‘Turkish Sunken-Ships Project: Blue Heritage’, a 1500-year-old trade shipwreck was found off the coast of Ayvalık district of Balıkesir.
Under the direction of associate professor Harun Özdaş, director of the Underwater Research Center (SUDEMER) at Dokuz Eylül University, the mapping of the underwater cultural heritage of the Ayvalık region was carried out with approval from the Ministry of Culture and Tourism. The research was carried out using domestically developed robotic underwater vehicles.
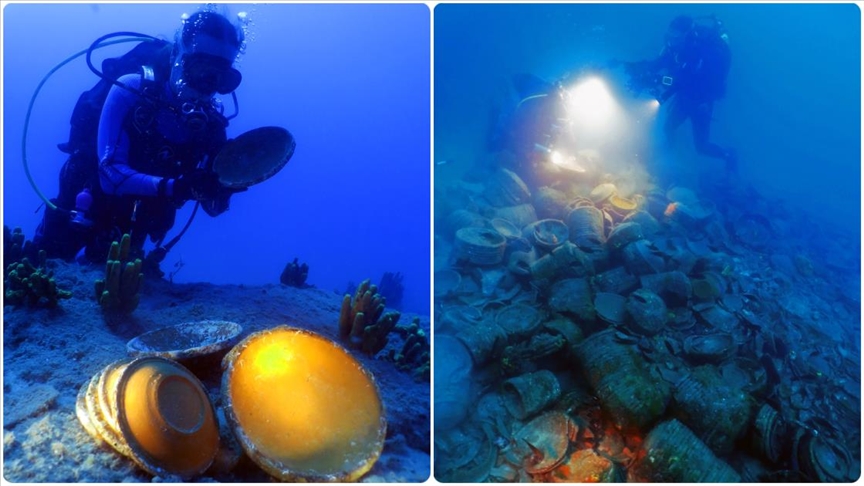
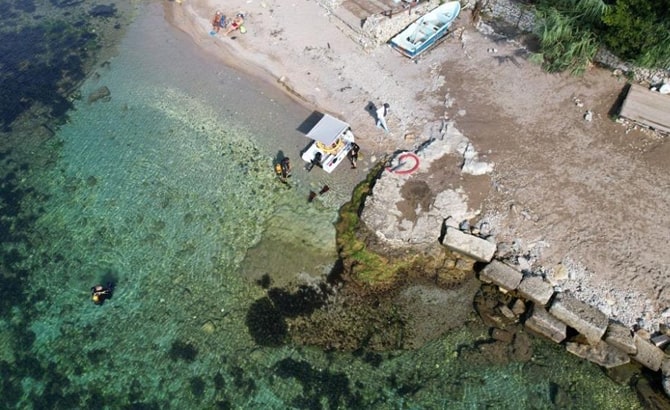
The shipwreck, located approximately 2.5 miles off the coast of Ayvalık, was identified by associate professor Nilhan Kızıldağ, the deputy director of SUDEMER, and her team. The wreck is dated to the late fifth century A.D. based on preliminary findings.
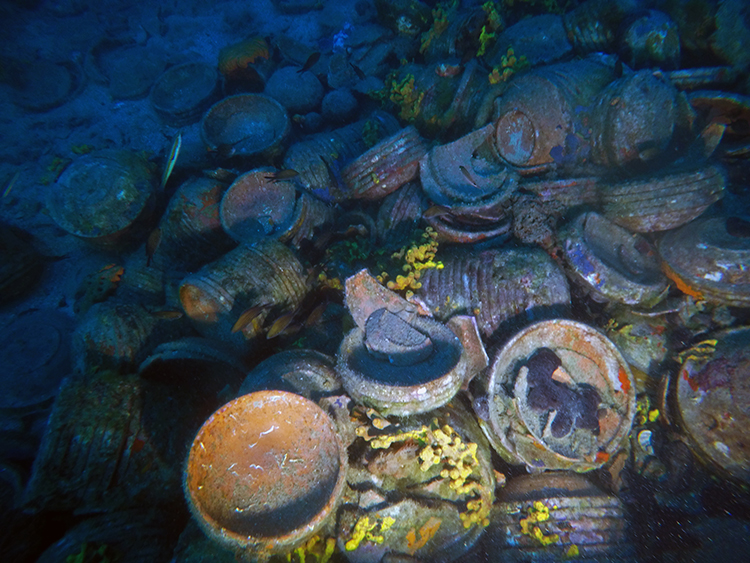
It was stated that the wreck containing approximately 10 thousand ceramic dishwrecks is ‘the largest plate wreck found in the Aegean and Mediterranean’. It was stated that the find, which shows the plate trade on the Aegean and Mediterranean coasts, due to its location in open waters, the wreck has been exceptionally well-preserved.

Özdaş explained that they detected some anomalies at a depth of 43 meters and gave the following information:
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
‘We made dives to these anomalies with our high-tech devices and determined the location of the wreck. This discovery was made thanks to our advanced robotic systems because it is about 2.5 miles off the coast at a depth of 43 meters. We encountered a large pile in an area outside of geography that can be found with standard dives. The characteristic of this pile is that it consists of intertwined dishes, each in clusters of about 15-20, not the amphorae we usually detect in our studies. To date, we have found the largest shipwreck of dishes known in the Aegean and Mediterranean. Based on the first determinations, we think that the ship came from North Africa or Cyprus. It probably sank off the coast of Ayvalık after a storm.’
The wreck is estimated to be about 15 meters (49.21 feet) long and 9 meters wide, with only a small number of amphorae found alongside the dishes.
The team believes the ship may have originated from either North Africa or the island of Cyprus, with the wreck possibly resulting from a storm.
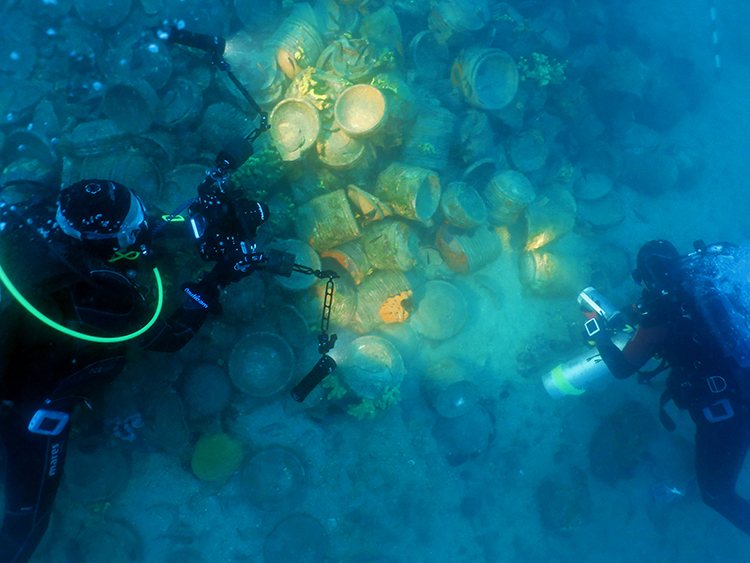

Additionally, Özdaş pointed out that ceramics made in places like Syria, Egypt, North Africa, and Cyprus were frequently traded and shipped to Anatolia, Greece, or Italy. But as of yet, there hasn’t been any convincing underwater proof of these kinds of trade activities. With almost 10,000 plates in its cargo, the discovery of this shipwreck is unprecedented in both scope and importance.
“There are at least 5-6 different types of plates among the cargo,” said Özdaş. “In our 30 years of underwater research in Turkish waters, finding such wealth is a source of great happiness for us. The ship’s main cargo was ceramic plates and photogrammetric studies show that there are 10,000 plates on the site. This wreck is of great importance, especially because it has remained untouched and preserved in its original state. The variety and quantity of artifacts here represent a significant collection.”
According to Özdaş, the discovery is substantial enough to warrant the creation of a museum based on the artifacts uncovered. “We have found enough artifacts to open a museum,” he said.
Cover Photo: AA