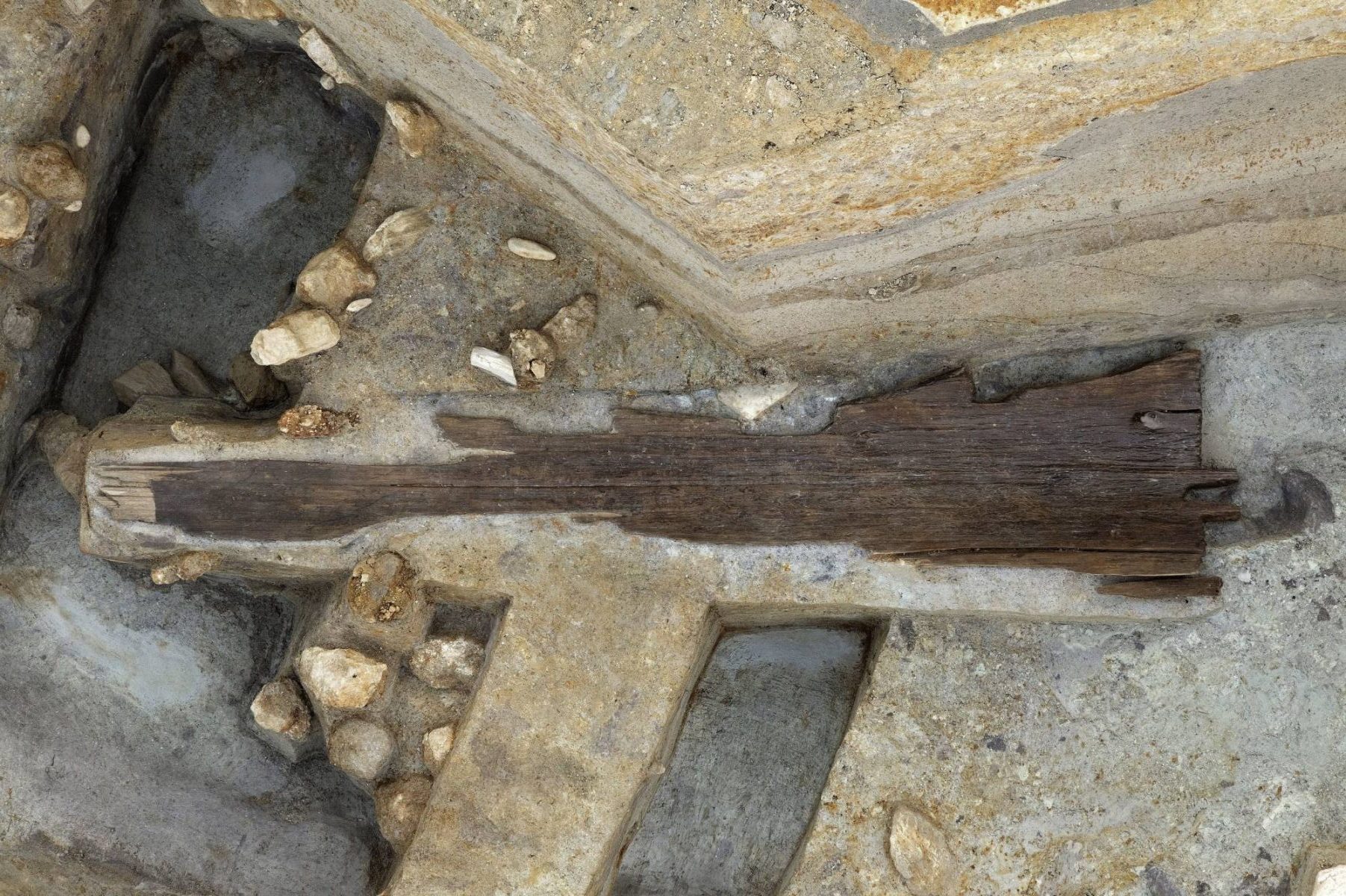
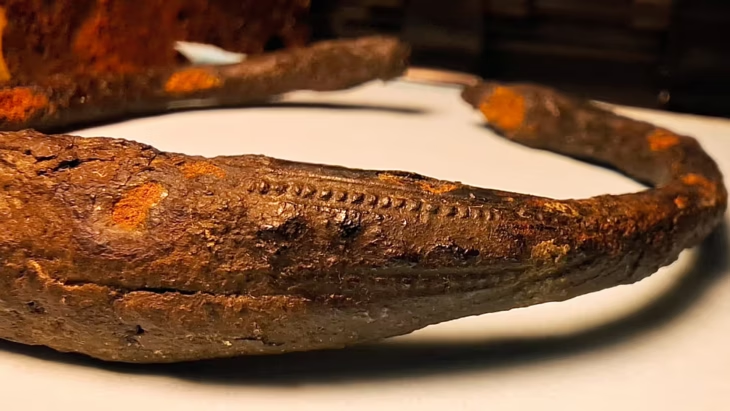The remains of a 3.5-meter-tall wooden “haniwa” statue have been discovered at one of the “kofun” ancient burial mounds that comprise the Mozu-Furuichi Kofun Group, a UNESCO World Heritage Site in western Japan, according to a local education board on Thursday.
The statue is thought to be one of the largest wooden haniwa found in Japan, with parts measuring 75 centimeters wide and around 8 cm thick.
Haniwa are large hollow funerary objects. Massive amounts of haniwa, many of which were nearly life-sized, were carefully placed on top of colossal, mounded tombs known as kofun (“old tomb” in Japanese). During the Kofun Period (c. 250 to 600 C.E.), haniwa evolved in a variety of ways, including their shape, placement on mounded tombs, and, presumably, their specific function or ritual use.
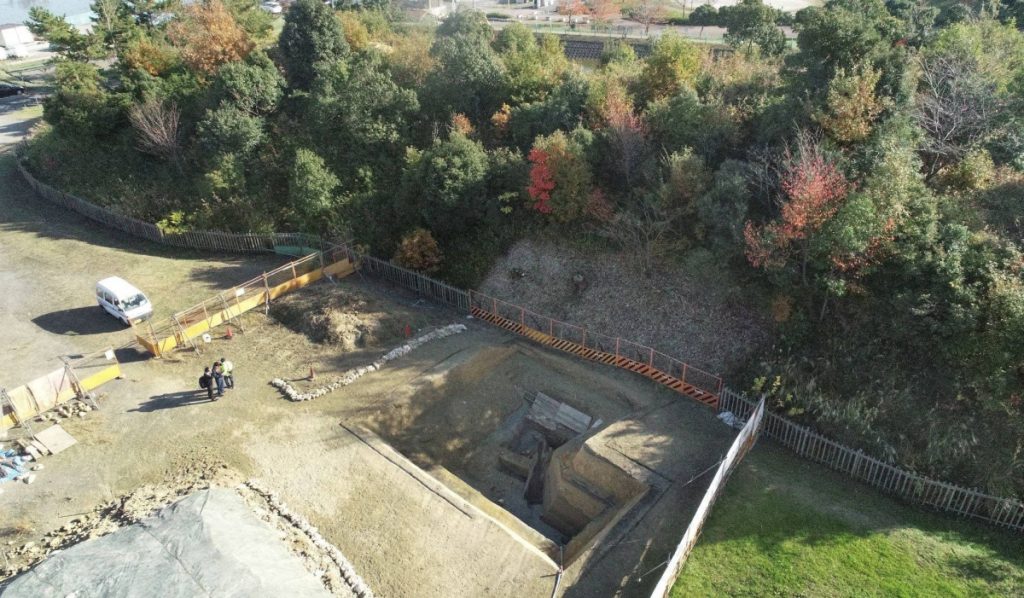
The haniwa was discovered during an excavation of a moat surrounding the 96-meter-long Minegazuka Kofun, which is thought to have been built at the end of the fifth century, according to the city of Habikino’s education board.
The statue is an Iwami-style haniwa, which “has only been found at 15 kofun tumuli in Japan so far,” according to an official of the education board.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

“The haniwa is a very rare artifact as it is made of kōyamaki (Japanese umbrella pine), which was a type of wood favored by people in power at the time,” the official said.
According to the Habikino education board, the haniwa is the tallest ever discovered, surpassing the 2.6-meter-tall Iwami-style specimen excavated from the Ohakayama Kofun in the city of Tenri in neighboring Nara Prefecture.
Studies of kofun indicate that a powerful state had emerged by around 250 C.E. in Japan. This state is identified by various names (such as the Yamato polity) and was generally centered in what is now Nara, Kyoto, and Osaka prefectures.
Many monumental tombs (kofun) were built in the shape of a keyhole, or zenp ken fun (“front squared, rear rounded tomb”). The square section is the front, while the round section is the back and houses the deceased’s body (or bodies). Keyhole-shaped tombs were adopted as a kind of signature style of this state.
Nara prefecture is home to the majority of the earliest surviving keyhole-shaped colossal tombs from the third century. One of these is Sakurai’s famous Hashihaka kofun, which measures approximately 280 meters in length and 30 meters in height. In comparison, the Khufu pyramid in Giza measures approximately 230m in length and 146m in height.
The earliest haniwa, from c. 250 C.E. to around the 450s, were simple forms and most were cylindrical. While the positioning of the haniwa varied from tomb to tomb, they were frequently lined up along the outermost perimeter of the tomb surface, seemingly to delineate boundaries.
Cover Photo: Remaining parts of a 3.5-meter-tall wooden haniwa statue unearthed from the Minegazuka Kofun in Habikino, Osaka Prefecture | HABIKINO BOARD OF EDUCATION / VIA KYODO