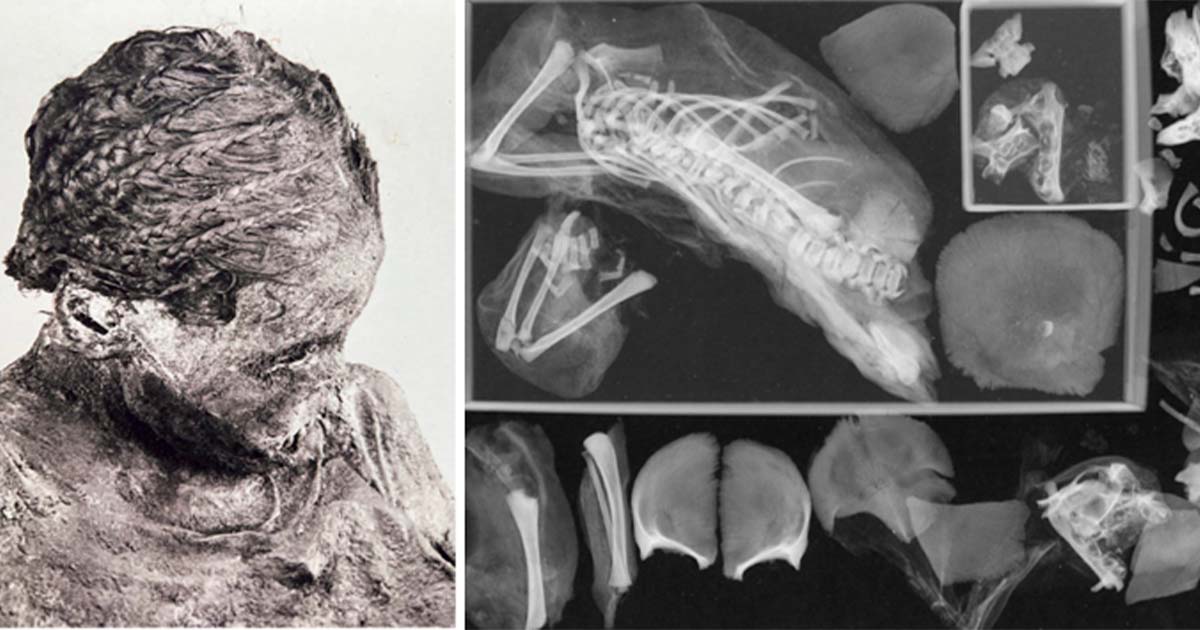
Archaeologists have made a shocking discovery after re-examining the mummified remains of a teen mom aged just 14-17 who died in childbirth more than 1,500 years ago.
What makes the find both horrifying and extraordinary at the same time, is one fetus and placenta found in the pelvic area, and another in the chest.
Researchers analyzed the mummified remains of a teenage girl who died during childbirth in ancient Egypt, revealing that the young mother-to-be was in the process of delivering twins when she died. Unfortunately, the labor took a negative turn when the first baby’s head became stuck in the birth canal, resulting in the deaths of both infants and the mother.
In Egypt’s Kharga Oasis, the teen mom was discovered in 1908 at the El Bagawat cemetery. The researchers noted that she had been extensively layered with “a great quantity of salt,” an ancient Egyptian practice known for its desiccating properties that effectively dried out the entire body. The body was dated to the Late Dynasty in ancient Egyptian history, spanning from 404 to 343 BC.
Field notes from the time reveal that she was found with a fetus and placenta between her legs, leading to the conclusion that she had died from obstetric complications.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Using computed tomography (CT) scans of the body, the George Washington University team revisited the mummy after over a century to ascertain precisely what might have gone wrong. The scans revealed the presence of a second fetus within the woman’s chest cavity, indicating that she was carrying twins.
More startling revelations were to come when the researchers noted that the infant placed between the woman’s legs was missing its head. Upon closer examination, they realized that the baby’s head was still lodged in the mother’s pelvis, leading them to suspect that the fetus had become decapitated during the birthing process.
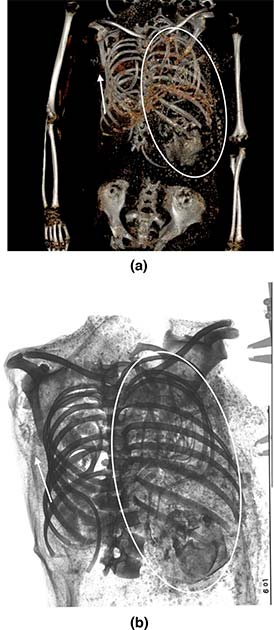
The study authors describe this outcome as a case of “traumatic fetal decapitation,” a rare consequence of breech presentations, i.e., feet first during childbirth.
“This is a rare find,” Francine Margolis, one of the study authors, told McClatchy News. “There are several examples of women dying during childbirth in the archaeological record (one was a twin pregnancy). However, there has never been one found in Egypt.”
The second fetus discovered in the woman’s chest cavity raised some mystery. According to the researchers, it’s possible that the embalmers were not aware of the twin pregnancy and forgot to remove the second fetus before mummification. According to IFL Science, the unborn twin may have moved from the womb to the chest cavity as the mummy’s diaphragm dissolved.
“This examination of the mother and her children at birth reconfirms how dangerous pregnancy, labor, and delivery was, especially during this time period,” write the study authors.
The ancient Egyptians held a deep reverence for symbolism, balance, and order, and these beliefs extended to their views on procreation and childbirth.
A spell found on ancient papyrus, the Oracular Amuletic Decree, said, “We shall (cause her) to conceive male children and female children. We shall keep her safe from a Horus-birth, from an irregular birth and from giving birth to twins.”
Spells and incantations like this one reveal a cultural aversion to twin births, seeking protection from “irregular birth” and giving birth to twins. The tragic story of this young mother and her unborn twins is a tragic reminder of the difficulties that ancient women faced during childbirth.
The study – including images of the mummy – is published in the International Journal of Osteoarchaeology.
https://doi.org/10.1002/oa.3275
Cover Photo Source: Francine Margolis, David R. Hunt/onlinelibrary.wiley.com