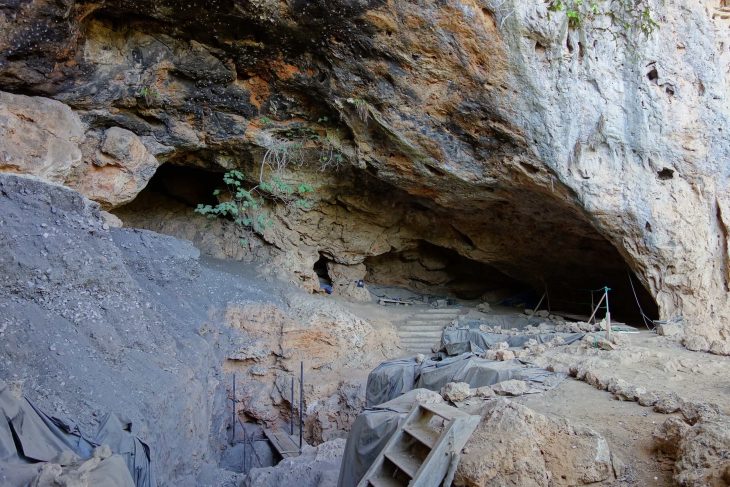
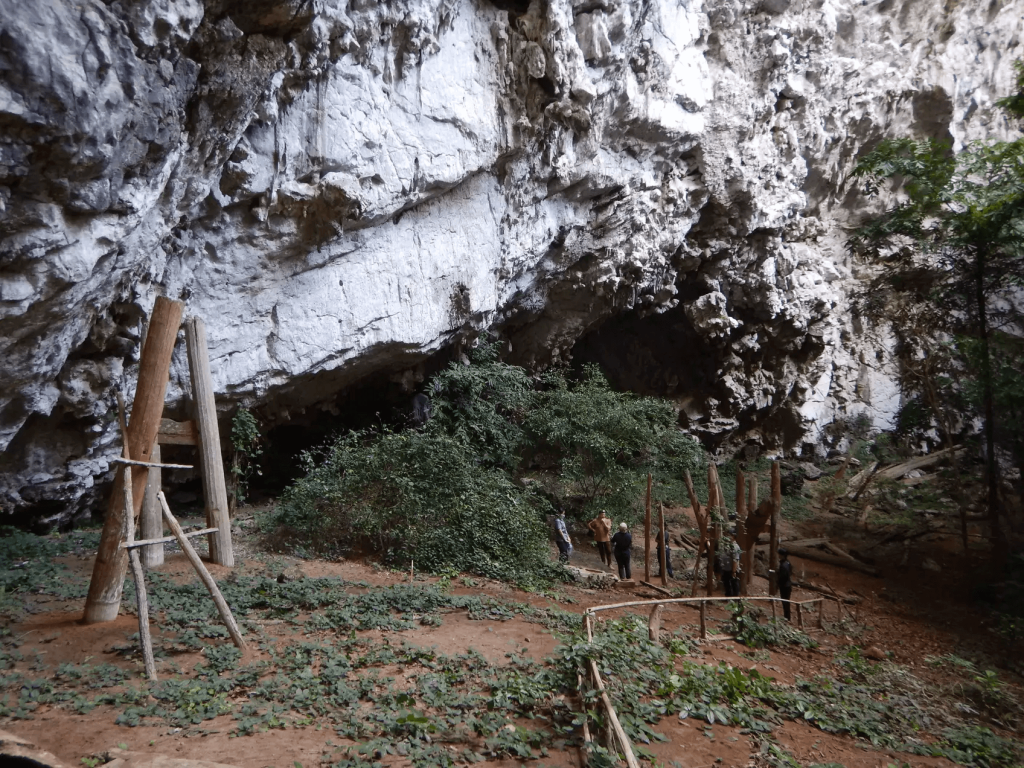
The Northwestern Thailand highlands region of Pang Mapha is dotted with dozens of caves that contain some incredibly odd prehistoric human burials. The region is a historical treasure trove, known for its unique mortuary practice from the Iron Age – the Log Coffin culture.
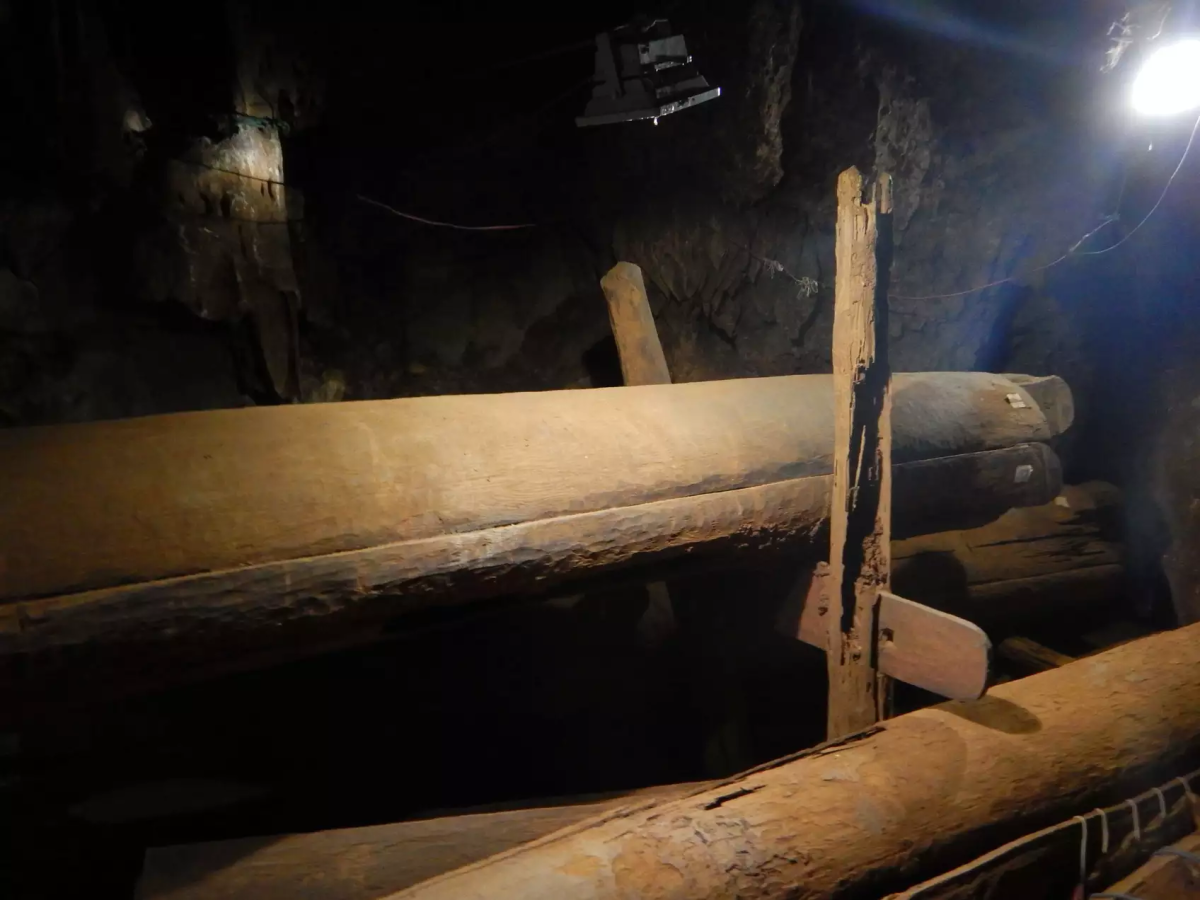
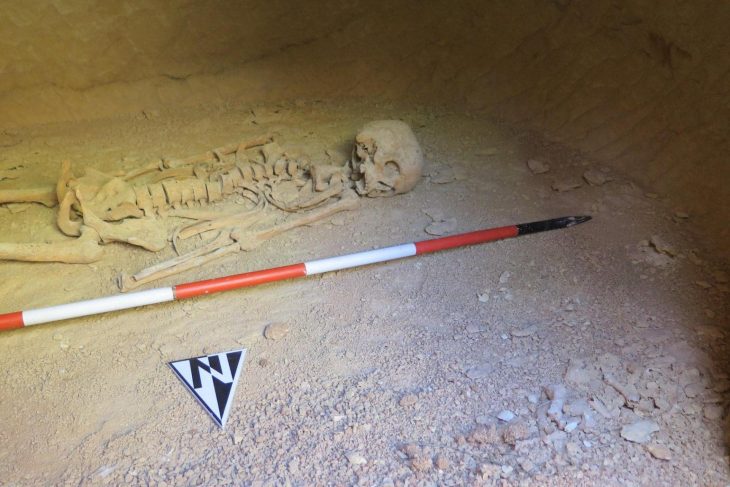
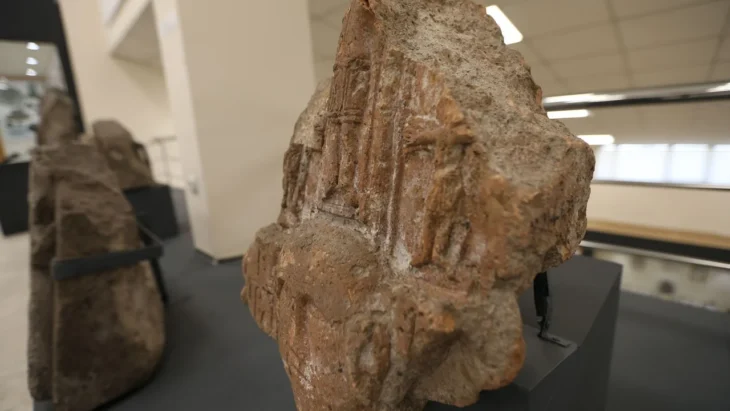
The individuals were laid to rest in large wooden coffins, most of which were found perched on stilts within caves and rock shelters. In this culture, people were buried in large wooden coffins that were carved with intricate designs and made from single teak trees.
A new study delves into the genetic profiles and community structures of these ancient societies, revealing a complex genetic landscape and substantial connections across different river valleys.
The approximately 40 burial sites are the work of a mysterious Iron Age culture that lived in the Mae Hong Son province of northern Thailand between 2,300 and 1,000 years ago.
To understand the genetic profile of the Log Coffin-associated communities, and the connection of individuals buried in different caves, an interdisciplinary team of researchers from Germany and Thailand has analyzed the DNA of 33 ancient individuals from five Log Coffin sites and discovered a complex pattern of biological relatedness within these early communities.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The Log Coffin culture’s mortuary traditions appear to be heavily influenced by genetic relatedness. The study discovered close genetic relatives buried in the same cave systems, indicating that familial ties influenced burial site selection. This discovery represents the first community-level analysis in Southeast Asian archaeology, providing new insights into the social structure of these ancient communities.
Despite the difficult conditions for DNA preservation in tropical regions, the researchers successfully identified two distinct farmer-associated ancestries among Log Coffin-associated individuals. One group had genetic ties to the Yangtze River Valley, while the other was linked to the Yellow River Valley in China. These findings point to cultural differences within communities and suggest distinct spheres of influence and migration routes during the Neolithic period.
The complex genetic landscape of mainland Southeast Asia during the post-Neolithic era is highlighted by this duality in ancestral roots. It also offers important insights into the genetic and cultural diversity of the Iron Age population in the area.
Furthermore, the discovery of distinct ancestries with roots in various parts of China offers a novel viewpoint on the demographic dynamics of early Southeast Asia. It illuminates unique migration patterns and cultural influences, deepening our comprehension of the intricate historical history of this area.
However, The new study doesn’t delve too deeply into these questions, such as the significance of long-log coffins and why an Iron Age culture go to such great lengths to raise the long trucks onto stilts.
The study is published in the journal Nature Communications.
Cover Photo: In Thailand’s Iron Age Log Coffin culture, coffins were made from a single teak tree and decorated with refinement. Photo: © Selina Carlhoff