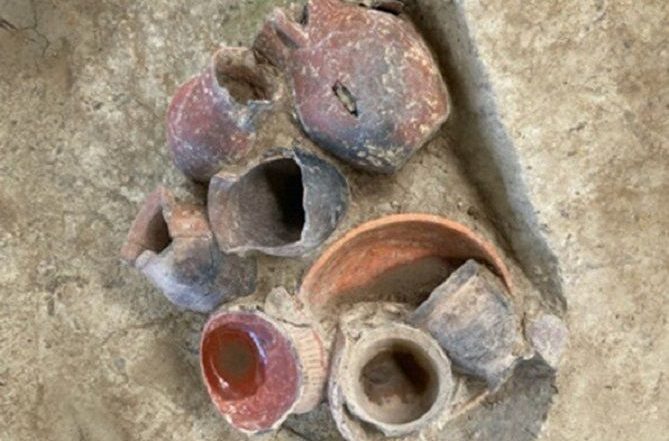
Archaeologists in southeast China have discovered evidence of beer consumption in ceramic vessels at the burial site called Qiaotou.
The researchers discovered ancient crud—starches, fossilized plant waste, and fungal remains—in those pots, indicating that some of those containers carried alcohol. The team’s findings were published in PLOS One last month.
The researchers write in their study that alcoholic drinks played a significant part in ancient societies’ rituals, and they discovered the earliest evidence of beer consumption in the context of burial rites in southern China during the early Holocene epoch.
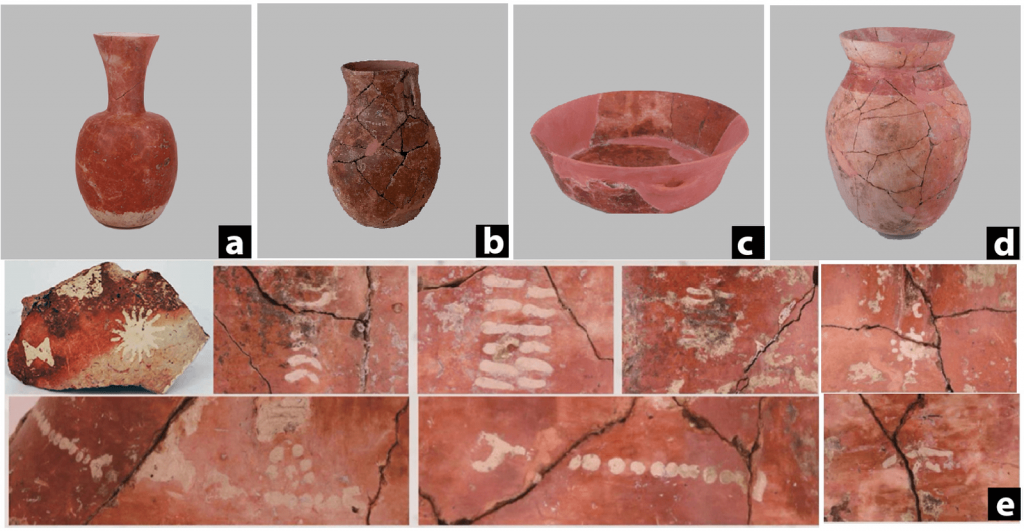
Several long-necked hu pots found in excavations at the site contained starches, fossilized plant residue, mold, and yeast remnants, indicating that they originally carried a fermented alcoholic beverage. In later periods, these Hu pots were used to drink alcoholic beverages.
Co-author Jiajing Wang, assistant professor of anthropology at Dartmouth, said in a statement, “Through an analysis of pots from Qiaotou, our results revealed that the pottery residue vessels were used to hold beer, in its most general sense—a fermented beverage made of rice ( Oryza sp.), a grain called Job’s tears (Coix lacryma-jobi), and unidentified tubers. This ancient beer though would not have been like the IPA that we have today. Instead, it was likely a slightly fermented and sweet beverage, which was probably cloudy in color” he said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The results also revealed that phytoliths from rice husks and other plants were found in the pots. They might have been used as a fermentation agent in the beer.
Given their location, the ancient people of Qiaotou utilizing rice in their beer is not unexpected; that area of southern China remains a major rice grower. Rice was still in its early days of domestication when the site at Qiaotou was inhabited.
Although the Yangtze River Valley in southern China is now recognized as the country’s rice heartland, rice domestication developed gradually between 10,000 and 6,000 years ago, thus rice was still in its early stages of domestication 9,000 years ago.
Given the laborious nature of rice harvesting and processing, the beer at Qiaotou was most likely a ritually significant drink/beverage, according to the researchers.
“We don’t know how people made the mold 9,000 years ago, as fermentation can happen naturally,” Wang says in the statement. “If people had some leftover rice and the grains became moldy, they may have noticed that the grains became sweeter and alcoholic with age. While people may not have known the biochemistry associated with grains that became moldy, they probably observed the fermentation process and leveraged it through trial and error.”
The beer at Qiaotou isn’t the earliest beer ever discovered—evidence of beer has been discovered at sites in Israel and Turkey dating back over 10,000 years—Earlier examples in the Mediterranean region, date to 13,000 years ago but its circumstances illustrate the importance of such alcoholic beverages in ancient cultural events.
The hu pots themselves, as well as other containers, were another unique item at the site. According to the study, they are among the world’s oldest known instances of painted ceramics. Some have abstract patterns on them. According to the experts, no additional pottery of the same type has been discovered at other locations during the same period.
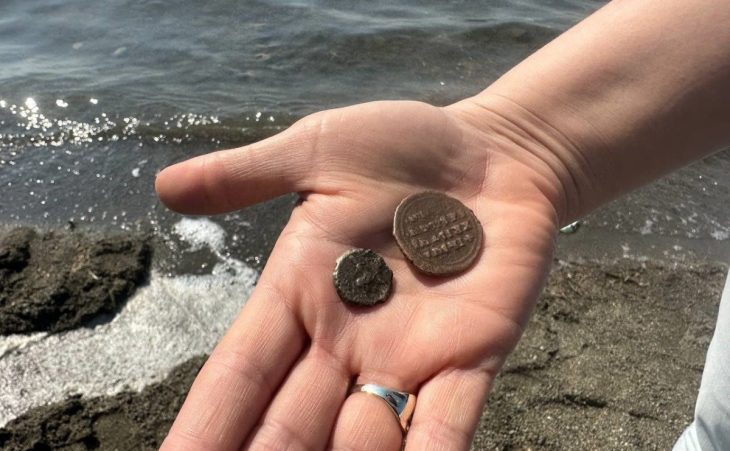
Cover Photo: Some of the vessels contained residue from an alcoholic brew. (Jiajing Wang)
















