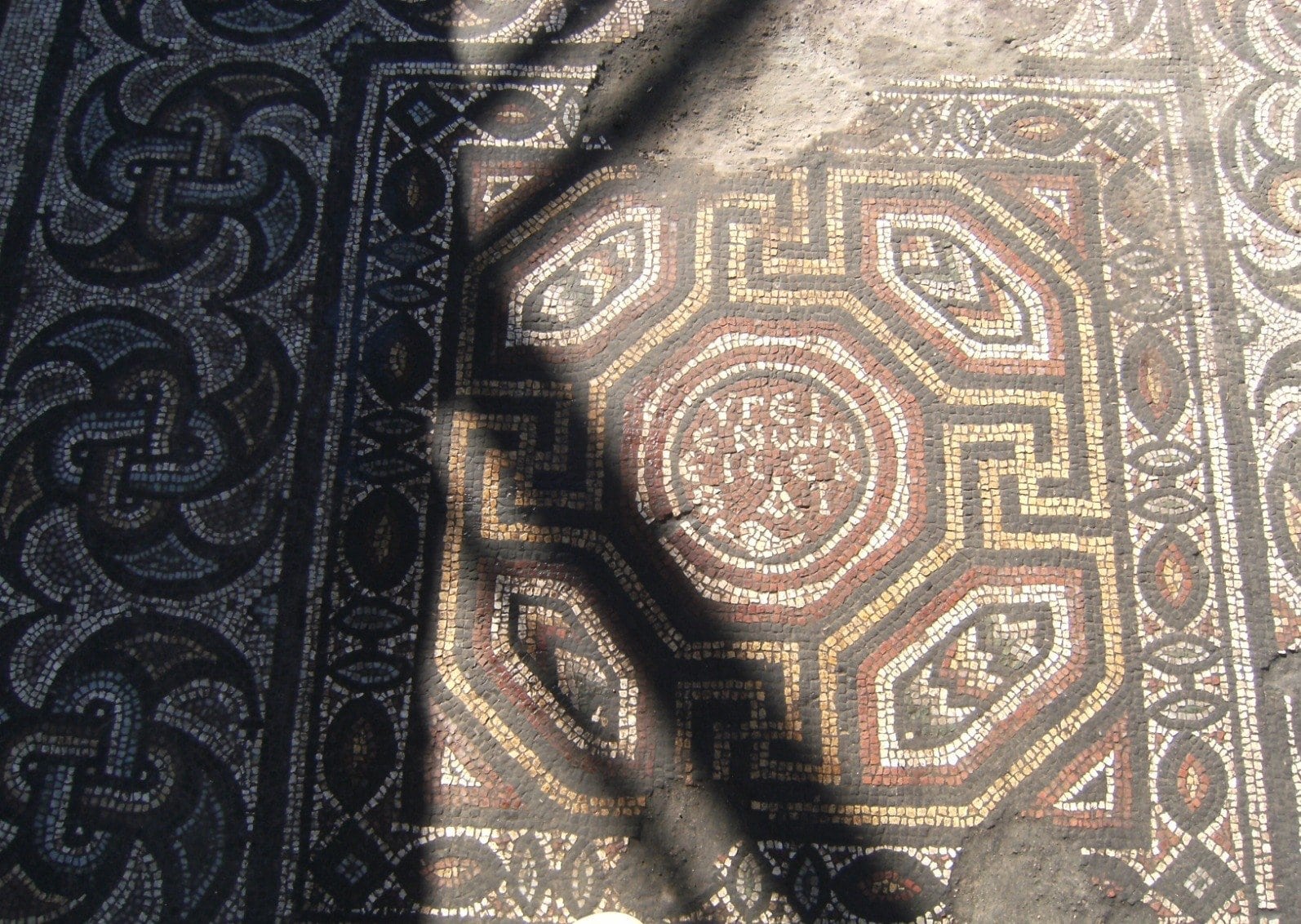
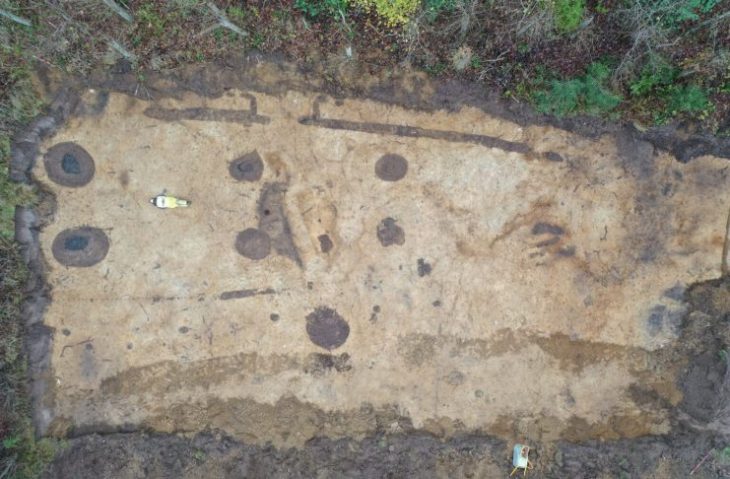
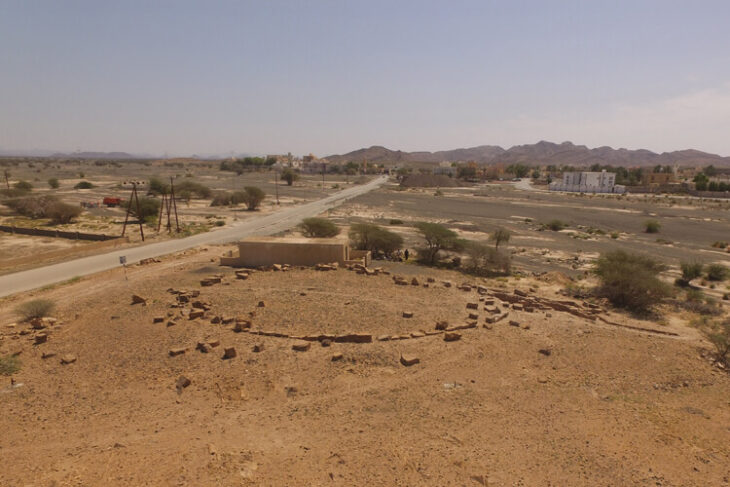
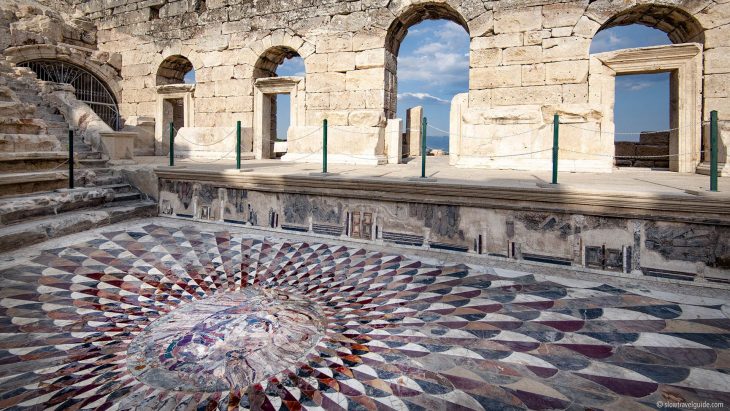
A 300-square-meter (3,330 square feet) floor mosaic belonging to the Late Roman-Early Byzantine period was discovered during excavation work in Turkey’s Kayseri province. It is the largest mosaic structure from the Byzantine period in central Anatolia.
Archaeological excavations have begun under the supervision of the Kayseri Museum Directorate, with the cooperation of the Metropolitan Municipality of Incesu, according to a statement issued by the Kayseri municipality on Wednesday. Examples of late Roman and early Byzantine homes, decorative patterns in floral and geometric motifs, and Greek and Latin inscriptions were unearthed during these excavations.
The Byzantine mosaic construction, on the other hand, stands out among the finds due to its excellent preservation. More than 10 rooms were also discovered in the structure, which has approximately 300 square meters of solid mosaic floor tiles and is the largest mosaic in Central Anatolia.
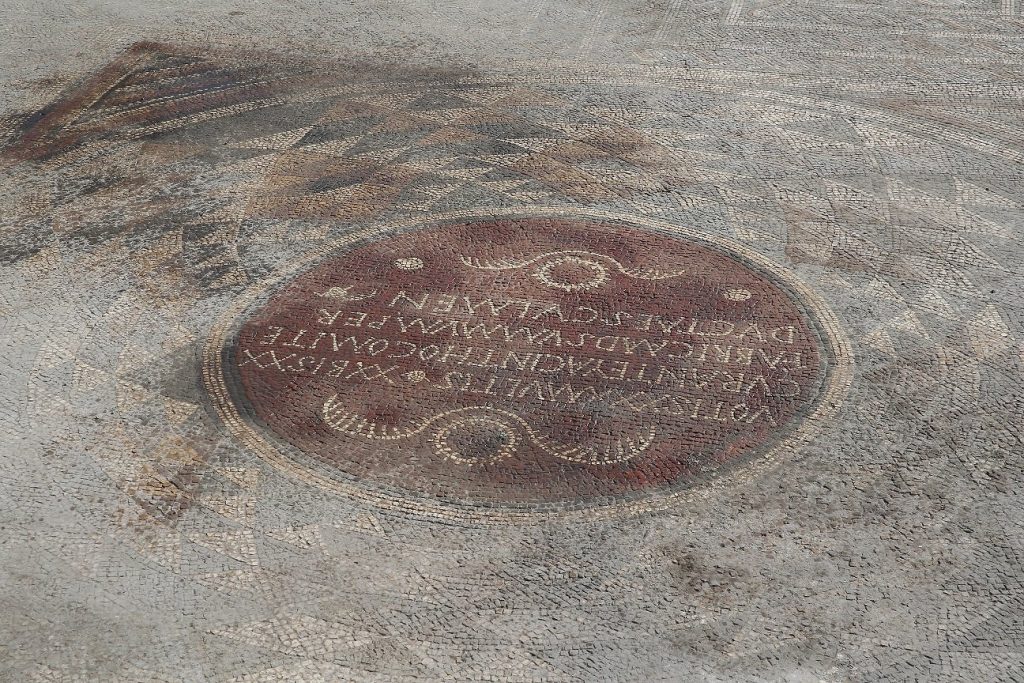

Two mosaic inscriptions were also unearthed in the building as a result of salvage excavations. A mosaic with Latin script was located at the base of a rectangular building, while another mosaic with Greek script was found on the floor of another partially preserved walled building.
The Latin mosaic reads: “On the occasion of its 30th anniversary and with our prayers for it to reach its 40th anniversary. This building (Fabrica) was built under the leadership of his friend (Comes) Hyacinthos. You, O building, have now reached the most magnificent level.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
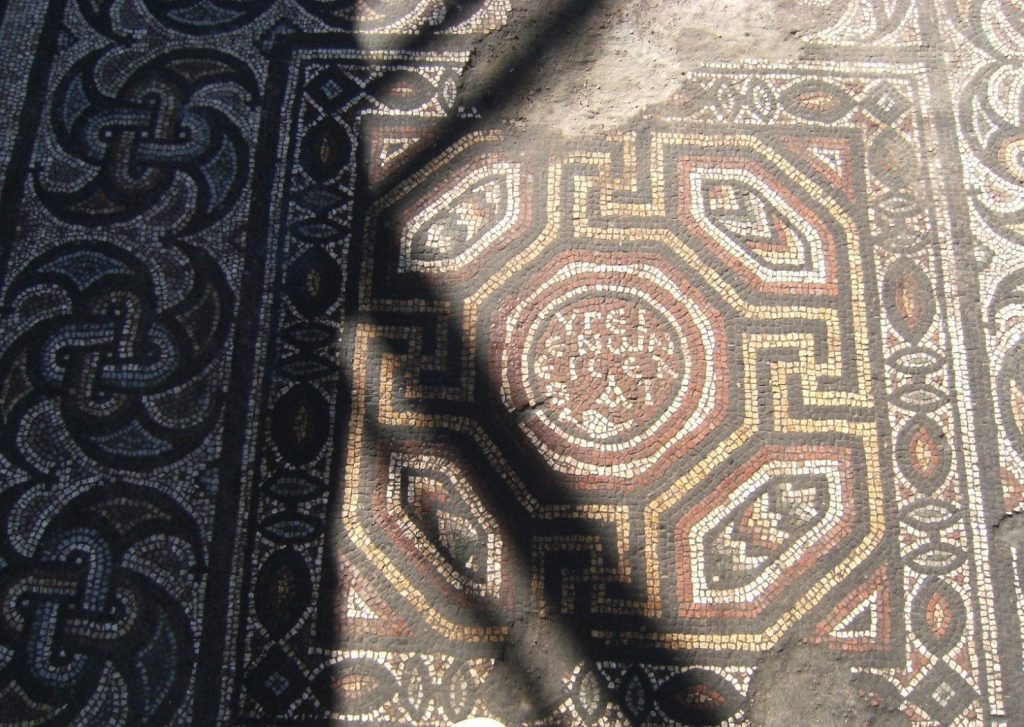

The Greek mosaic reads: “Enter in a healthy way” or “Enter if you are healthy.”
During previous studies in the Central Anatolia region, archaeologists had been discovered a 3,500-year-old mosaic that may be one of the oldest in the world.
This important discovery was made in Uşaklı Höyük, located within the borders of Büyük Taşlık Village in Sorgun District of Yozgat.
AA