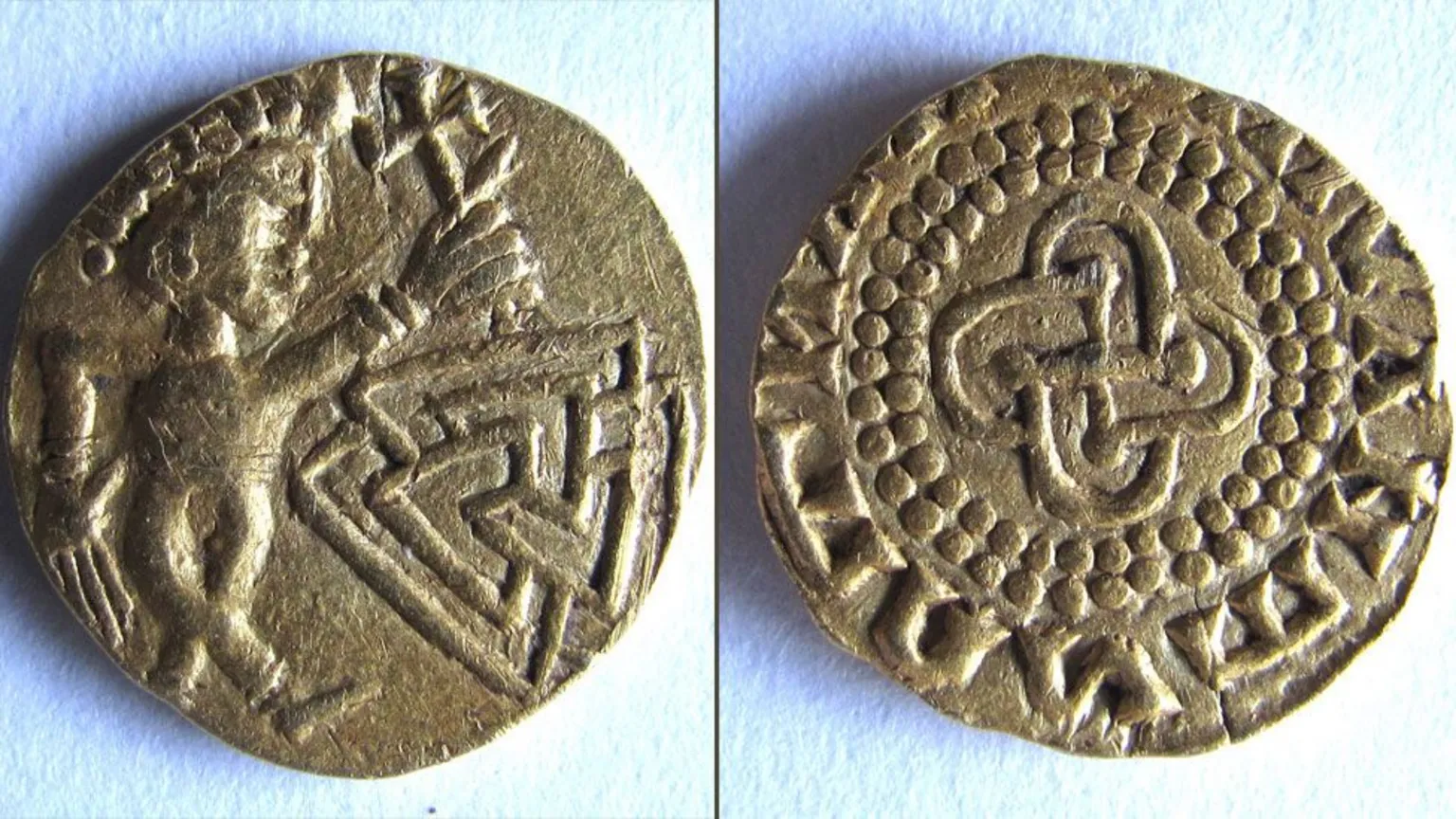
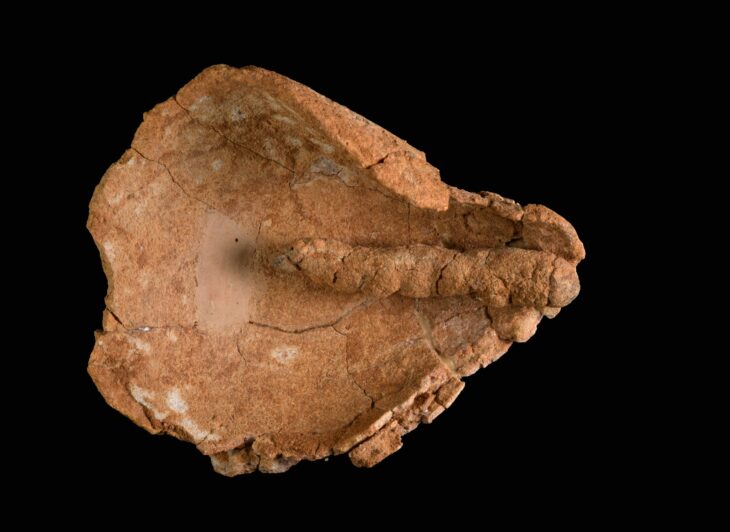
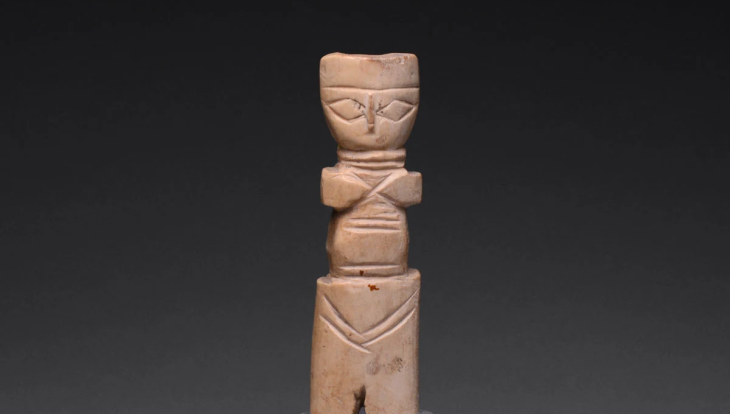
A rare gold coin dating back to the early Anglo-Saxon period has been discovered near Norwich, UK, by a metal detectorist. Experts say it is the oldest known coin from East Anglia, dating between 640 and 660 A.D., and represents a remarkable blend of Christian and Pagan iconography during a time of major religious transformation in England.
This period marks a pivotal chapter in early medieval England, as Anglo-Saxon kingdoms began gradually converting to Christianity following missions from Rome and Ireland. Pagan traditions, however, remained deeply rooted in the culture, resulting in a transitional era where religious symbols and practices often overlapped.
A prime example of this syncretism is King Rædwald of East Anglia, who is believed to have embraced both belief systems—reportedly keeping altars to Christ and Pagan gods side by side. The famous Sutton Hoo ship burial, widely associated with Rædwald, contains grave goods reflecting both Christian and pre-Christian symbolism. Artefacts like this newly discovered coin provide rare, tangible evidence of how these two spiritual worlds coexisted and influenced one another during the 7th century.
Discovery Marks Milestone in Anglo-Saxon Numismatics
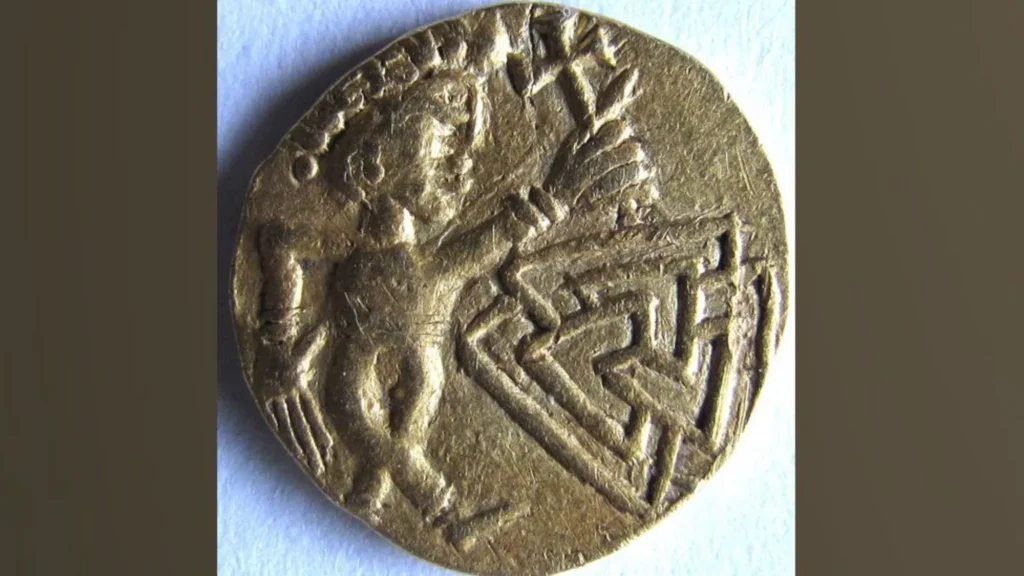
The coin, identified as a thrymsa (a type of early Anglo-Saxon shilling), features a diademed male figure with crossed legs in a dancing pose on the obverse. The figure holds a Christian cross above a valknut — a symbol of three interlocking triangles linked to the Norse god Odin, often associated with death and the afterlife. The reverse displays a quatrefoil enclosing a cross-like design and an imitation Latin inscription made by a non-literate die cutter.
Dr. Adrian Marsden, numismatist at the Norfolk Historic Environment Service, described the artifact as “massively significant,” calling it a groundbreaking addition to the study of Anglo-Saxon coinage. “It’s the first of its type,” said Marsden. “New shilling designs almost never turn up, and this one uniquely bridges the Pagan and Christian eras.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

High Gold Purity Suggests Royal Origin
Metallurgical testing revealed the coin is composed of 56%–60% gold, a notably high purity compared to similar coins from the same period. According to Marsden, the rich gold content and regal portrait suggest this was part of an early East Anglian royal coinage, possibly minted just before the full Christianization of the kingdom.
Echoes of Sutton Hoo
The coin’s imagery evokes the famous Sutton Hoo ship burial, which also mixed Pagan and Christian symbolism. As with Sutton Hoo, this coin reflects a time when Anglo-Saxon England was undergoing significant cultural and spiritual change — where rulers and communities incorporated both belief systems in their daily life and death rituals.
National Significance and Legal Recognition
This is only the second artifact in Norfolk to benefit from the UK’s updated Treasure Act, amended in 2022 to include historically significant items regardless of their material value. A coroner will determine if the coin qualifies as official treasure.
Dr. Marsden has published detailed findings in The Searcher, further highlighting the piece’s scholarly and cultural importance.
Norwich Castle Museum hopes to acquire the coin for its collection. If officially declared treasure under the UK’s Treasure Act, the coin could become a cornerstone of the museum’s early medieval collection, offering the public a rare glimpse into the religious and political dynamics of 7th-century East Anglia.
Cover Image Credit: This 7th-century gold coin, no larger than a fingernail, offers a rare glimpse into early Anglo-Saxon artistry and symbolism. Credit: Adrian Marsden