A new wave of archaeological research at Mount Tangkil is reshaping academic understanding of West Java’s ancient landscapes. Recent investigations by the National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN), supported by the Prabu Siliwangi Museum and local researchers, suggest that the forested mountain may hold one of the region’s most significant megalithic sites.
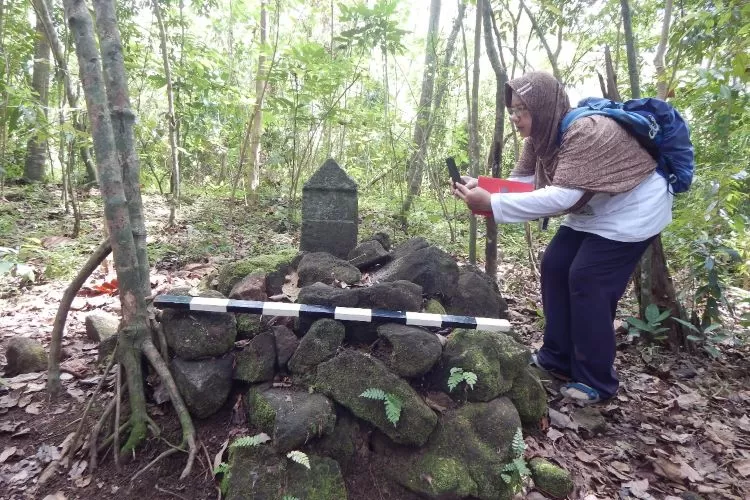
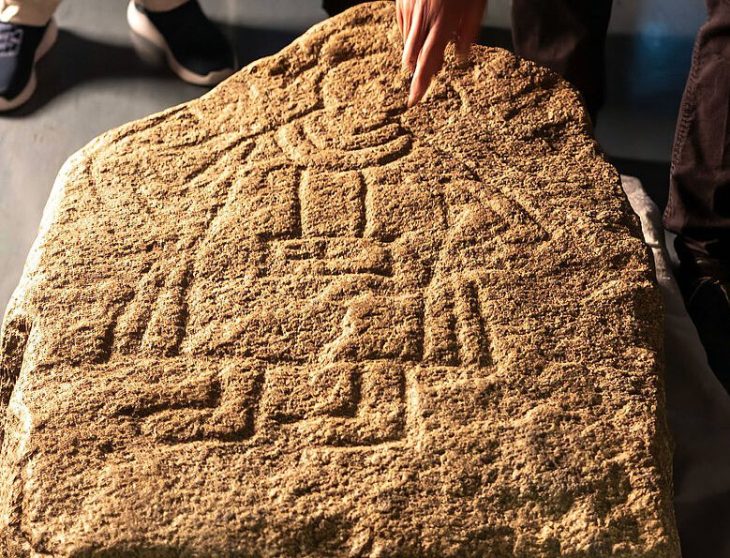
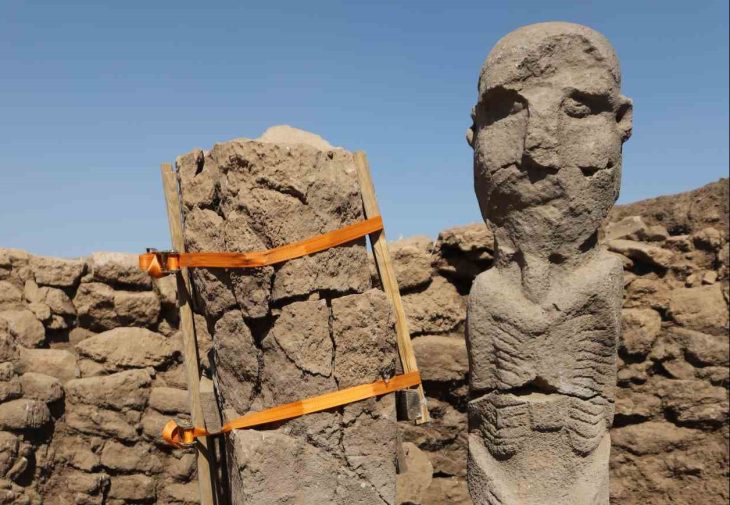
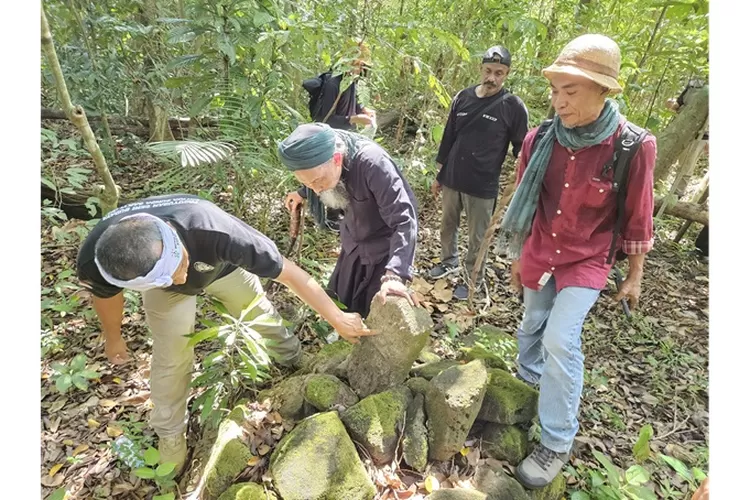
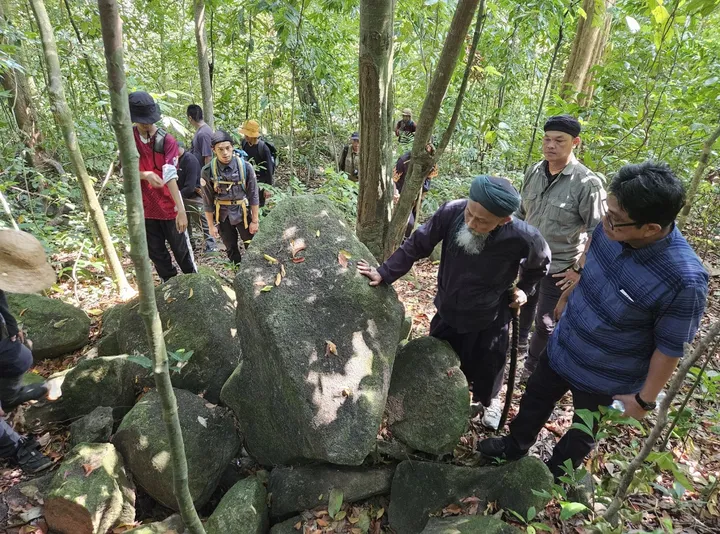
The discovery began earlier this year when researcher Zubair Mas’ud identified a fragment of stone sculpture in a remote area of Mount Tangkil’s densely vegetated slopes. Preliminary analysis showed that the artifact’s lithic composition closely resembles megalithic objects stored in the Prabu Siliwangi Museum. According to cultural heritage advocate KH Fajar Laksana, who presented the findings during an archaeology seminar in July, the similarities point to a likely shared origin. “The composition and characteristics indicate a strong connection. This is a very promising discovery,” he said.
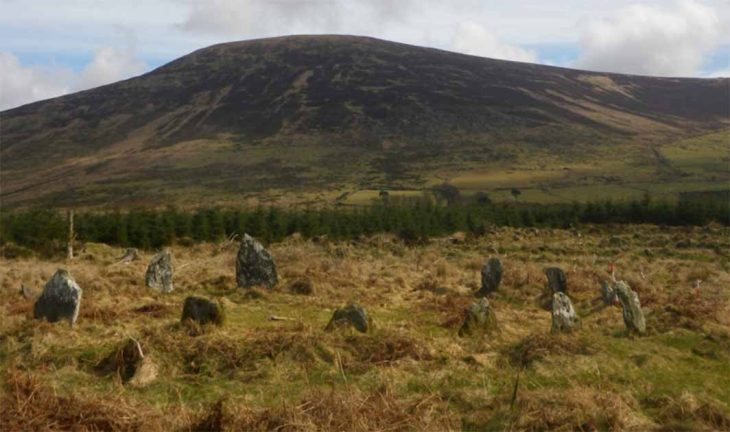
Although Mount Tangkil has not yet been designated an official cultural site, scattered discoveries in nearby locations — including a menhir in Tugu Village and similar stone remnants on Mount Karang — have strengthened hypotheses that the area was once part of a broader megalithic network in West Java.
LiDAR Technology Provides Breakthrough Evidence
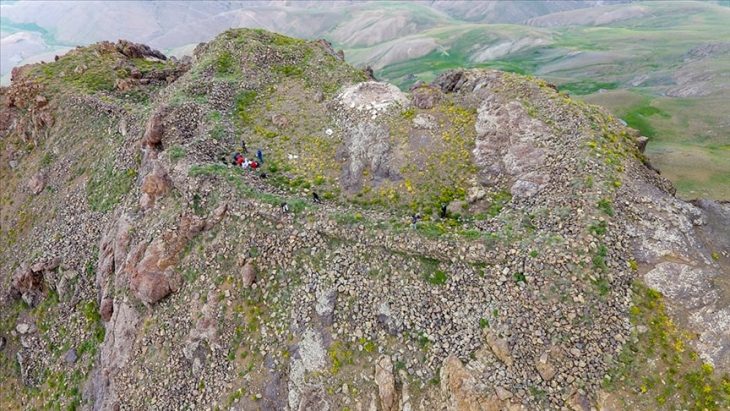
From 16–20 September 2025, BRIN deployed LiDAR technology (Light Detection and Ranging) over parts of Mount Tangkil, marking the most advanced survey of the site to date. The laser-based method, capable of penetrating thick forest canopy, revealed previously hidden stone arrangements and surface anomalies.
M. Irfan Machmud, Head of BRIN’s Research Center for Prehistoric and Historical Archaeology, said the newly detected formations strongly suggest deliberate human design. “We’ve identified concentrated stone structures in elevated zones, indicating that the area was not used randomly but followed environmental patterns suitable for ancient human activity,” he explained.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The LiDAR data points to four main terrace clusters:
First terrace: fragments of stones, menhirs, a potential statue, and remnants of a stone pathway.
Second terrace: structured stone arrangements resembling traditional dakon layouts.
Third terrace: mounded stones, possible ritual features, and vertical marker stones.
Fourth terrace: elongated stone formations and additional upright stones.
Researchers also detected anomalies believed to be remnants of ancient pathways and terraced platforms, indicating sophisticated land modification.

Ceramic Findings Reveal Long-Term Trade Connections
Alongside the stone structures, BRIN’s earlier field surveys uncovered hundreds of ceramic fragments dating from the 10th to 20th centuries. Ceramic experts on the team note that the pieces reflect centuries of interaction between the Indonesian archipelago and Chinese maritime traders. This, they argue, suggests that Mount Tangkil’s surroundings may have once been linked to regional trade routes, expanding its significance beyond ritual or ceremonial functions.
“These ceramics provide evidence of extensive economic interaction,” one researcher said. “It’s not only crucial for archaeology, but also for understanding regional trade history.”
Challenges in a Protected Conservation Area
While the findings are compelling, further research faces environmental and regulatory limits. Mount Tangkil lies within the protected Sukawayana nature reserve, restricting excavation and prohibiting damage to surrounding vegetation. Even trimming branches requires special permission.
“The challenge is that we cannot yet excavate key areas,” Irfan said. “For now, we remain limited to surface analysis and aerial surveys. We need more coordination with forestry authorities before proceeding.”
Despite these limits, Irfan believes the site holds exceptional research potential: “The conservation area means the data has remained largely undisturbed. For archaeological integrity, this is an ideal condition.”
Academic Interest and Cultural Importance Growing
Interest in Mount Tangkil is also rising among scholars. Prof. Ali Akbar of the University of Indonesia — known for his involvement at the famous Gunung Padang site — has stated that the mountain may be linked to other megalithic centers across West Java. Such connections could make Mount Tangkil an essential piece in understanding prehistoric cultural networks in the region.
Mount Tangkil also remains significant to local communities who continue ancestral rituals at several points in the area. Researchers argue that these living traditions strengthen the case for official recognition.

Calls for Cultural Heritage Status Intensify
Given the mounting evidence, researchers from BRIN and cultural leaders have formally encouraged both regional and national governments to establish Mount Tangkil as a cultural heritage site. “What began as a routine museum verification effort has developed into strong indications of a major archaeological site,” said KH Fajar. “We urge the government to protect Mount Tangkil as cultural heritage.”
BRIN is preparing for another research phase in early September, involving drone mapping and expanded LiDAR scanning to refine structural interpretations and identify possible buried features.
If validated and protected, Mount Tangkil could become one of Indonesia’s most important newly identified megalithic areas — offering insights into ancient engineering, trade, and cultural practices hidden for centuries beneath the dense Sukabumi forest.
Cover Image Credit: MUSEUM PRABU SILIWANGI