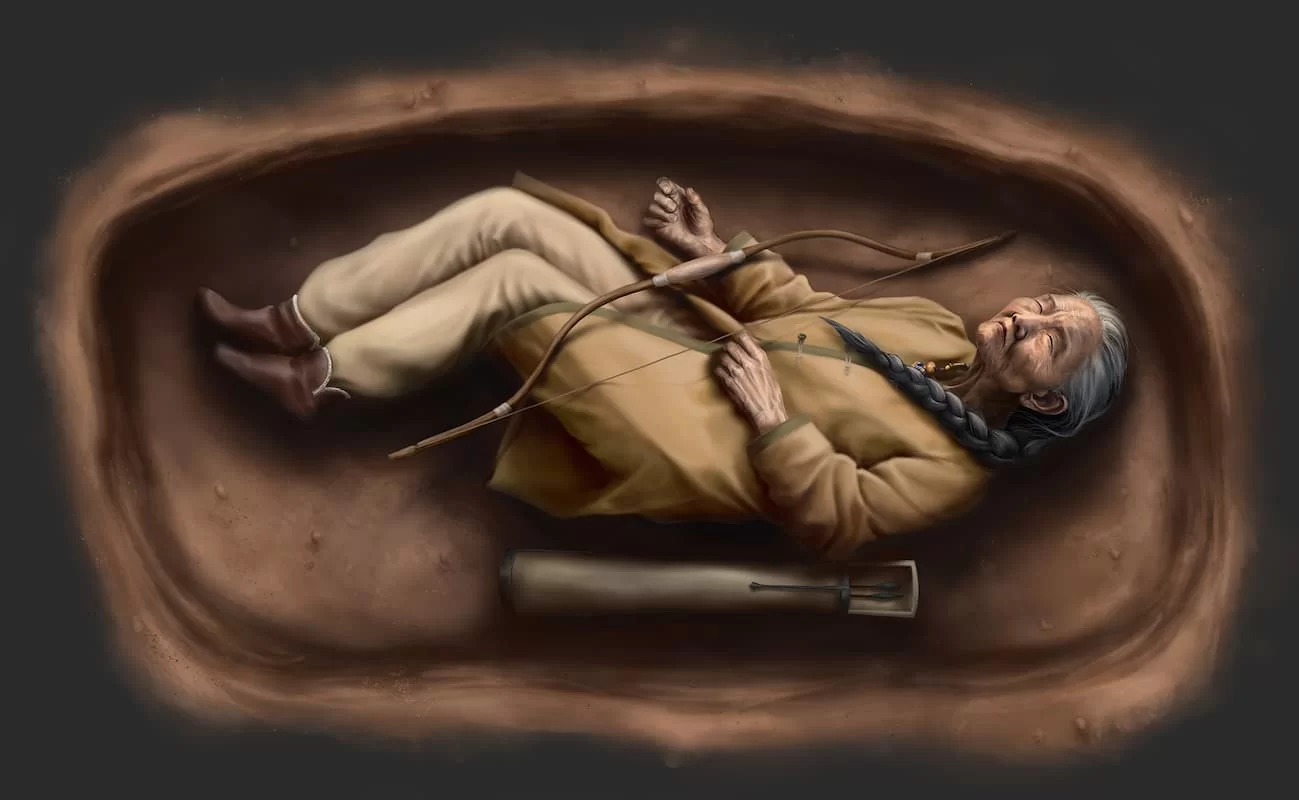
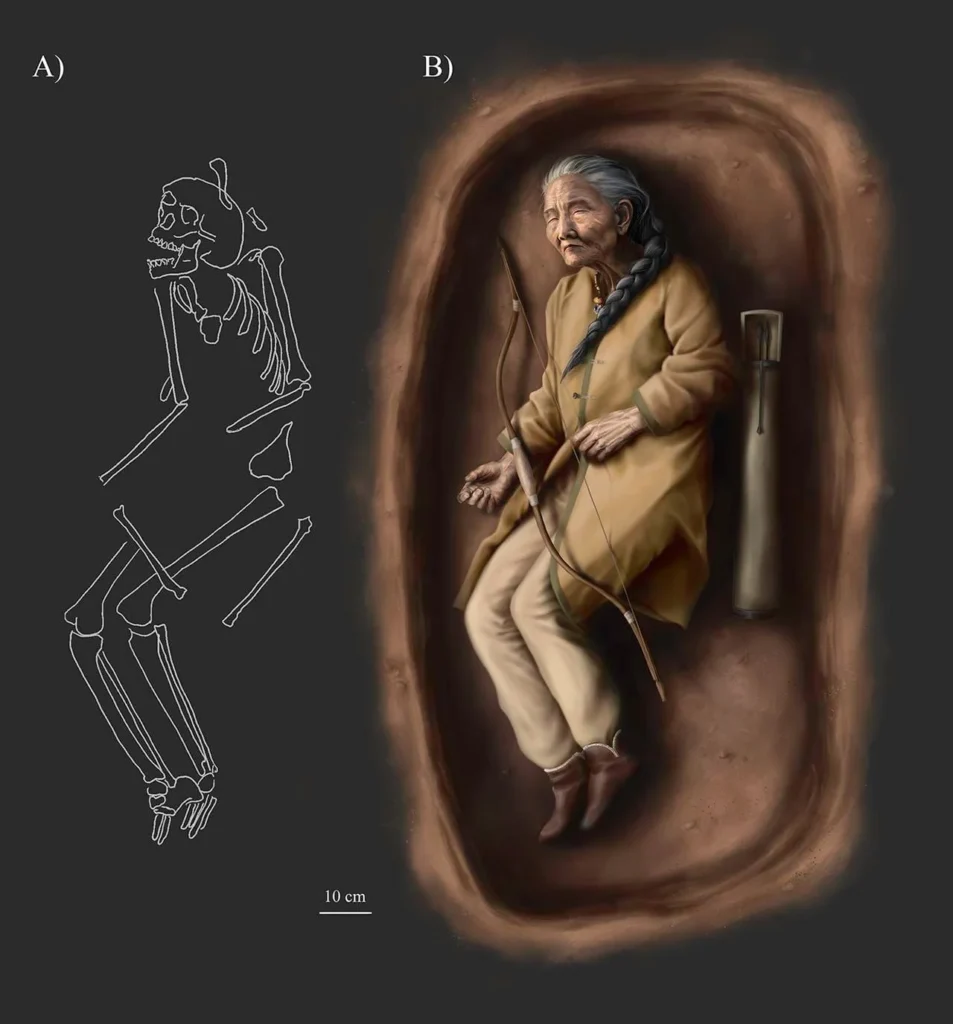
A team of archaeologists led by Balázs Tihanyi of the Department of Biological Anthropology and the Department of Archaeology at the University of Szeged, and the Department of Archaeogenetics at the Institute of Hungarian Research, dated the first known female burial with weapons in the Sárrétudvari-Hízófóld Cemetery in Hajdú-Bihar County, Hungary, to the 10th century, the period of the Hungarian Conquest.
From the Eurasian steppes, the Maygars (Hungarians) migrated to the Lower Danube region circa 830 AD. By the late 9th or early 10th century, they had arrived in the Carpathian Basin. The Kingdom of Hungary was established at the end of the tenth century after they quickly gained control of the region. In the Carpathian Basin and in battles throughout much of the rest of Europe, Hungarian mounted archers established a formidable reputation during this period. During this time, it is common to find warriors buried with various weapons, such as composite bows, arrows, quivers, bow-cases, axes, spears, sabres, swords, and swords with sabre hilts.
However, the existence of female burials with weapons has always been a topic of great interest and debate for scholars and the general public. These graves are difficult to interpret because finding weapons in a female burial site does not automatically equate that woman with a warrior.
In the study published in Plos One, archaeologists conducted both morphological and genetic analyses to determine whether the individual was female. Despite the skeleton’s poor preservation, the skull and genetic markers from different regions in the body indicated the interred was a female.
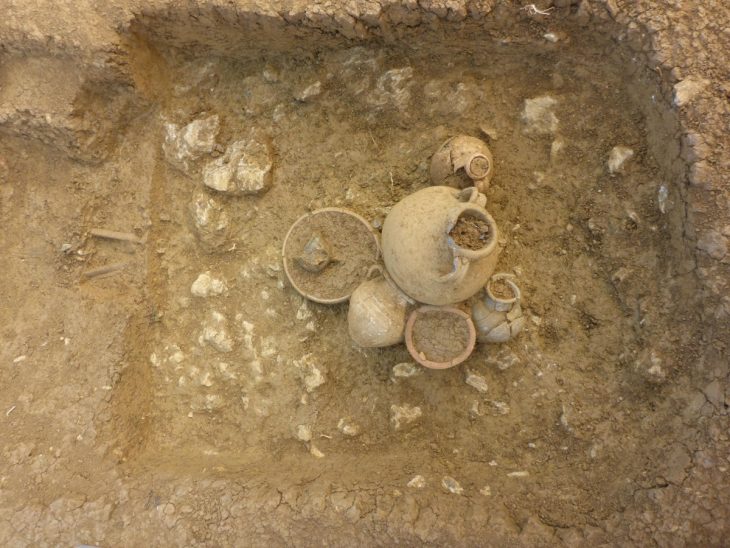
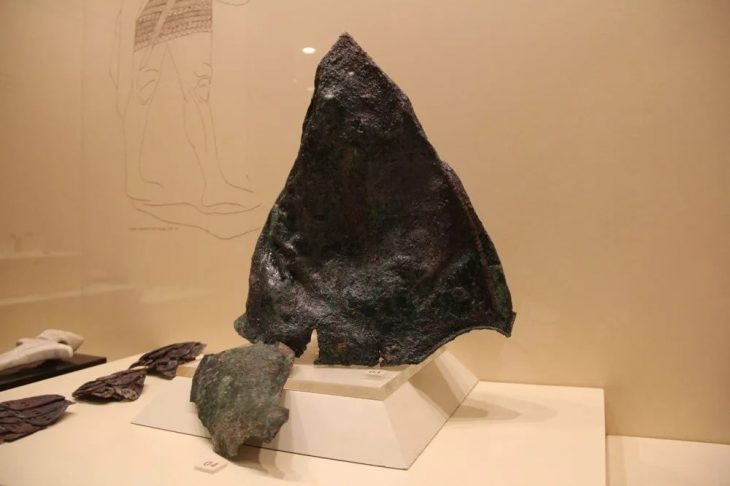
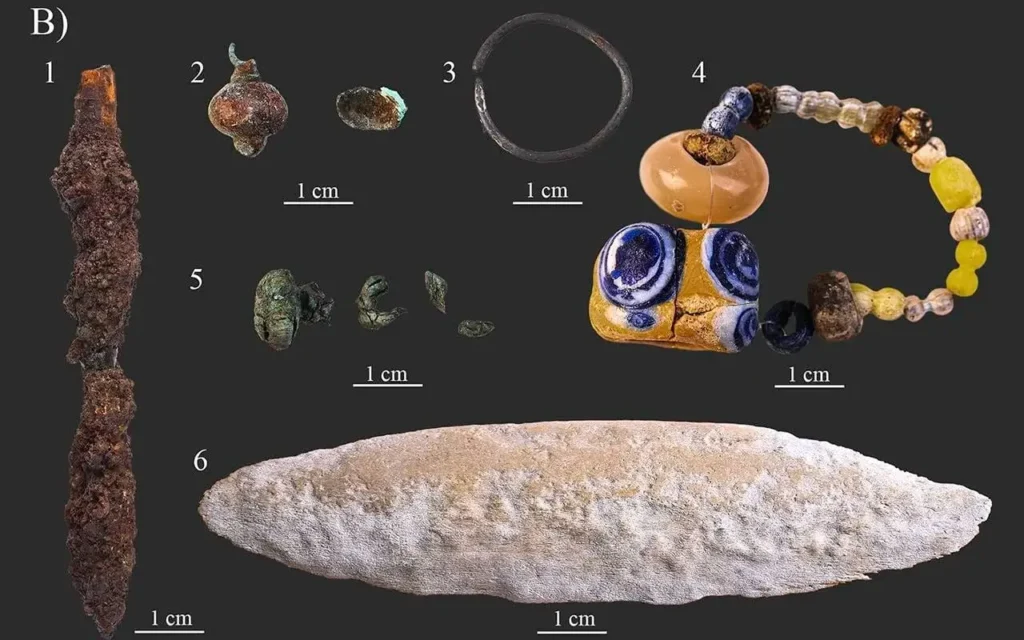
This study focuses on tomb number 63, which was excavated between 1983 and 1985 but was thoroughly examined using new interdisciplinary methods. The inventory of SH-63 was relatively simple but unique. A quiver, arrow fragments, a silver hair ring, glass beads, and semi-precious stone beads were among the items found in the tomb that set it apart from other tombs in the cemetery. In addition, there was a bow with a horn plaque.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Determining the sex of SH-63 by morphological means was challenging due to the poor preservation of the skeleton, especially the pelvis. The skull did appear to show some feminine traits, but this was not deemed sufficient to assign sex to the skull by previous studies. The petrosal process of the temporal bone, one humorous tooth, and genetic material were all extracted by Tihanyi et al. All three of these suggest that the person was female, and the pars pretrosa sample provides enough evidence to exclude the possibility that the person was male.
Archaeologists have discovered women buried with weapons in the past, such as during the Sarmatian and Avar eras in this area. These graves contained one weapon or talismanic item but did not prove that women were soldiers. The SH-63 burial from the Hungarian Conquest period is distinct. It demonstrates a distinct combination of gender, burial items, and social complexity.

This find’s uniqueness is further enhanced by the unusual object arrangement and the body’s slightly skewed position, which are uncommon in cemeteries from that era. According to the researchers, there has never been a female burial with a complete set of weapons recorded in this region, raising questions about the roles these women may have played in Hungarian society during the conquest.
Tihanyi B, Maár K, Kis L, Gînguță A, Varga GIB, Kovács B, et al. (2024) ‘But no living man am I’: Bioarchaeological evaluation of the first-known female burial with weapon from the 10th-century-CE Carpathian Basin. PLoS ONE 19(11): e0313963. Doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0313963
Cover Image Credit: Illustration of the burial based on archaeological, anthropological, and archaeogenetic data (drawing by Luca Kis). Credit: PLOS ONE (2024).