs is of the long, straight spatha variety, which in the third century A.D. replaced the short gladius as the preferred infantry weapon. The silver crossbow brooch, the first of its kind to be found in Wales, identifies him as a person of high rank in the military or civil administration.
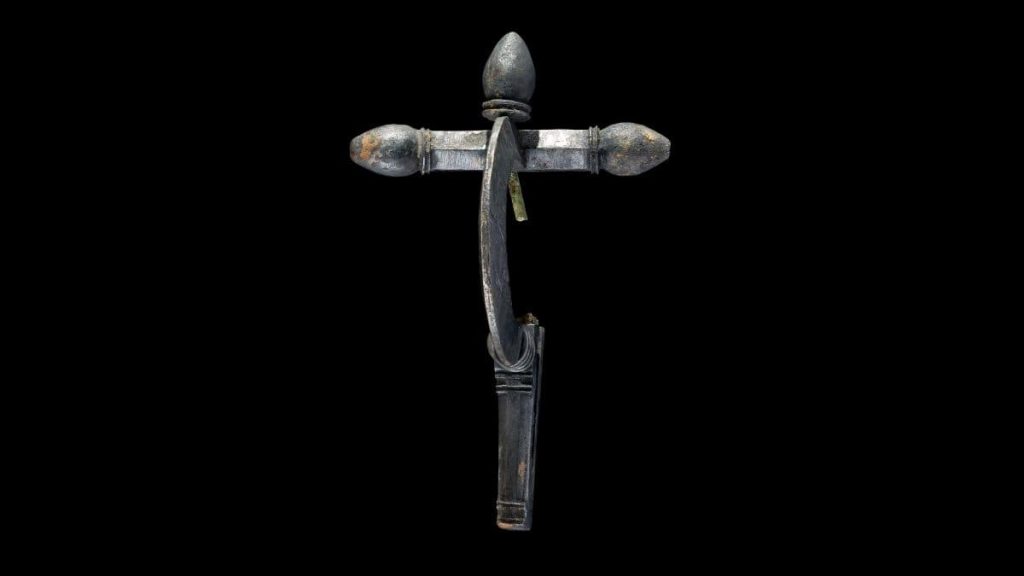

Crossbow fibulae/brooch were first used in the Western and Byzantine Empires in Late Antiquity, from the late third century to the middle of the sixth century A.D. They were worn as cloak fasteners by military officials and civil servants and became strongly associated with military and civil authority.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Analysis of the man’s bones and teeth revealed that he suffered from mastoiditis, a bacterial infection, at the time of his death. He was between 21 and 25 old when he died. Although this condition is easily treatable with antibiotics today, it could have been fatal during Roman times.
The man most likely grew up in the eastern region of Wales or elsewhere, according to additional analysis of isotopes in the man’s bones and tooth enamel. This begs the question of why a wealthy man like him would be discovered dead on a farm in south Wales.
The prone position of the man’s burial is notable, along with the discovery of a nearby grave containing a decapitated individual whose skull was placed at their feet. Similar burials in Roman Britain raise the possibility of a link between prone and decapitated burials. While atypical burial patterns have been observed in Western Europe during the Roman period, there is no single explanation for their occurrence.
This Roman soldier, buried facedown with his regalia, remains an enigmatic figure who may never be fully comprehended.
This Roman soldier is therefore something of a mystery — one that may never be solved. “It is interesting that he was buried prone but still with his ‘regalia,’” Mark Collard, managing director of Red River Archaeology said. “Raises more questions than answers!”
Cover Photo: The burial of the elite Roman man dates to the third or fourth century A.D. Image credit: © Red River Archaeology Group