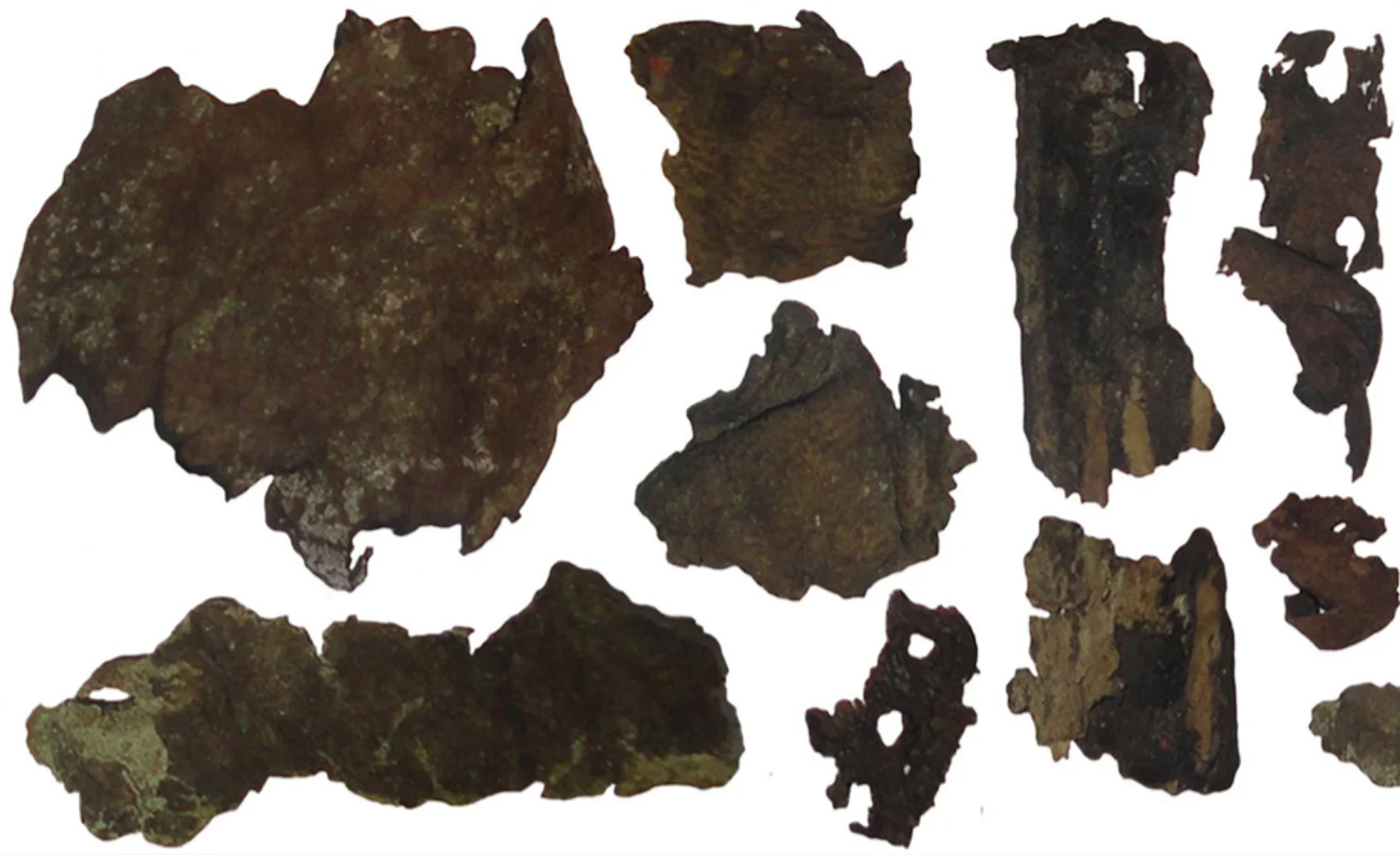
The ancient Scythians’ history as fearsome warriors dates back more than 2,000 years, and now research from a multi-institutional team of anthropologists confirms that they are pitiless warriors. Researchers have discovered that Scythian warriors carried their arrows in leather quivers made from the skin of their defeated enemies.
The Scythians (6th to 3rd centuries BC) were a nomadic people known for their fierce nature and mastery of horsemanship in the ancient Eurasian steppes. Their lives were deeply intertwined with the wild, expansive landscapes they roamed. Living in harmony with the harsh environment, they developed a formidable reputation as warriors and skilled riders.
Their nomadic lifestyle meant they were in constant movement, adapting to the ever-changing conditions of the steppe. They were expert archers, able to shoot accurately from horseback while galloping at high speeds—a skill that made them formidable in battle.
In their project, reported on the open-access site PLOS ONE, the researchers tested an account by the Greek historian Herodotus regarding certain behaviors of ancient Scythian warriors.
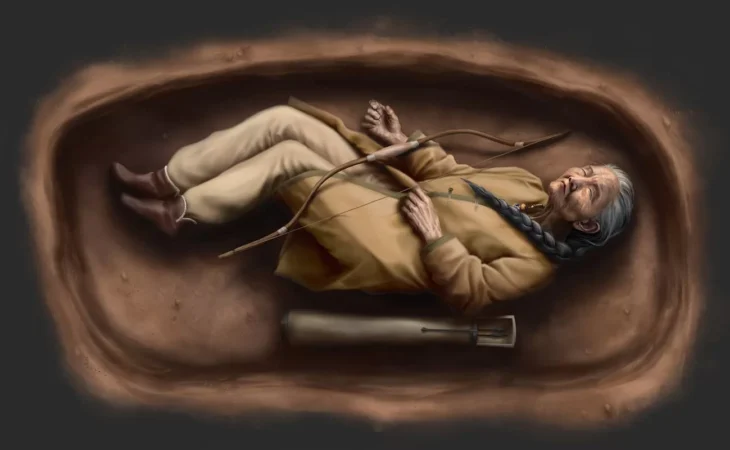
Herodotus reported that the nomadic warriors used the skulls of their victims as drinking cups drank the blood of their enemies and used their scalps as hand towels. “Many too take off the skin, nails and all, from their dead enemies’ right hands, and make coverings for their quivers,” he wrote.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
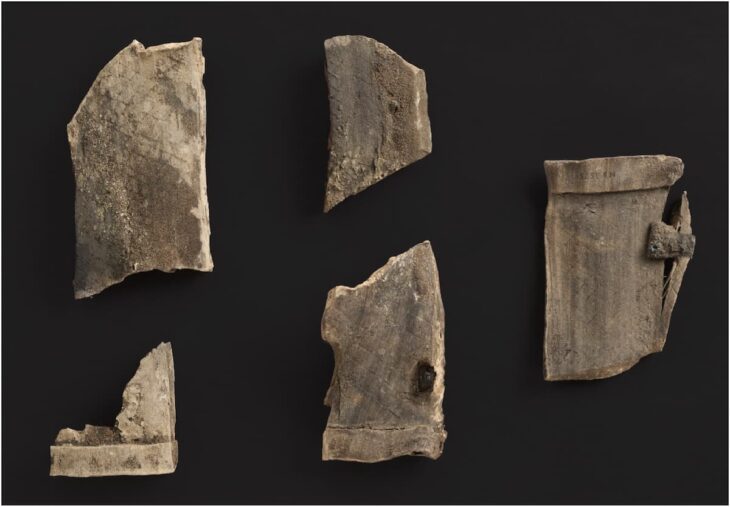
We had to take Herodotus’ word for it until now, but the authors of a new study have finally provided scientific validation for these grizzly claims. The researchers were able to identify the species from which each piece of skin was taken by using a series of techniques to analyze the proteins in 45 leather samples recovered from 14 different Scythian sites in southern Ukraine.
The researchers analyzed 45 leather samples collected from 14 Scythian dig sites using a variety of paleoproteomics techniques. They were able to determine the origin of all but two of them, which were made from horse, cattle, goat, or sheep skin. The other two had a human source to back up what Herodotus said.
However, the researchers discovered pieces of leather derived from human skin in two of the quivers they examined. Further examination of the two human skin leather samples revealed that they were only used on the top parts of the quivers; the rest of the quivers were made of animal leather.

It is important to note that the Scythians were not the first to use human skin for leather. Human skin has been used for a variety of purposes throughout history, including bookbinding and the creation of macabre artifacts. The discovery of human skin leather among the Scythians, on the other hand, provides valuable insights into their cultural practices.
According to one theory, the use of human skin in leather production may have been linked to religious or ritualistic beliefs. The Scythians were well-known for their intricate funerary practices, which frequently included elaborate burial rituals and the inclusion of valuable items in tombs. Human skin leather may have been used to honor or commemorate the deceased.
Another possibility is that the use of human skin leather was a means of conquering or dominating enemies. The Scythians were skilled warriors who frequently clashed with neighboring tribes. The creation of leather items from defeated enemies’ skins could have been a way for them to assert their power and intimidate their opponents.
The researchers propose that their results not only validate legends about the prehistoric Scythian fighters but also demonstrate that the fighters were making their quivers from easily accessible materials.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294129
Cover Credit: Brandt et al / PLOS ONE / CC BY 4.0
















