New research, utilizing ancient DNA analysis, is challenging long-held assumptions about kinship and societal structures in one of the world’s most iconic Neolithic settlements: Çatalhöyük. Published in Science, the study reveals a fascinating story of strong female-centric lineages and surprisingly stable kinship patterns over centuries, despite the dynamic nature of this bustling prehistoric city.
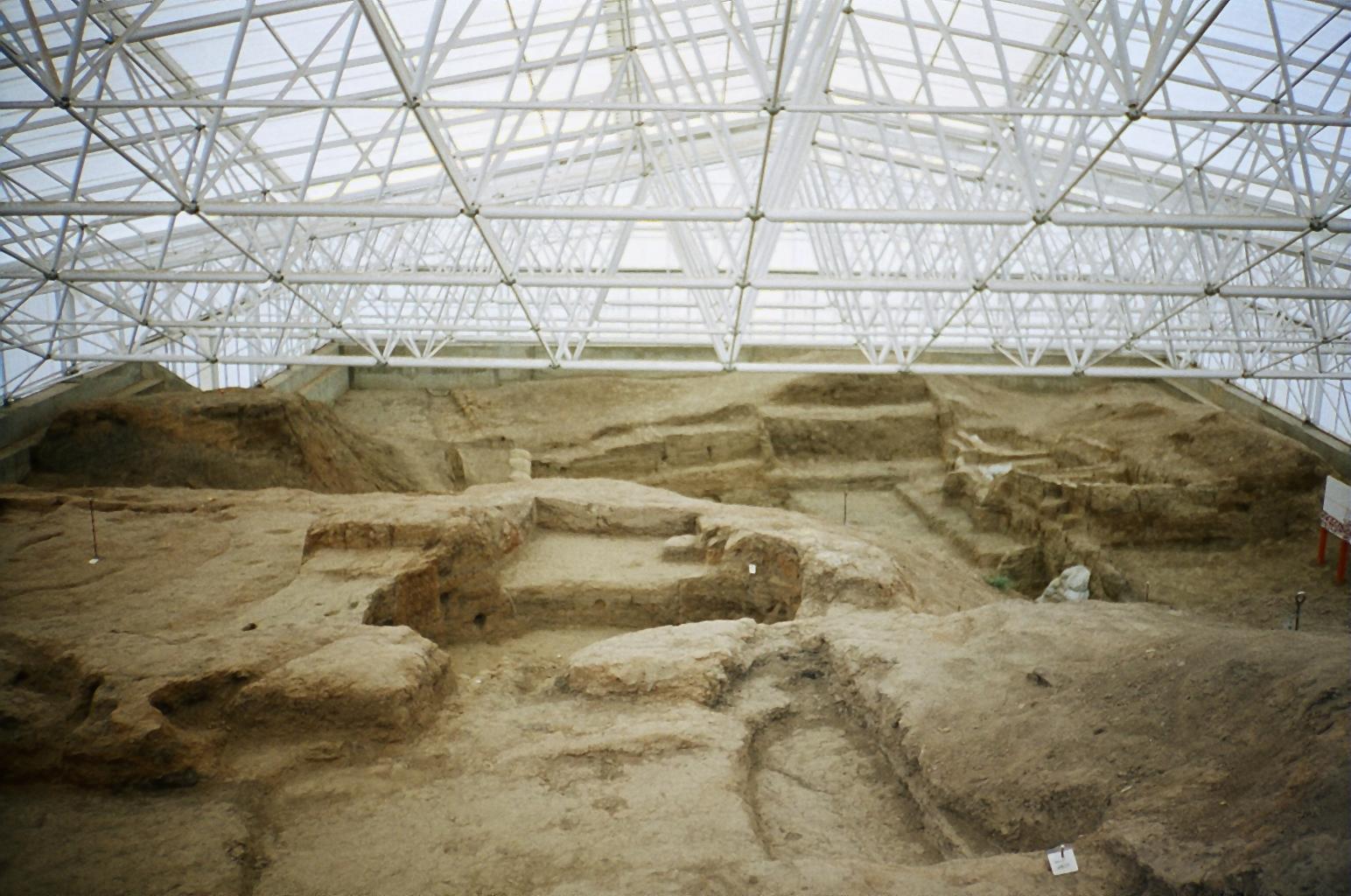
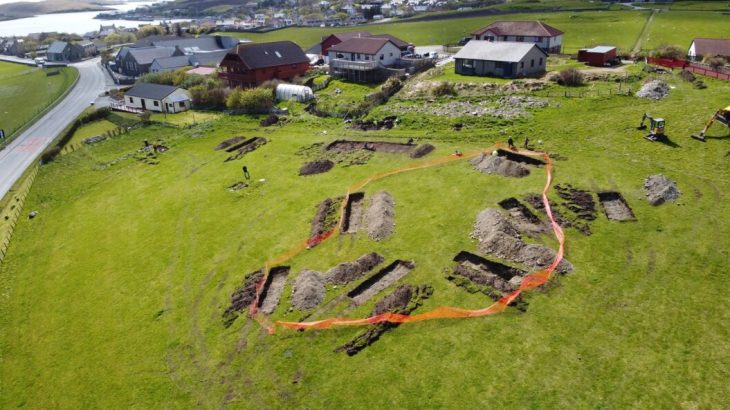
For decades, archeologists have grappled with the social organization of Çatalhöyük, a densely populated settlement famous for its unique architecture where houses were built directly against each other, accessible through roof openings. Without clear evidence of streets or public spaces, understanding family units and their relationships has been a complex puzzle.
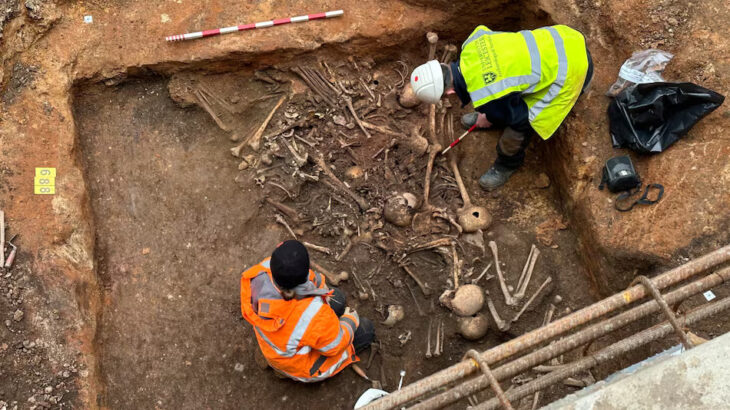
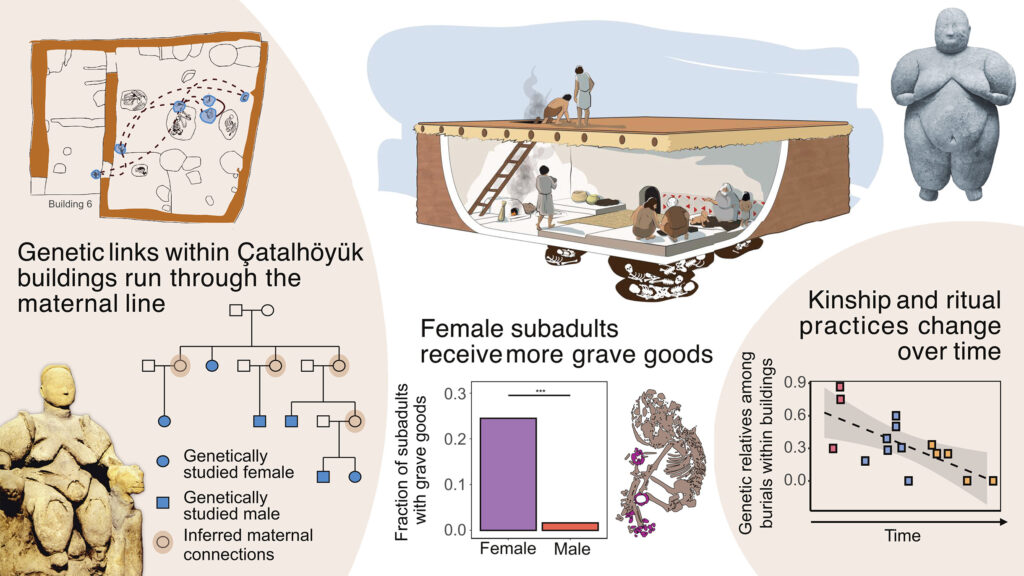
The new study, led by an international team of researchers, analyzed mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) from human remains excavated at the site. mtDNA is particularly valuable for tracing maternal lines as it is inherited solely from the mother. The findings suggest that maternal kinship played a more significant role than previously imagined.
“We found compelling evidence of persistent female lineages within certain areas of Çatalhöyük,” stated Dr. Eva Rosenstock from the Bonn Center for ArchaeoSciences. “This indicates that women may have been central to maintaining social cohesion and perhaps even the transmission of property or cultural practices across generations.”
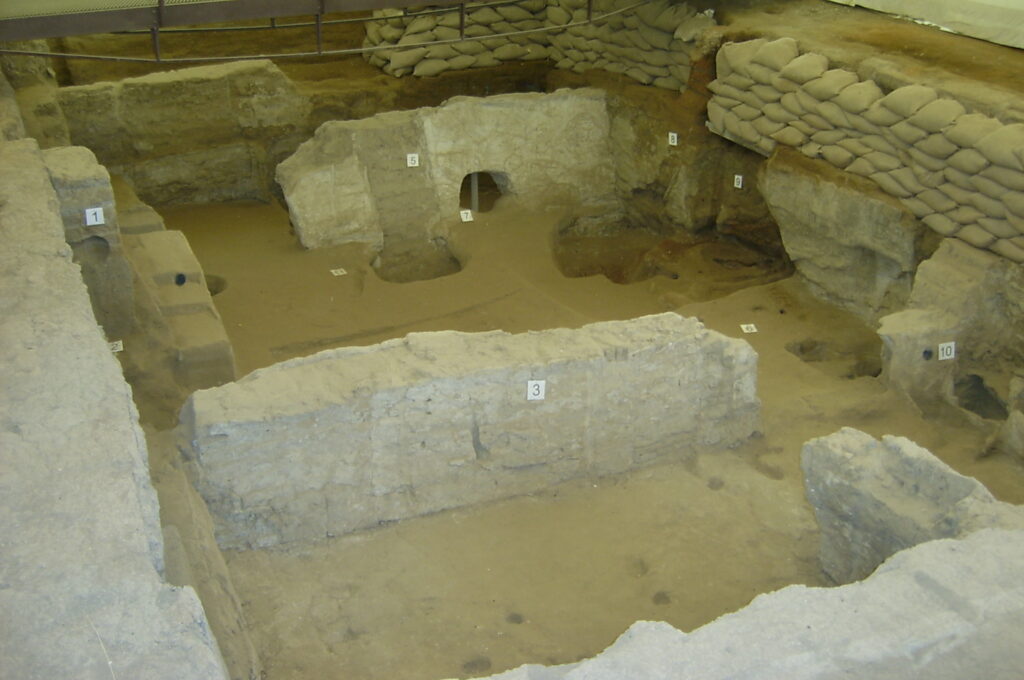

Ongoing excavations at Çatalhöyük continue to unveil the mysteries of this ancient settlement. Credit: Wikipedia Commons
The analysis revealed that individuals buried within the same household, often over many generations, frequently shared a common maternal ancestor. This pattern suggests a strong emphasis on maintaining a continuous presence of maternal relatives within specific domestic units.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Even more surprisingly, the research indicates a remarkable stability in these kinship patterns over hundreds of years, spanning multiple phases of Çatalhöhöyük’s occupation. This challenges the notion of a rapidly shifting or highly fluid society, suggesting a deeper, more enduring social fabric than previously understood.
“Despite the continuous rebuilding and changes in architectural styles at Çatalhöyük, the underlying social structure, particularly concerning maternal lines, appears to have been remarkably resilient,” commented Dr. Eva Rosenstock. “This points to deeply ingrained social norms and perhaps even a form of early ‘matrilocality,’ where daughters remained close to or within their maternal households.”
Did the people of Çatalhöyük live in a society dominated by women? Notions of a prehistoric matriarchate date back to ancient times and have been revisited repeatedly ever since. “Even the very first person to dig here, James Mellaart, suspected that women were very important in Çatalhöyük—primarily based on the female figurines and other objects that were found,” Rosenstock says.
This research provides crucial insights into the complexities of early agricultural societies. It moves beyond simplistic interpretations of Neolithic life, highlighting the diverse ways in which human communities organized themselves and maintained social order. The findings from Çatalhöyük offer a unique window into the intimate lives and enduring familial bonds of our ancient ancestors, reminding us that the echoes of their social structures can still be found in the genetic code they left behind.
Yüncü, E., Küçükakdağ Doğu, A., Kaptan, D., Kılıç, M. S., Mazzucato, C., Güler, M. N., Eker, E., Katırcıoğlu, B., Chyleński, M., Vural, K. B., Sağlıcan, E., Atağ, G., Bozkurt, D., Pearson, J., Sevkar, A., Altınışık, N. E., Milella, M., Karamurat, C., Aktürk, Ş., . . . Somel, M. (2024). Female lineages and changing kinship patterns in Neolithic Çatalhöyük. Science, 384(6690), 1461-1466. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adr2915
Cover Image Credit: Public Domain