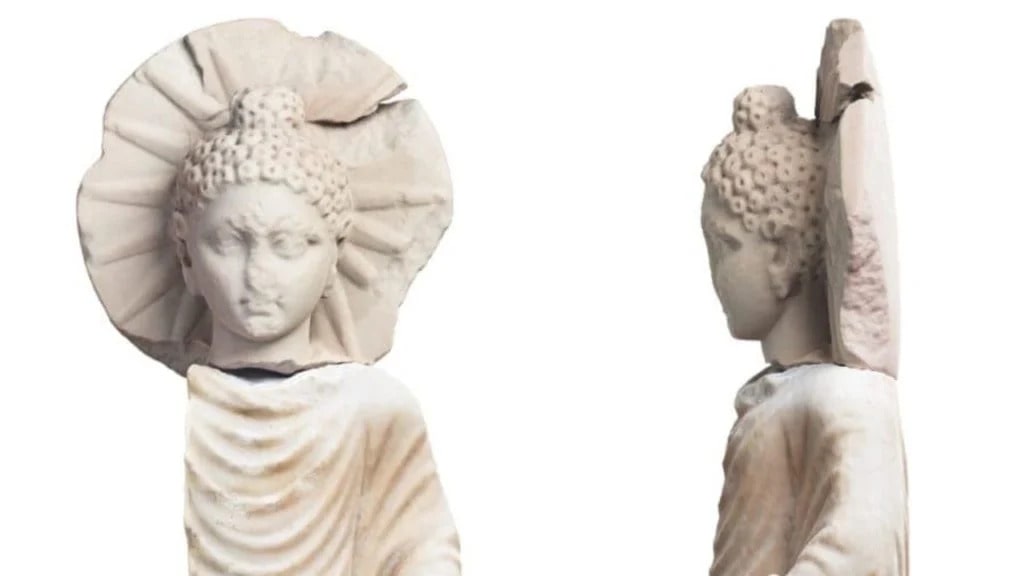
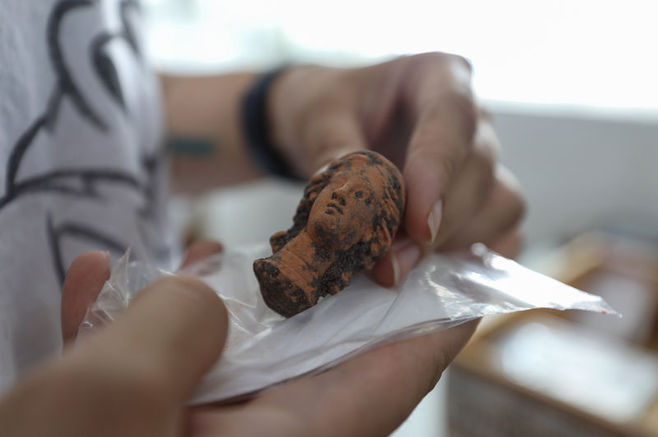
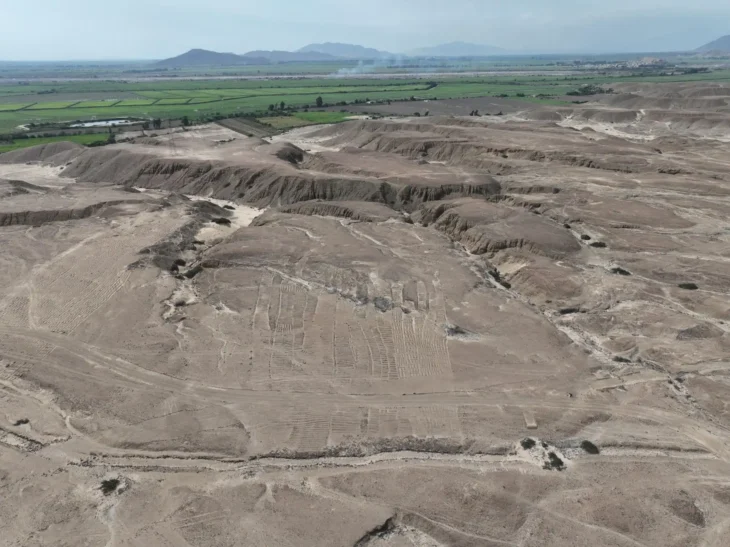
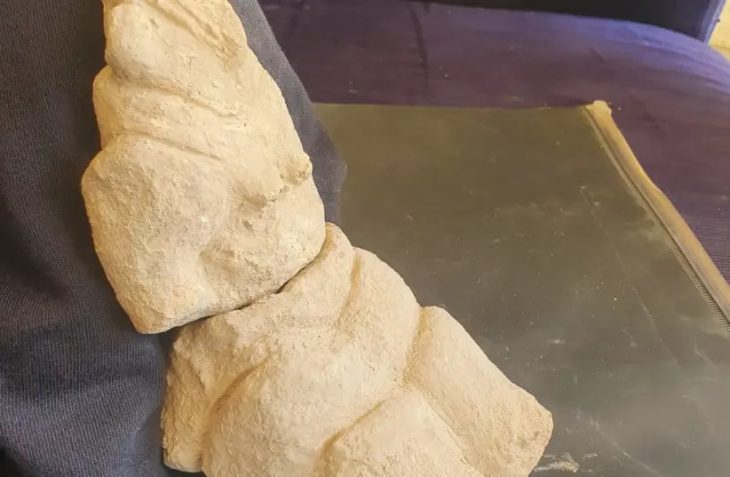
Archaeologists excavating in the ancient Egyptian seaport Berenice Troglodytica on the western shore of the Red Sea have unearthed a curious ancient Buddha statue that dates from the 2nd century AD.
The ancient Egyptian seaport of Berenice Troglodytica, also known as Berenike was founded by Ptolemy II Philadelphus (285-246 BC). The city served as one of the main waypoints for the trade of war elephants and exotic goods like pepper, semi-precious stones, cloth, and ivory between India, Sri Lanka, Arabia, and Upper Egypt during the Roman era, between the first and second centuries AD.
The discovery was announced by the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities on Thursday.
The figurine found at Berenike by American and Polish archaeologists, the 71-centimeter statuette, dating from the Roman era, depicts a robed Buddha missing his limbs on the right side, with a halo surrounding his head, representing the sun’s rays.
According to Dr. Marius Goyazda, the stone used for the statue may have originated from a region south of Istanbul, with one theory suggesting that traders from India had the statue carved locally and dedicated to the nearby temple.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Under the supervision of the Supreme Council, the archaeological mission has been operating at the site since 1994.
The find reveals important trade links between the Roman Empire and India, the Egyptian authorities said.
Egypt was “at the heart of the trade route linking the Roman Empire to many parts of the ancient world,” said Mostafa Waziri, secretary general of the Supreme Council of Antiquities. Ships arrived from India, loaded with spices, jewellery, textiles and ivory.
Dr. Stephen Sidbotham, head of the American archaeological team, said that the mission also succeeded, during its work at the temple, in uncovering an inscription in Hindi (Sanskrit) dating back to the Roman Emperor Philip the Arab (Marcus Julius Phelps) (244 – 249 AD. ).
The Buddha statue, which is likely much older, and the other Greek inscriptions in the same temple, which date to the early first century BC, do not seem to be from the same era as this inscription.