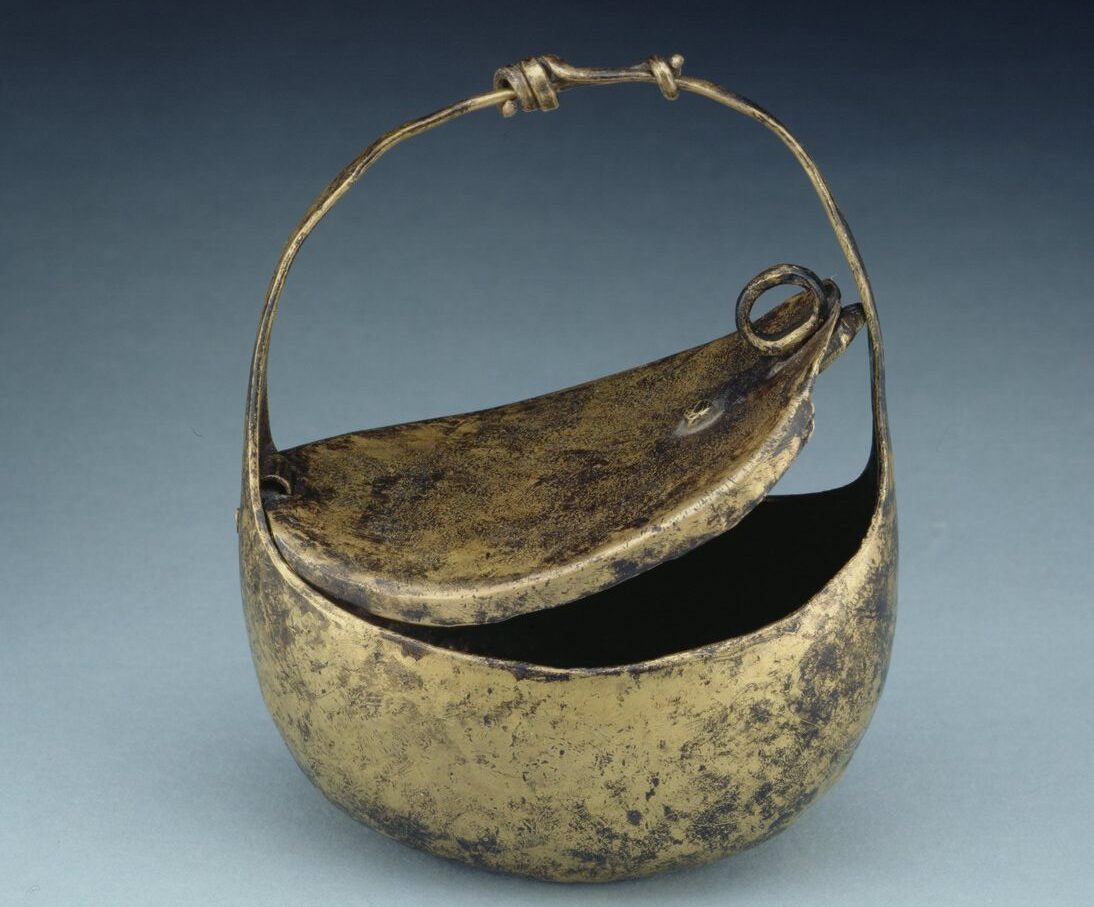
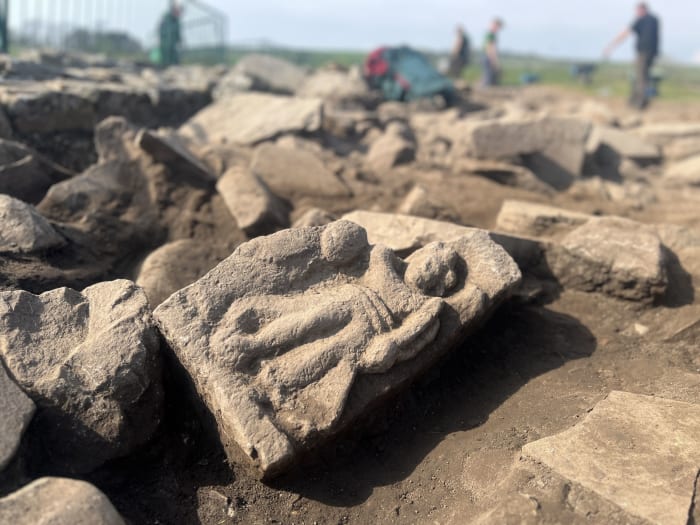
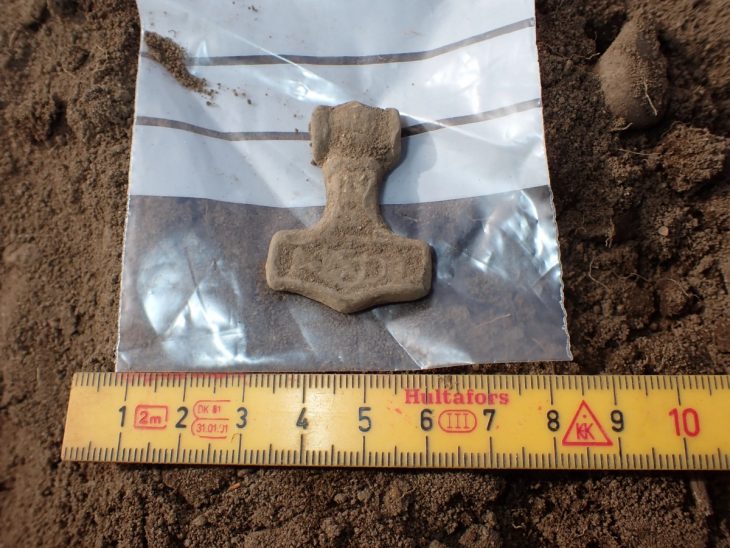
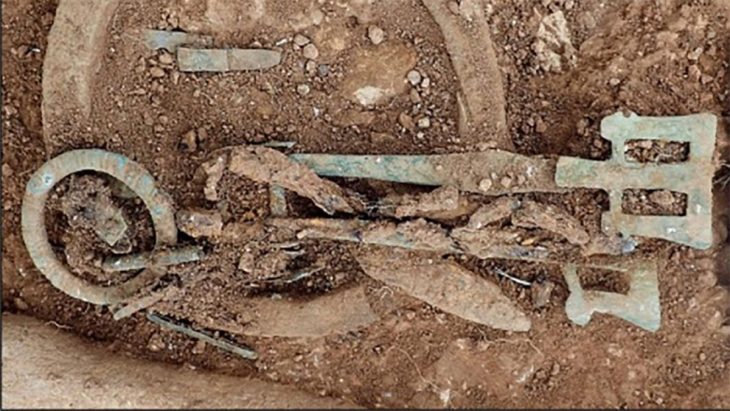
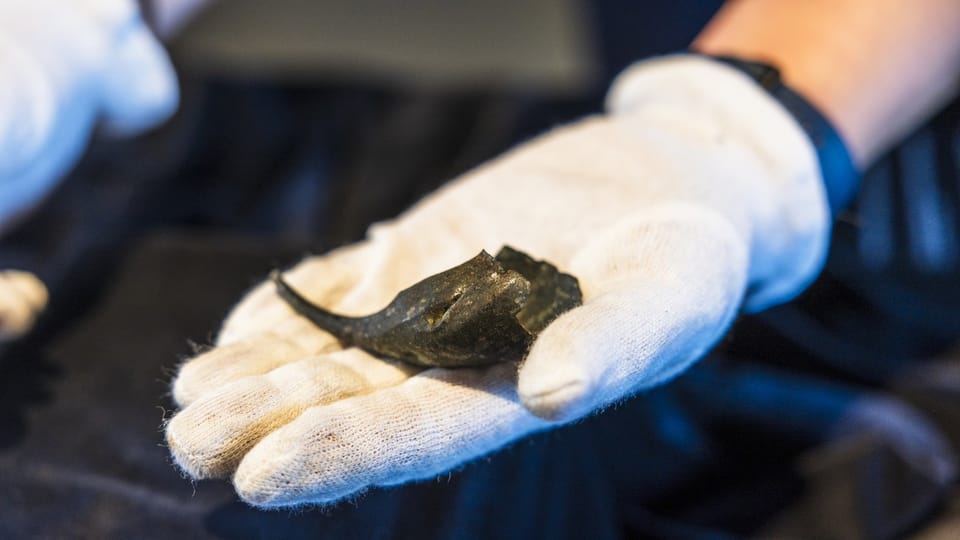
Archaeologists in South Moravia have unearthed a remarkable and historically significant artifact: a bronze fragment of a Roman soldier’s wrist purse. Dating back over 1,800 years, this discovery on Hradisko Hill is believed to be the oldest purse of its kind ever found in the territory of modern-day Czechia.
The rare find, made in January, comes from the site of a fortified camp once occupied by the 10th Roman Legion during the reign of Emperor Marcus Aurelius. While only about 30 percent of the original purse remains, experts quickly identified it as a type of forearm purse commonly used by Roman soldiers.
Speaking to Radio Prague International, Balázs Komoróczy from the Czech Academy of Sciences elaborated on the design: “It is more like a small money box. It was worn by sliding it onto the arm or forearm. The tension around the arm kept it closed and secure.”
While similar objects have been found in former Roman territories, particularly in military contexts from Britain to the Danube, this marks the first instance of such a purse being discovered in what was then considered enemy territory. No coins were found within the purse itself, but the abundance of Roman silver money discovered nearby helped archaeologists date the artifact.

“Most of the coins found at the site and in the surrounding area date back to the reign of Marcus Aurelius,” noted archaeologist Tomáš Antoš. “They typically feature either the emperor himself or his wife, Faustina.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Experts estimate the purse could have held approximately 50 silver denarii, a substantial sum for the time, though not quite a full year’s pay for an ordinary soldier. This suggests the purse may have belonged to a junior officer or someone responsible for managing unit expenses during military movements. It’s also possible it contained a mix of personal funds and “service cash” for logistical needs. Based on its design, it would have been worn on the left arm, keeping the right hand free for combat.
The 10th Legion was stationed on Hradisko Hill between 172 and 180 AD. Emperor Marcus Aurelius had ambitions to establish a new province, Marcomannia, in the region, extending from the Danube to northern Moravia. However, continuous conflicts with the Marcomanni ultimately thwarted this plan. Following the emperor’s death, his son Commodus, famously portrayed in the film Gladiator, ordered the Roman army’s withdrawal from the area.
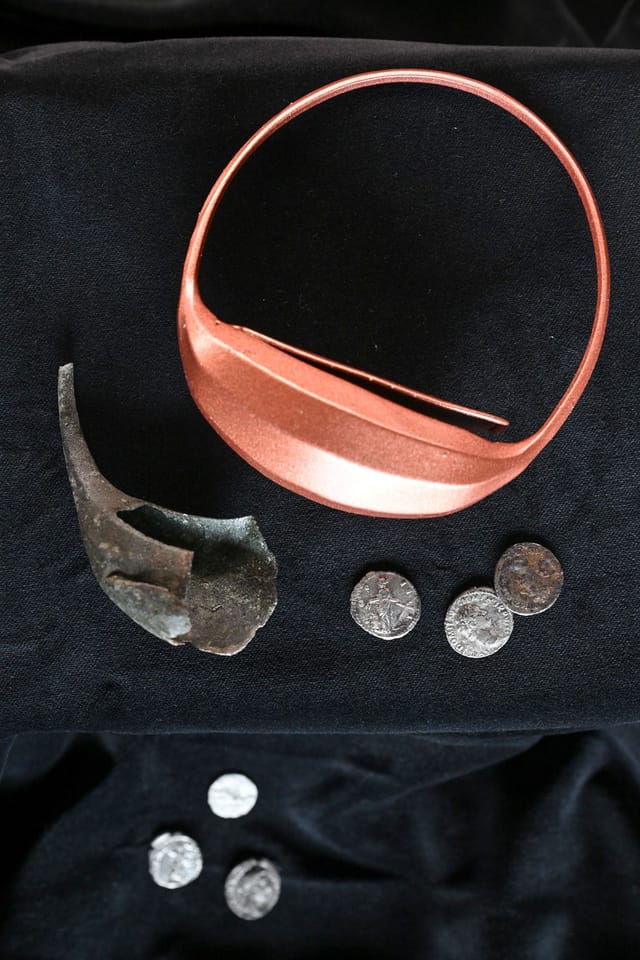
The newly discovered bronze fragment is now on display at the Mušov Visitor Centre in Pasohlávky. It is featured as part of the “Gateway to the Roman Empire” exhibition, offering visitors a unique opportunity to view the original piece, a full reconstruction of the purse, and several coins unearthed at the site. These artifacts provide a rare and valuable glimpse into the daily lives and financial realities of Roman soldiers stationed at the far reaches of the empire
Cover Image Credit: Representative Image: A Roman Bronze Arm Purse from Vindolanda at the Ashmolean Museum, shown as a representative example of the type of artifact discussed in the article.
















