Iranian archaeologists believe they have discovered the first evidence of early administrative management in an eastern Iranian province, which they think will provide fresh information about the people who lived there 6,000 years ago.
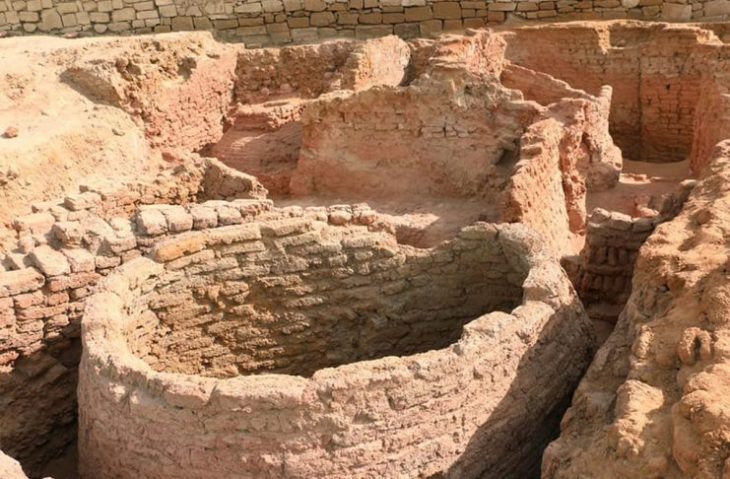
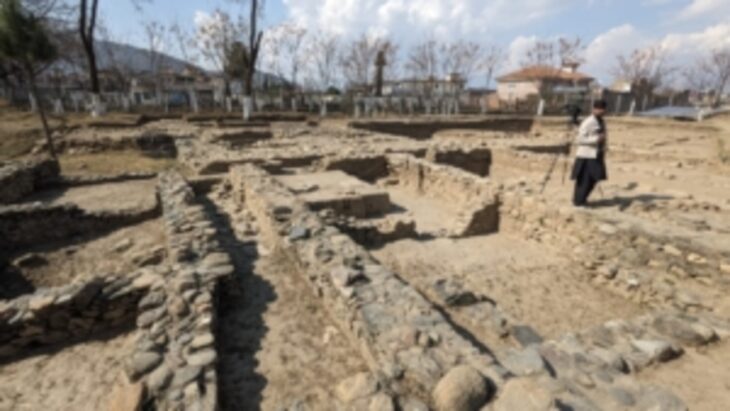
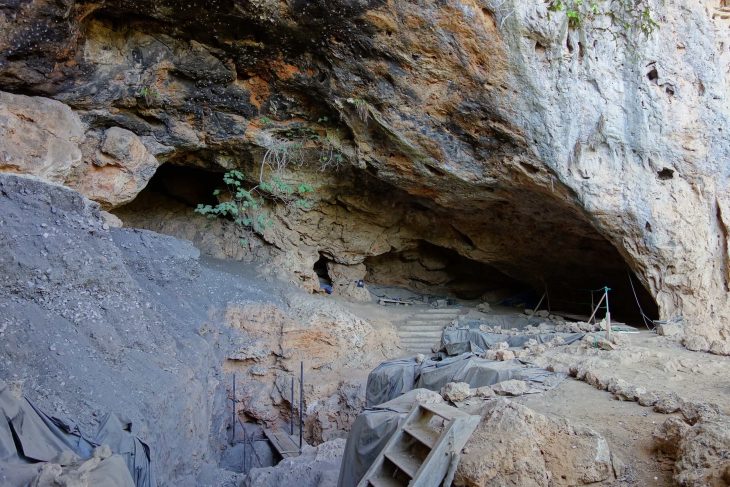
The discovery was made during the third archaeological excavation season which is currently underway in Kale-Kub, which is situated in Sarayan county of South Khorasan province.
Kale Kub is a prehistoric site that is located in Ayask town, in Sarayan District, South Khorasan Province, eastern Iran.
This exploration is very important because Eastern Iran, especially in the prehistoric period, is a completely unknown region on the Iranian archaeological map. More than one hundred years after the beginning of archaeological excavations in Iran, the eastern regions have received little or no attention from archaeologists for various reasons, and there are very limited publications as well.
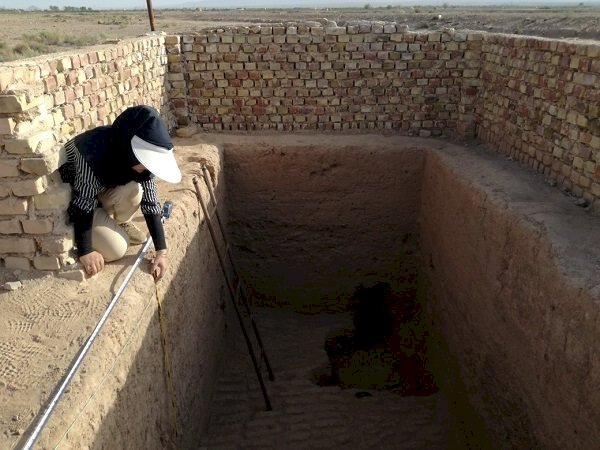

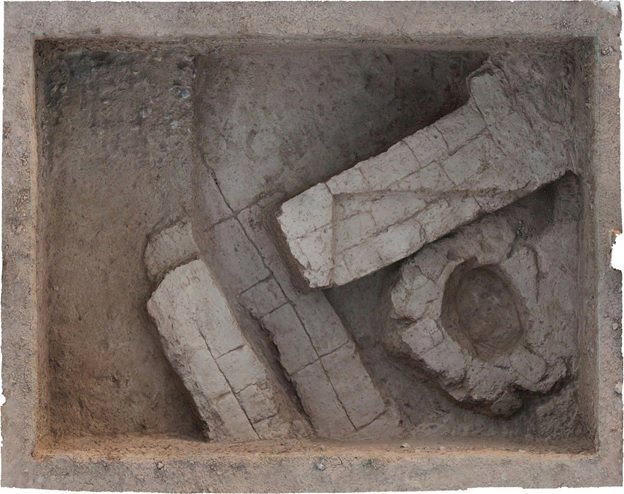
“More than ten days after the start of the excavation, we found remnants of industrial architecture, adobe brick walls, and potteries, which offer evidence of social complexity and an administrative management system,” CHTN quoted archaeologist Mohammad-Hossein Azizi Kharanaghi as saying recently.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Kale-Kub is one of the few historical sites in the region that has archeological evidence of the sequences of different cultures from the fifth to the second millennium BC, Azizi Kharanaghi, who leads the survey, explained.
Referring to previous excavations of the site, the archaeologist has said: “In 2018, two trenches were opened to identify the stratigraphy of the high amount of beveled rim bowls in addition to other pottery styles belongs to fourth millennium BC which are already known in southwestern Iran.”
The archaeologist hopes their studies would clarify the importance of the Kale-Kub site for identifying the dispersal zone of “Beveled rim bowl pottery style” through the classification and typology of the discovered potteries and then a comparison between the pottery style in this site with other sites related to this period.
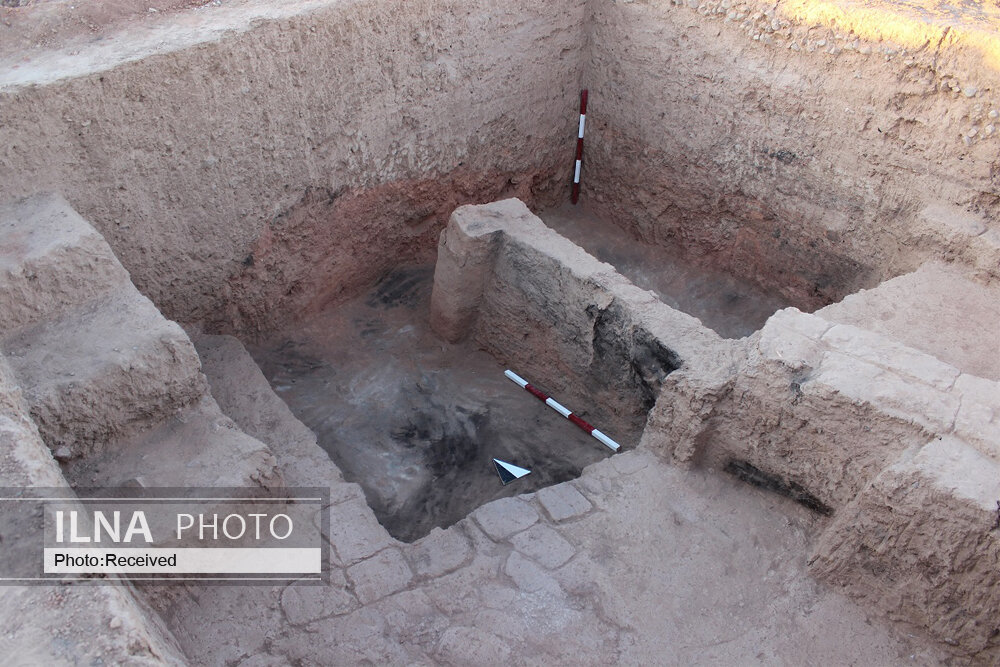

“Also, we attempt to trace the possible routes for this pottery style to the East and the interaction between the east and west of Iran. Pottery collection from the excavation in Kale-Kub includes a high amount of beveled rim bowls, Banesh tray, and some other pottery styles which are well-known from the fourth millennium BC such as nose handle and spouted wares.”
In modern Iran, these pottery styles are reported from the southwest, central Zagros, central plateau, and southeast. Experts believe findings in Kale-Kub show the extension of this culture to the east part of Iran.
The late 4th millennium BCE Mesopotamian beveled rimmed bowl is: a crude piece of pottery easily cupped in two hands and has straight sides that terminate in a beveled rim. Bevel-rimmed bowls (abbreviated BRB) are unsightly, sturdy, and inexpensively constructed, as they are created with a mold rather than a wheel. Because of the coarseness of the pottery, the bowl is porous and will not hold liquid. Their size is surprisingly stable.
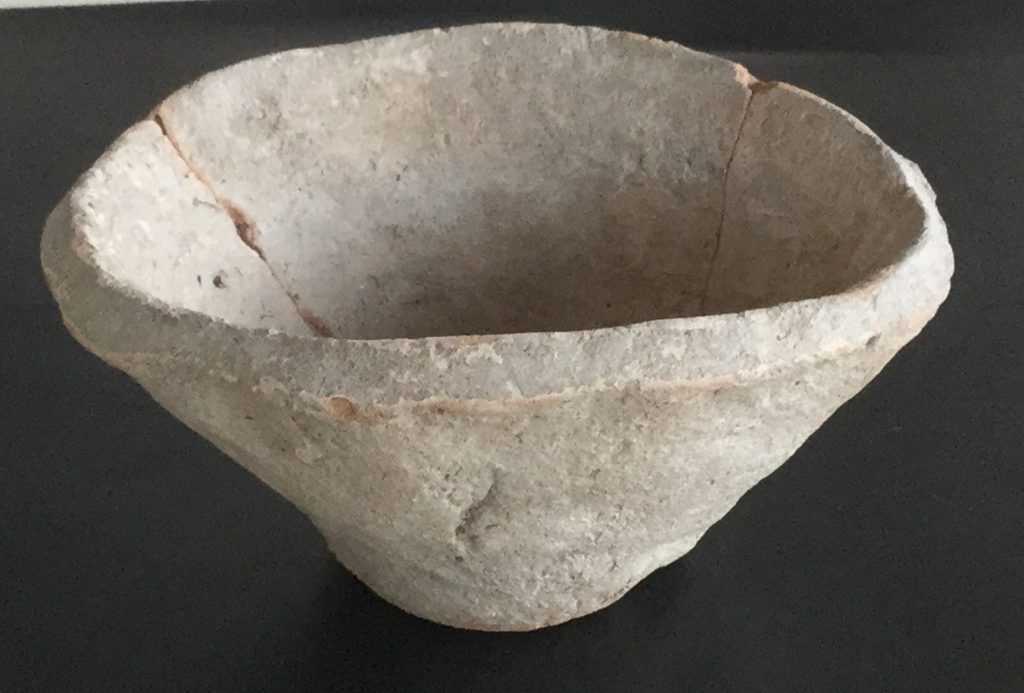

Beveled rim bowls are supposed to have been used to measure portions of barley and oil. The rations would be given as payment to laborers for services rendered. Moreover, Beveled rim bowls are one of the most iconic ceramic types found during the Uruk period in Mesopotamia.
Inter-regional interactions had a significant effect on the movement of raw material and production in the extended area. Because of the geographical situation of Kale-Kub in the east of Iran and the existence of metal mines in the region, this site possibly appeared as a supplier place in the interaction networks for the southwest of Iran during the fourth millennium BC.
These cultural evidences, which can be considered to belong to the Susa II horizon or late Uruk cultures, include the typical pottery of this period, such as bevelled rim bowls, rough Banesh trays, tubular and nose handle jars, and fine and painted wheel-made pottery, which is well known in the south-western, western, north-western, south-eastern regions and central plateau of Iran, but which have now been identified and introduced for the first time in eastern Iran.
On this site, three cultural periods have been identified so far. They have been classified from the bottom level and the top of the virgin soil are 1: KALE KUB I (Chalcolithic period, fifth millennium BCE), 2: KALE KUB II (Susa II horizon, fourth millennium BCE), and 3: KALE KUB III (Bronze age, third and second millennia BCE).