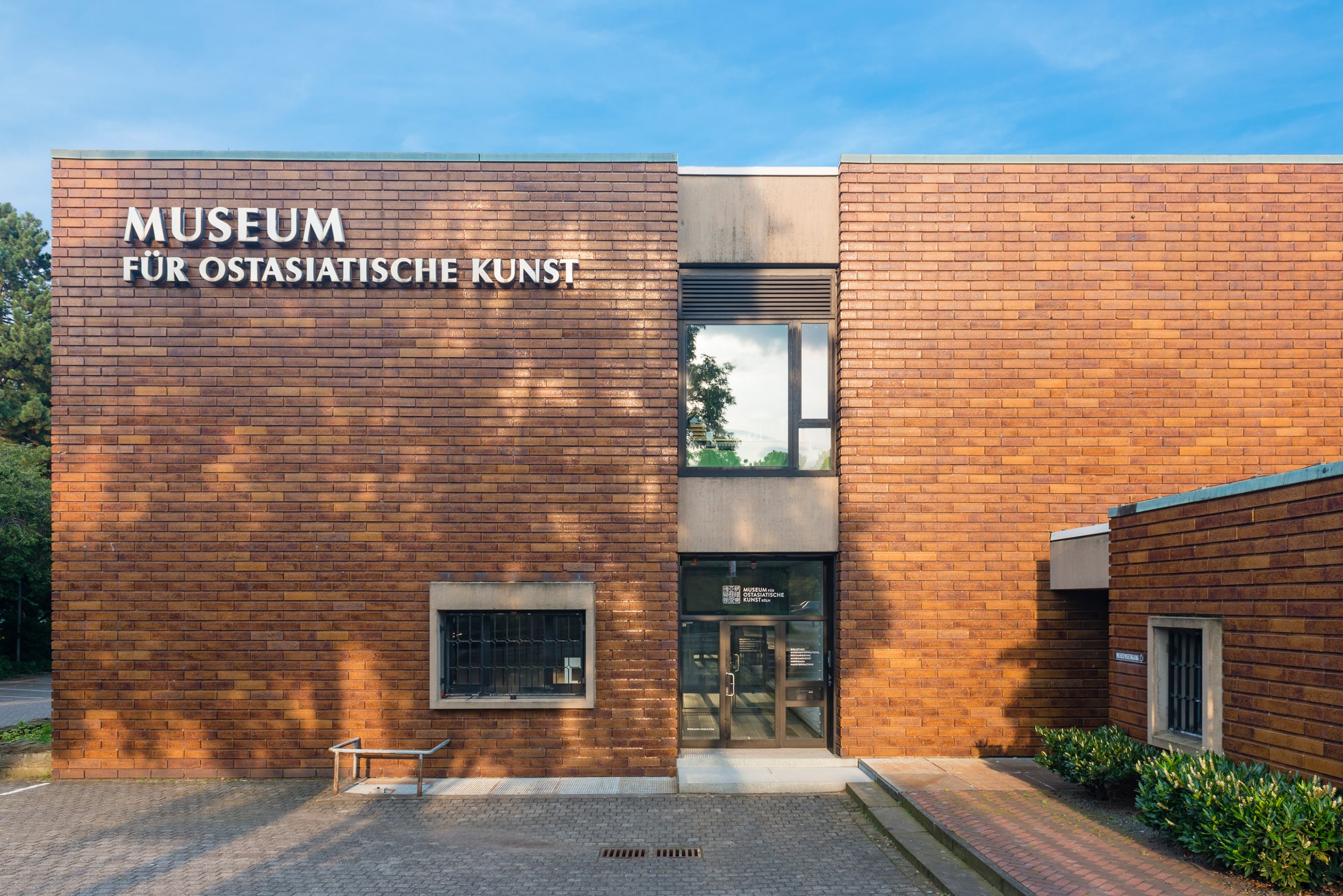
Nine pieces of historic Chinese porcelain worth around €1 million were stolen from the Museum for East Asian Art (Cologne) overnight, authorities in the German city said Wednesday.
“Unknown persons” managed to break into the Museum of East Asian Art through a window and steal the pieces from display cases, according to police. Nine items taken date from the 16th to the 19th century, city authorities said in a statement.
Nine pieces of ancient Chinese porcelain, estimated to be worth more than 1 million euros ($1,073 million), artifacts were mostly Chinese porcelain vases, plates, and bowls made during the Ming (1368-1644) and Qing (1644-1911) dynasties. Some of them were part of the museum’s founding collection.
According to a photograph purporting to show the museum’s “stolen relics list,” at least three Qianlong-period porcelain vases were stolen. They were created in Jingdezhen, China’s 1,000-year-old porcelain capital in East China’s Jiangxi Province, which was responsible for the country’s finest porcelain craftsmanship during the Qing Dynasty.
The museum, which opened in 1913, claims to be the first specialized museum of its kind in Europe. Accordingly, it houses – alongside the Museum of Asian Art in Berlin – the most important collection of art from China, Korea, and Japan in the Federal Republic.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Since the stolen items are well documented and easily identifiable, museum director Shao-Lan Hertel said she was hopeful they would eventually find their way back.

Yao Yu, a Chinese cultural expert, told the Global Times that he was “more stunned than angry and disappointed” by the “sluggish loose security management” of the museum, especially when the cultural institution is the “most prestigious of its kind in Europe.”
“It triggers a trust issue in Western museums for us,” Yao noted, adding that such a “brazen mistake” is the solidest evidence against such museums’ “false claim they are the best home for foreign relics.”
“Whenever the relic’s repatriation topic is proposed, Western museums often question the relic’s original country whether or not they can better care for them. This incident that happened is like a joke, or a slap in the face,” Yao noted.
“The current incident in Germany will likely trigger a new round of criticism targeting Western museums. And, this time, I think international anger will likely grow bigger,” Yao said.
Not even a month ago, the British Museum in London was embroiled in a massive scandal in which over 2,000 artifacts were stolen from the site.
The theft comes after five gang members were jailed in May for snatching priceless 18th-century jewels from a museum in Dresden. In what German media dubbed the biggest art heist in modern history, the thieves made off with a haul worth more than €113 million from the Green Vault museum in 2019.
The loot included a sword with a diamond-encrusted hilt and a shoulder piece which contained a 49-carat Dresden white diamond. Some, but not all, of those items were recovered.
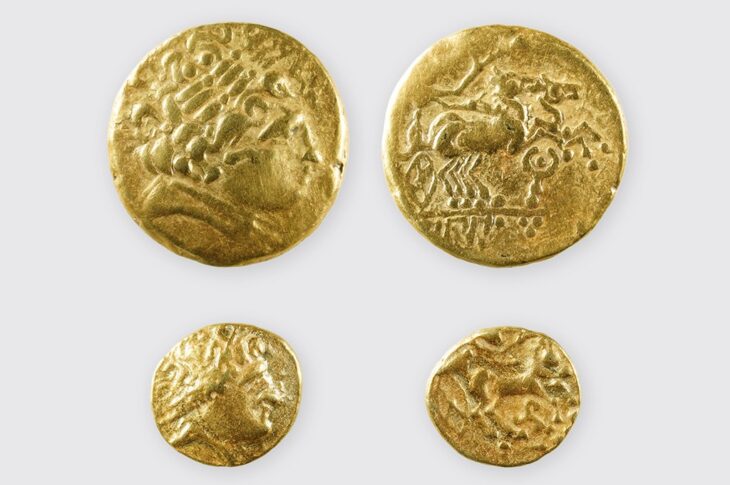
In another heist, burglars made away with a stash of Celtic coins worth several million euros from a museum in southern Germany’s Manching city last November.
Stefan Charles, the city councillor for arts and culture, announced a review of the museum’s security.