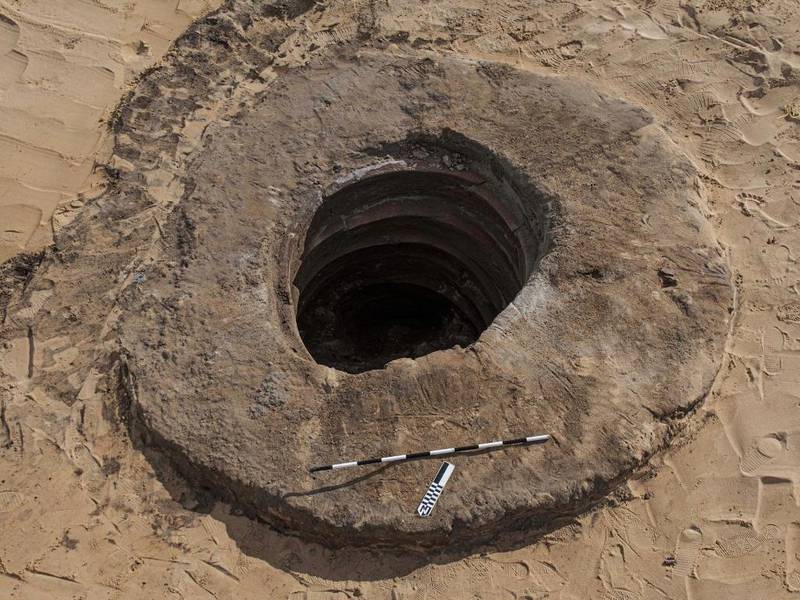
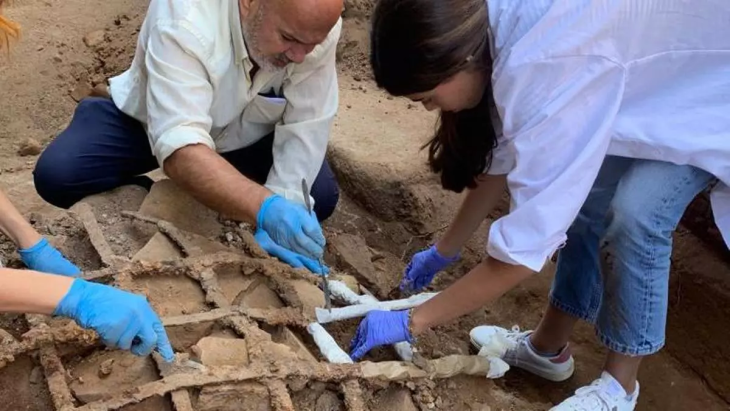
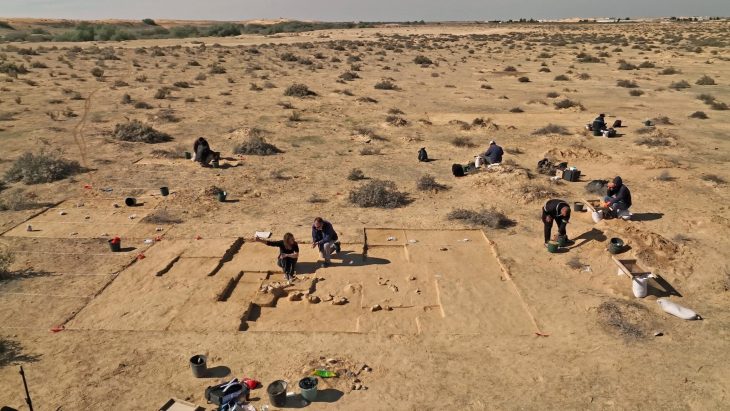
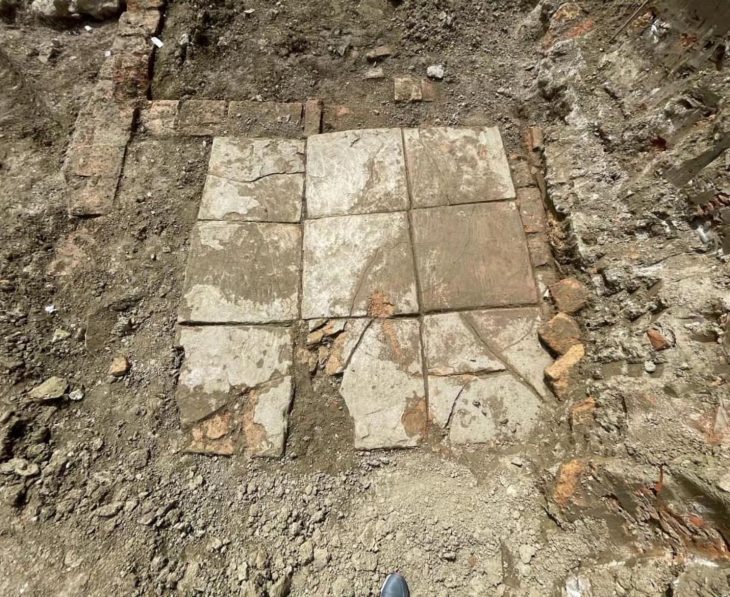
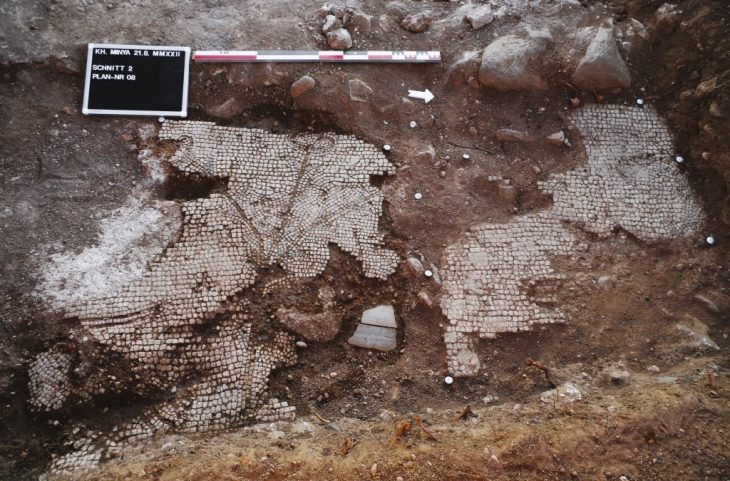
A team of Egyptian archeologists working in the Tell El Kedwa discovered five ancient wells which are believed to be from the 13th century BC in northern Sinai.
The Egyptian archaeological mission is working as part of the Sinai Development Project 2021-2022 and the mission is headed by the Director of North Sinai Antiquities and Head of the Mission Ramadan Helmy.
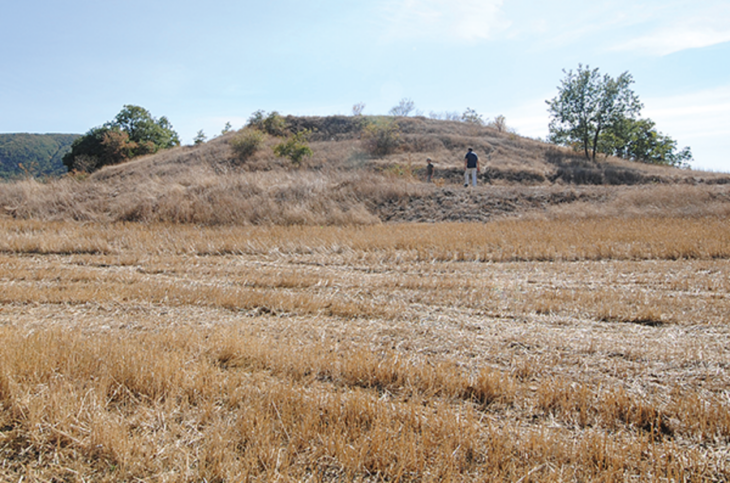
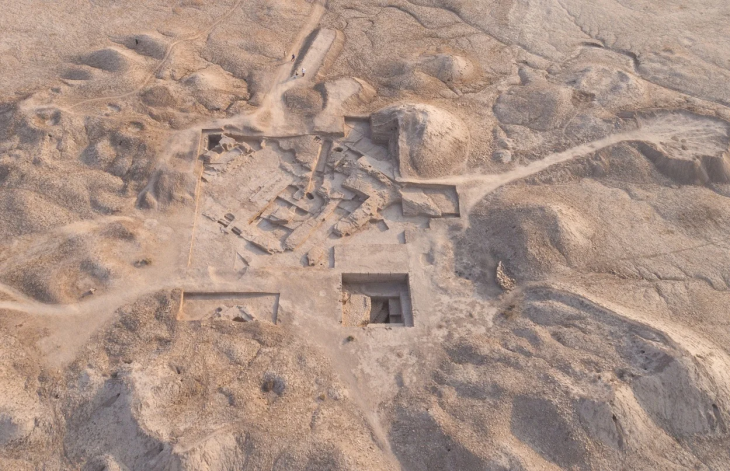
The wells were found outside the walls of the Tell El Kedwa fortress, one of several massive strongholds found in the area, which were used as military control points to protect Egypt’s eastern frontier and guard access to its northern regions.
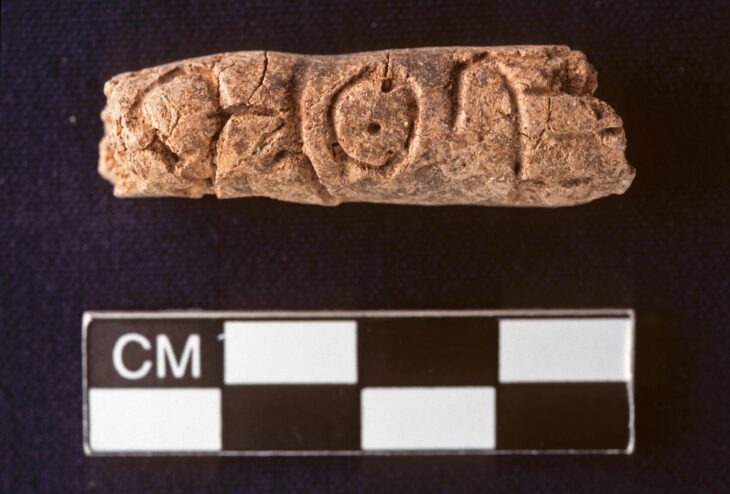
Egypt’s Tourism and Antiquities Ministry announced the find on the office’s Twitter account alongside images of several ancient artifacts.
The Egyptian Antiquities Ministry said that wells were built before the reign of Seti I (1292-1190BC), but it did not give an exact date. They are believed to have been a part of the expansive Horus Military Road, an ancient route that was used by pharaohs, the ministry said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Secretary-General of the Supreme Council of Antiquities Mustafa Waziri confirmed that these are the first water wells to be discovered in the region. The wells first appeared in the inscriptions engraved on the walls of Karnak Temple during the era of King Seti I.
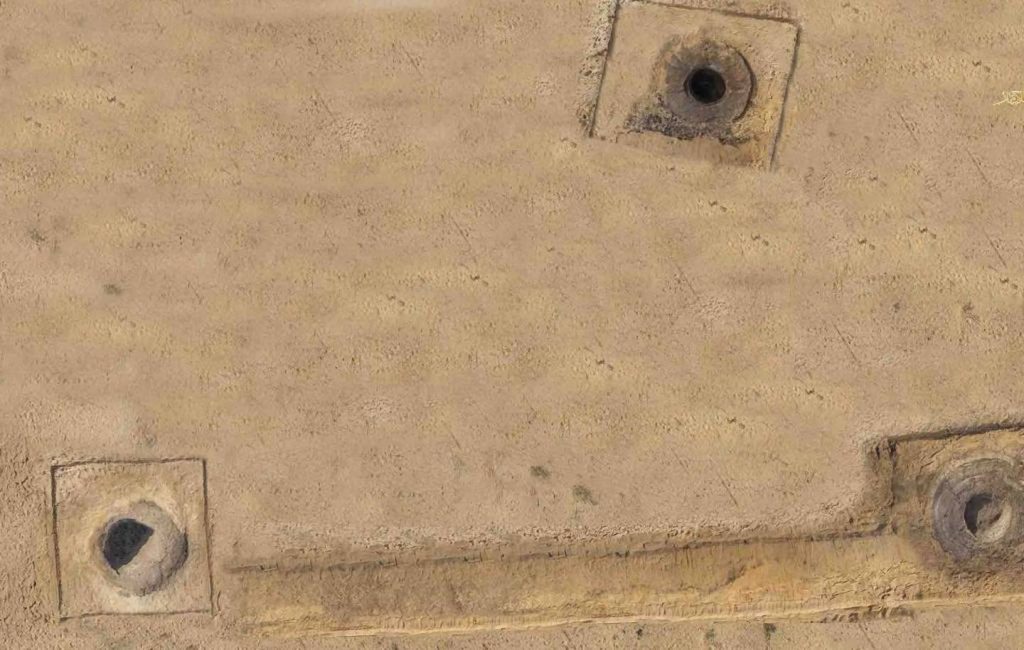

Waziri pointed out that five wells were discovered outside the walls of the castle of Tel el-Kedwa, in an area characterized by yellow sand.
The mission’s leader, Ramadan Helmy, said that four of the discovered wells were reportedly filled with sand to prevent the Persian army, which invaded Egypt in 525BC, from obtaining water.
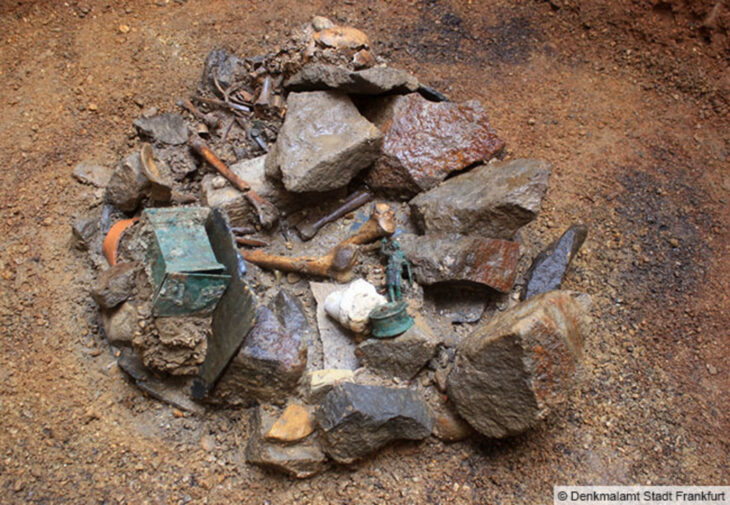
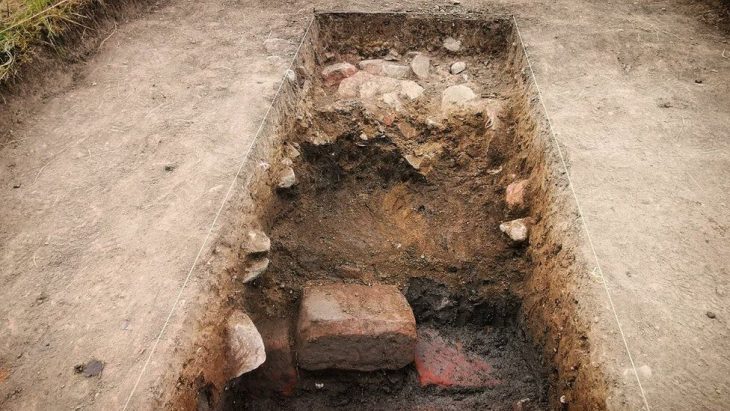
The fifth well, which was unfilled, measured nearly 10 feet deep, the ministry’s said.
Inside it, the mission found 13 pottery rings and several clay pots dating back to the 26th dynasty of ancient Egypt (664–525BC), also known as the Saite period.
Another archaeological team operating at the nearby Tell El Kedwa fortress discovered a large storage centre dating to the Saite period.
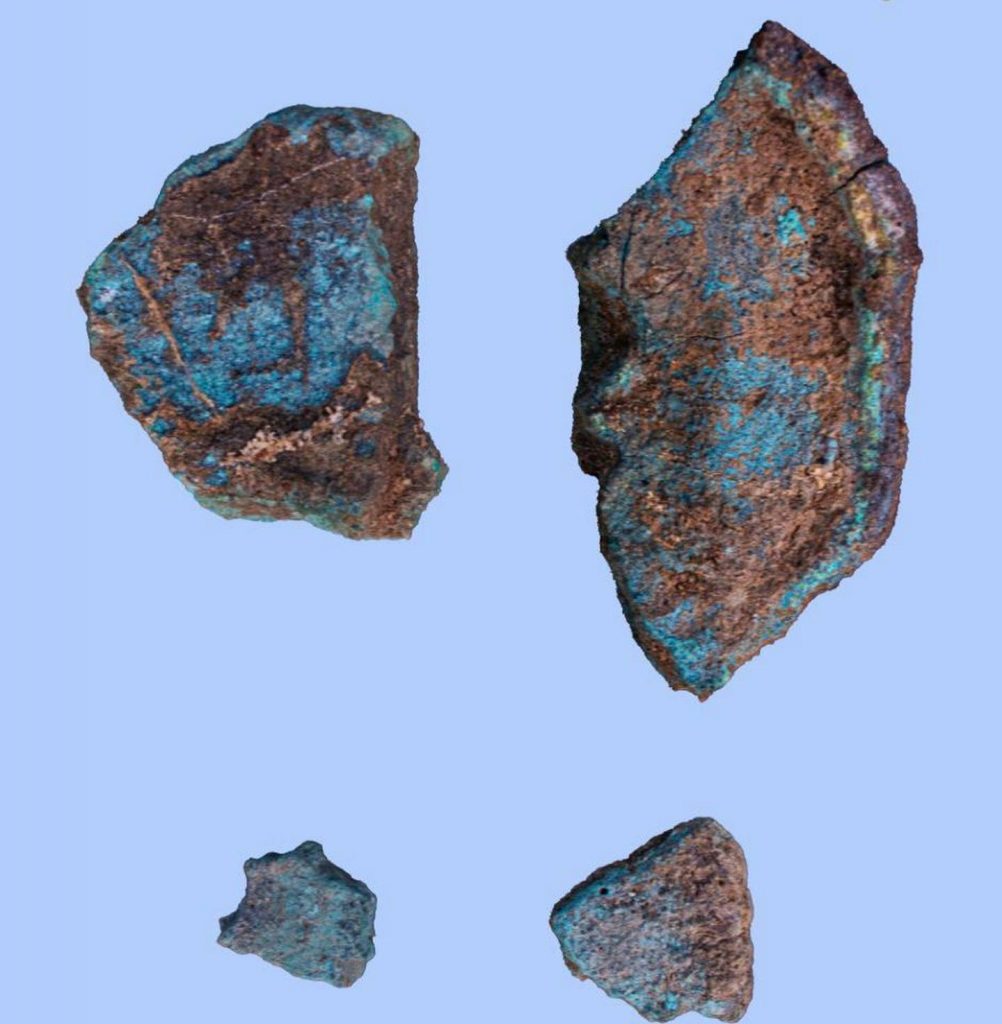

Moreover, the mission found the remains of kilns, from the El-Sawy era, likely to be a workshop for smelting copper ore. Circular-shaped copper alloy parts, as well as pottery bellows used in smelting, have also been found.
The Horus Military Route was used during the old, middle and new kingdoms of ancient Egypt and was depicted in inscriptions at some of Egypt’s other prominent archaeological sites, including Luxor’s Karnak Temple.
Cover Photo: One of five wells discovered by an Egyptian archaeological mission in North Sinai. Photo: Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities