A routine yard cleanup in New Orleans turned into an international archaeological mystery when a homeowner uncovered a 2nd-century Roman headstone — stolen decades ago from an Italian museum.
What began as a local curiosity quickly evolved into a global effort involving archaeologists, classical scholars, and the FBI’s Art Crime Team. The marble slab, inscribed in Latin, was discovered earlier this year in the backyard of a historic home in the Carrollton neighborhood, setting off an extraordinary chain of events that led from Louisiana to the ancient port of Civitavecchia, Italy.
A Startling Find in Carrollton
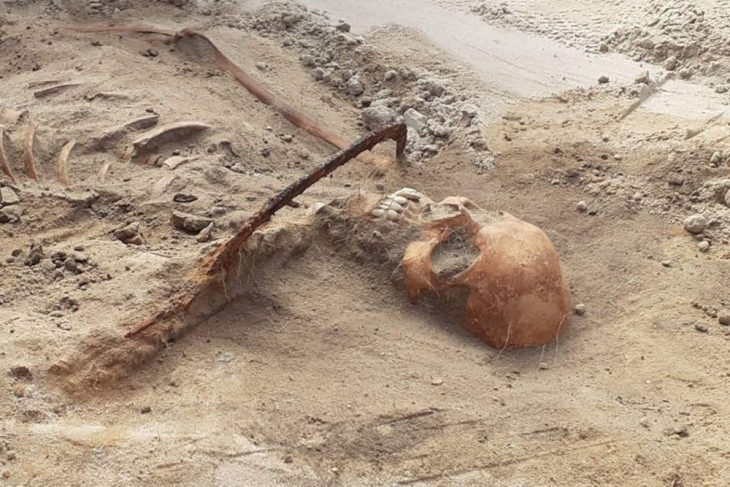
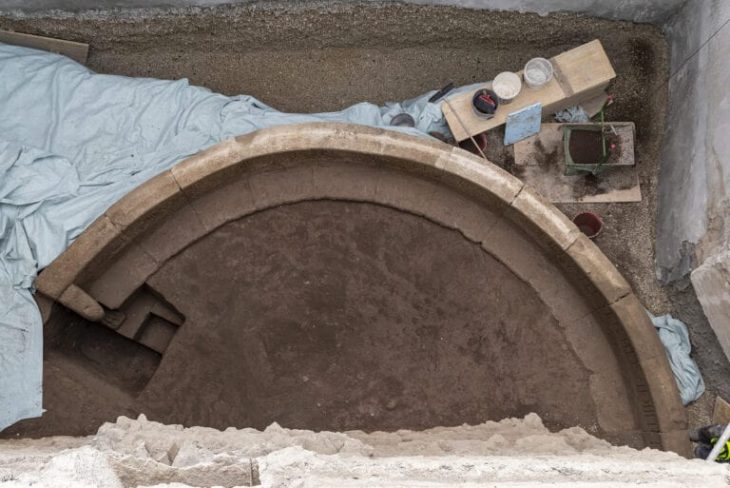
In March, Tulane University anthropologist Dr. Daniella Santoro and her husband Aaron Lorenz stumbled upon a flat marble stone while clearing undergrowth in their yard at 1106 Cambronne Street. The slab bore a Latin inscription that immediately caught Santoro’s attention. Concerned that it might mark a forgotten burial, she contacted archaeologist Dr. Ryan Gray from the University of New Orleans.
Gray, who has worked in New Orleans archaeology for over 25 years, confirmed that the property was not situated above a known cemetery. “We’ve mapped many historic burial sites, especially those connected to enslaved communities,” he explained. “But this wasn’t one of them. The inscription itself was the key.”
Realizing that his Latin was insufficient for translation, Gray sent photos of the artifact to colleagues in Austria and at Tulane University. Dr. Susann S. Lusnia, a classical studies expert at Tulane, quickly recognized the inscription — it was a Roman funerary dedication for Sextus Congenius Verus, a sailor who lived nearly 1,900 years ago. Even more astonishingly, Lusnia found that the stone exactly matched a missing piece from the Civitavecchia City Museum in Italy.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
From Backyard to FBI Custody
Once it became clear that the artifact had been stolen or lost from Italy, Santoro and Lusnia organized what they nicknamed “Team Tombstone.” Working with the Antiquities Coalition, led by Tess Davis, the group contacted the FBI Art Crime Team, which specializes in repatriating looted cultural heritage. The FBI soon took custody of the headstone, ensuring its protection until it can be formally returned to Italy.
The stone, dated to the 2nd century CE, had originally been found near Civitavecchia — known in Roman times as Centumcellae, a major imperial port northwest of Rome. During World War II, the area suffered intense bombing, and the city museum was nearly destroyed. Many artifacts disappeared in the ensuing chaos, including the headstone of Sextus Congenius Verus.
Tracing the Stone’s Journey
With repatriation underway, the next question was obvious: how did a Roman tombstone end up in a New Orleans backyard?
Historical records show that the Cambronne Street property was owned by the Simon family for much of the 20th century. Frank Simon, a shoe company manager, bought the house in 1909 and lived there with his wife Selma and their daughters until his death in 1945. The home stayed in the family until 1991.
Researchers initially suspected that a neighbor who served in the U.S. Navy during World War II might have brought it back from Italy as a souvenir. However, service records from the National World War II Museum revealed that the veteran had only served in the Pacific, not the Mediterranean.
Lusnia’s later research in Italy uncovered more clues. While the Civitavecchia museum remained closed until 1970, a 1954 inventory mentioned the lost inscription based solely on earlier documentation. This confirmed that the piece had likely gone missing during or just after the war.
U.S. Army records show that the 34th Division of the Fifth Army passed through Civitavecchia after the liberation of Rome in 1944. It’s plausible that an American soldier, unaware of the artifact’s significance, took it home as a war souvenir — a common, though illegal, practice at the time.
Returning a Piece of Roman History
Today, the headstone is safely in FBI custody and will soon make its way back to the Civitavecchia City Museum, where curators plan to celebrate its return. “It’s a rare case where local curiosity led to the recovery of an ancient artifact,” Gray said. “While we may never know exactly who brought it here, the important thing is that it’s going home.”
The museum staff in Italy are preparing to welcome the stone back after nearly 80 years of absence, calling the discovery “a triumph of collaboration between scholars, citizens, and law enforcement.”
As for New Orleans, the find has reminded locals that even in a city layered with centuries of its own history, global stories sometimes lie just beneath the surface — sometimes literally in the backyard.
Preservation Resource Center of New Orleans
Cover Image Credit: D. Ryan Gray