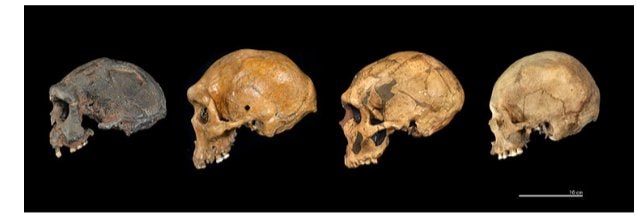
Over 300 fossils from the genus Homo have been measured for body and brain size by an interdisciplinary team of academics led by the Universities of Cambridge and Tübingen. They determined the exact environment experienced by each fossil while it was a live person by integrating this data with a reconstruction of the world’s regional climates during the last million years.
The findings show that human body size has changed dramatically over the last million years, with bigger bodies developing in colder climates. Larger bodies are considered to function as a buffer against cooler temperatures: when a body’s mass is enormous compared to its surface area, less heat is lost. The findings were just published in the journal Nature Communications.
Our species, Homo sapiens, first appeared in Africa approximately 300,000 years ago. The Neanderthals and other extinct, related species such as Homo habilis and Homo erectus belong to the genus Homo, which has been around for considerably longer.
The tendency of a growing body and brain size has been a distinguishing feature of our genus’ development; compared to previous species such as Homo habilis, we are 50% heavier and our brains are three times bigger. However, the reasons for such shifts are still hotly disputed.
“Our study indicates that climate — particularly temperature — has been the main driver of changes in body size for the past million years,” Professor Andrea Manica, from Cambridge University’s Department of Zoology, told Science Daily.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
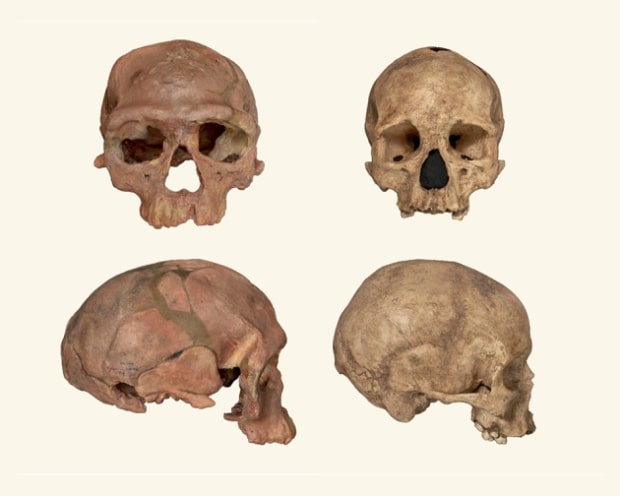
He added: “We can see from people living today that those in warmer climates tend to be smaller, and those living in colder climates tend to be bigger. We now know that the same climatic influences have been at work for the last million years.”
The researchers also investigated the influence of environmental variables on brain size in the Homo genus, although correlations were typically modest. When Homo lived in environments with less vegetation, such as open steppes and grasslands, but also in ecologically more stable places, brain size tended to be greater.
The findings, when combined with archaeological evidence, imply that humans living in these settings hunted huge animals for sustenance, a complex task that may have fueled the evolution of larger brains.

“We found that different factors determine brain size and body size — they’re not under the same evolutionary pressures. The environment has a much greater influence on our body size than our brain size,” said Dr. Manuel Will at the University of Tubingen, Germany, the first author of the study.
He added: “There is an indirect environmental influence on brain size in more stable and open areas: the amount of nutrients gained from the environment had to be sufficient to allow for the maintenance and growth of our large and particularly energy-demanding brains.”
Non-environmental variables, rather than climate, appear to be more significant in promoting larger brains, with the increased cognitive difficulties of increasingly complicated social lives, more diversified meals, and more sophisticated technologies being prominent possibilities.
According to the experts, there is strong evidence that the human body and brain are still evolving. The human body is still adjusting to various temperatures, with larger-bodied people living in colder locations on average nowadays. Since the beginning of the Holocene, our species’ brain size appears to have shrunk (around 11,650 years ago).
Over the next several thousand years, growing reliance on technology, such as outsourcing complicated work to computers, may lead brains to shrink even more.
“It’s fun to speculate about what will happen to body and brain sizes in the future, but we should be careful not to extrapolate too much based on the last million years because so many factors can change,” said Manica.