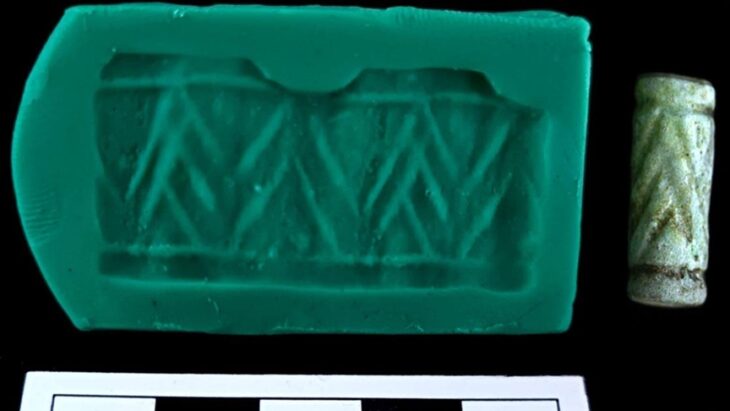
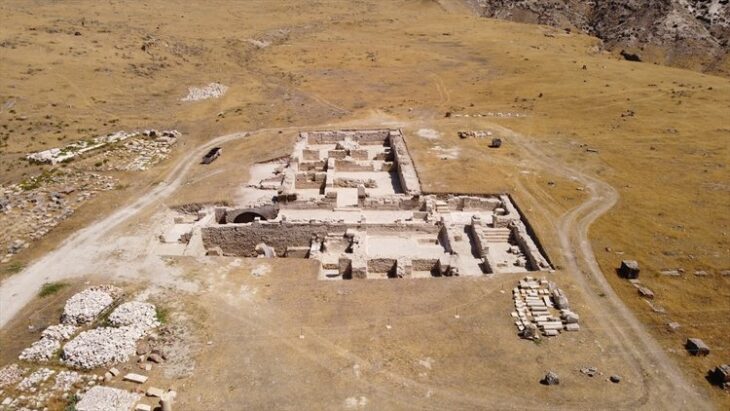
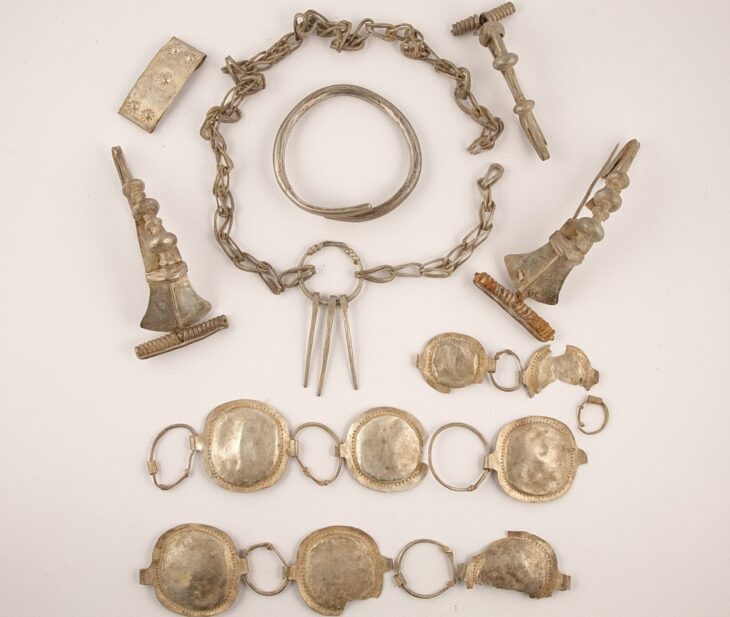
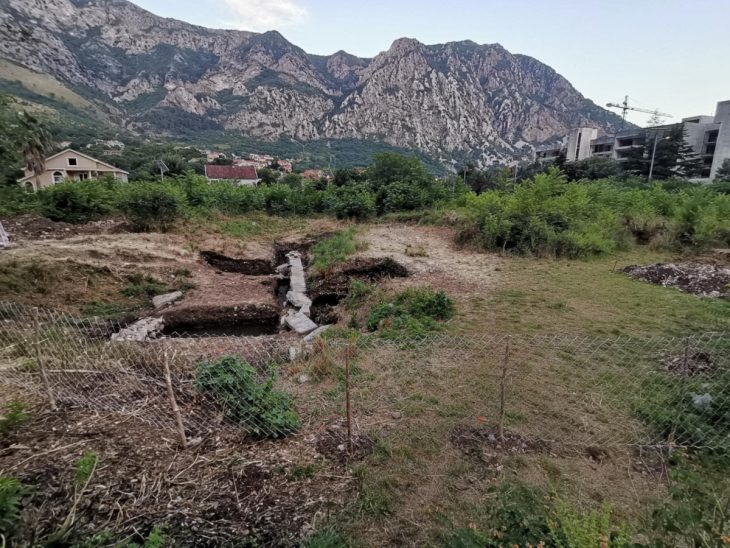
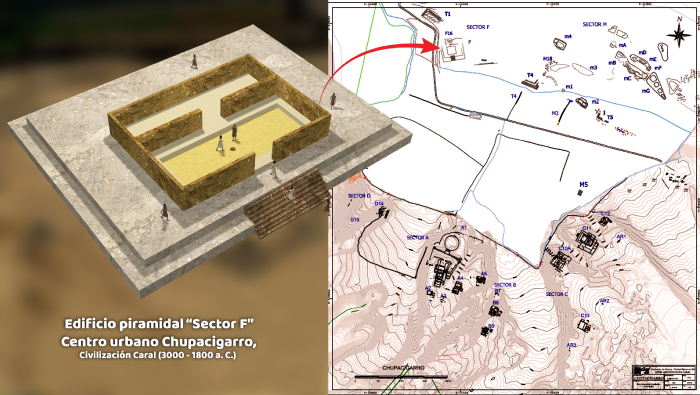
The team from the Caral Archaeological Zone has discovered a new pyramidal structure in the “Sector F” of the Chupacigarro archaeological site, located one kilometer west of the Sacred City of Caral-Supe, a World Heritage site, in the Supe Valley, Barranca province, Lima Region, Peru.
The discovery was made by a multidisciplinary team from the Caral Archaeological Zone, led by Dr. Ruth Shady. Originally covered with huarango trees and bushes, the structure later revealed stone walls with at least three superimposed platforms and large ‘huancas’ (vertical stones) marking the corners of the building.
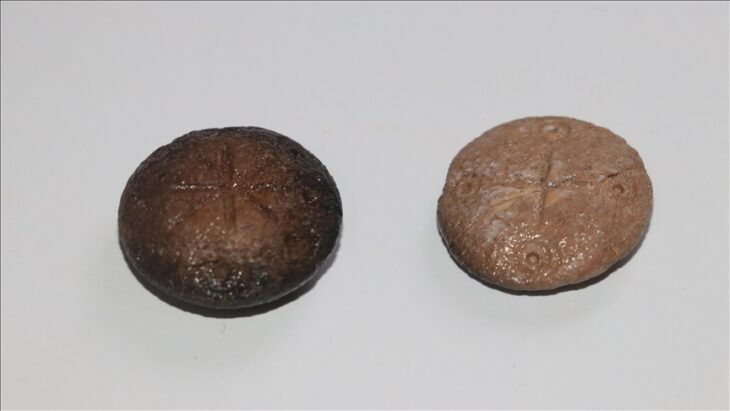
The structure, which is quadrangular in shape, features a central staircase that allows access to its summit. The “huancas” served not only a structural function but also a symbolic one, highlighting the ceremonial importance of the site.
The site contains 12 public or ceremonial structures distributed across hills, presided over by a Main Building with a sunken circular plaza. Additionally, residential areas have been identified on the periphery, suggesting a small urban center of 38.59 hectares with both public and private functions.
Chupacigarro is situated adjacent to a small water ravine, in proximity to the Sacred City of Caral Supe. The recently uncovered pyramid is an integral component of a broader network of architectural structures identified across multiple archaeological sites within the Supe Valley region.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The twelve identified structures, classified as either public or ceremonial edifices, are strategically dispersed throughout the landscape, positioned atop the small hills that characterize the ravine and encircling a central communal space. These constructions were erected by the Caral civilization, which thrived in ancient Peru from approximately 3000 to 1800 B.C.
The Caral civilization is one of the oldest and most advanced civilizations in ancient Peru, existing between approximately 3000 and 1800 B.C. in the Supe Valley. This civilization made significant advancements in agriculture, architecture, and social organization. Caral is known for its large pyramids, public buildings, and complex social structures. Additionally, while Caral did not use a written language, it possessed a complex social hierarchy and trade network. These characteristics contributed to Caral’s prominent status among Andean civilizations.
The architectural structures at the Chupacigarro site exhibit a diverse range of sizes, orientations, and formal characteristics, suggesting a correlation with their functional purposes. Notably, residential architecture has been identified along the periphery of the site. A prominent building oversees a series of smaller structures, featuring a sunken circular plaza that is characteristic of this historical period.
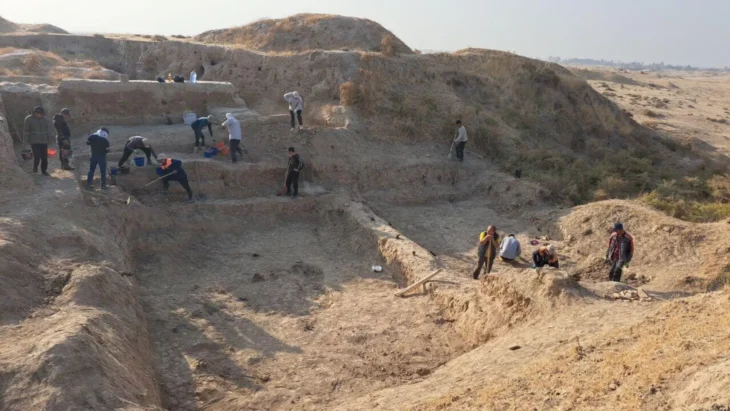
These significant findings have prompted experts to assert the existence of a small urban settlement that once thrived in the area, which spans nearly 38.59 hectares. Under the leadership of Dr. Ruth Shady, the research team responsible for the Chupacigarro discovery is now set to undertake a comprehensive mapping of the entire site to gain a clearer understanding of its overall dimensions and significance.
In addition to the architectural findings at Chupacigarro, one of the most remarkable discoveries is a geoglyph depicting a profile head in the Sechín style, which can only be observed from a specific vantage point. This significant finding underscores the ritual and symbolic importance of Chupacigarro, suggesting a connection to the Sacred City of Caral and the coastal populations of the Huaura Valley.
The geoglyph indicates that the site may have served as a focal point for cultural and ceremonial activities, facilitating access to both marine and agricultural resources that were vital to the communities in the region.
Cover Image Credit: Gob.pe