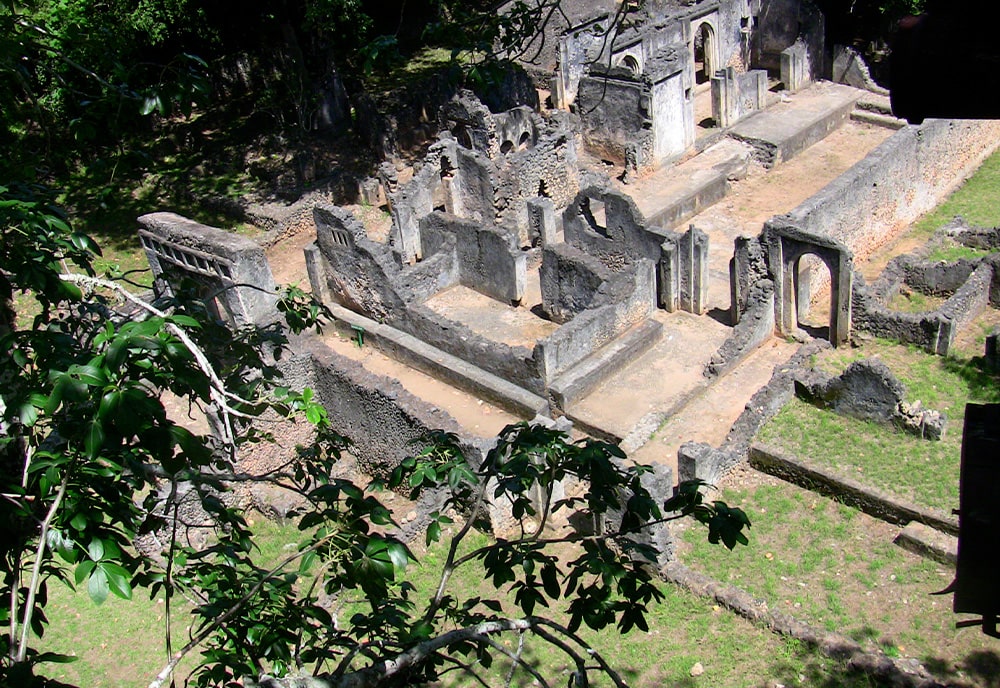
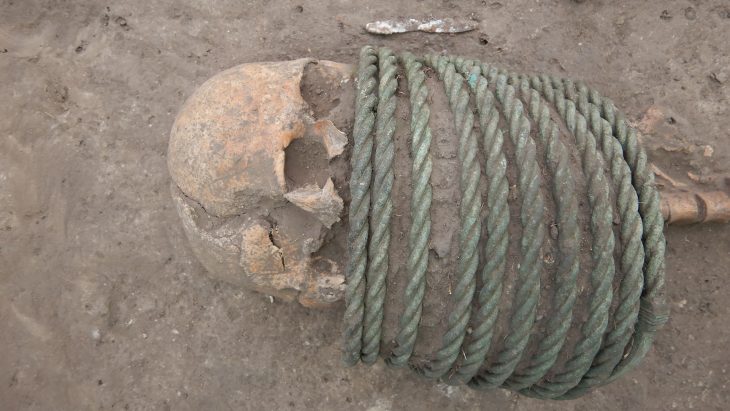
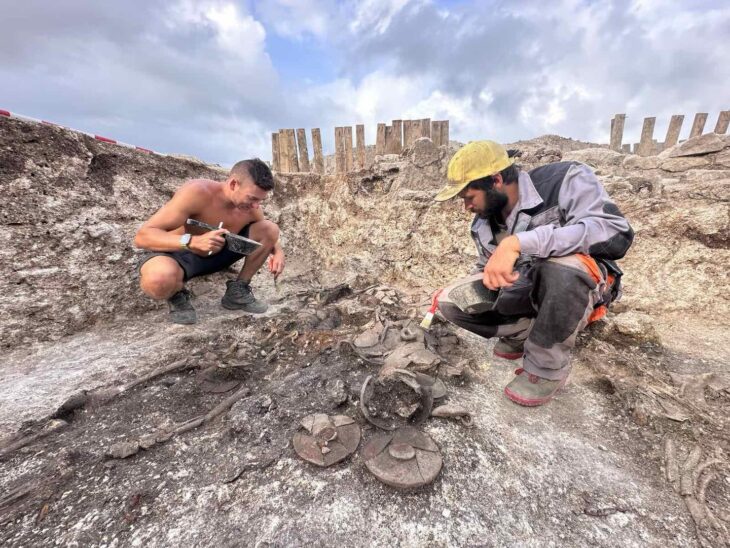
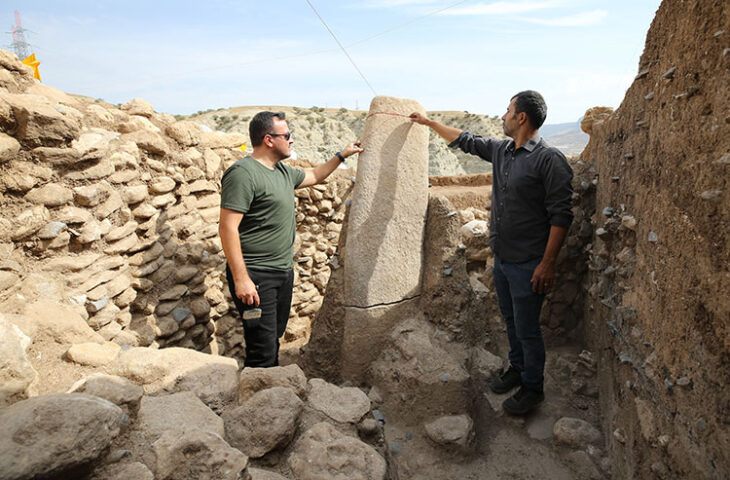
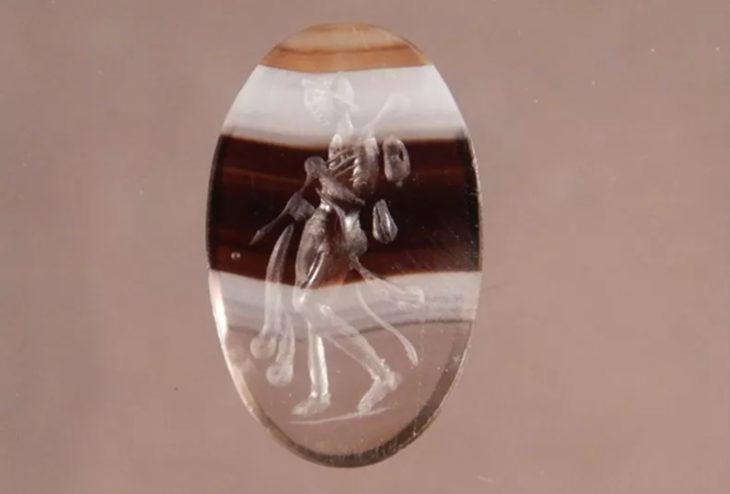
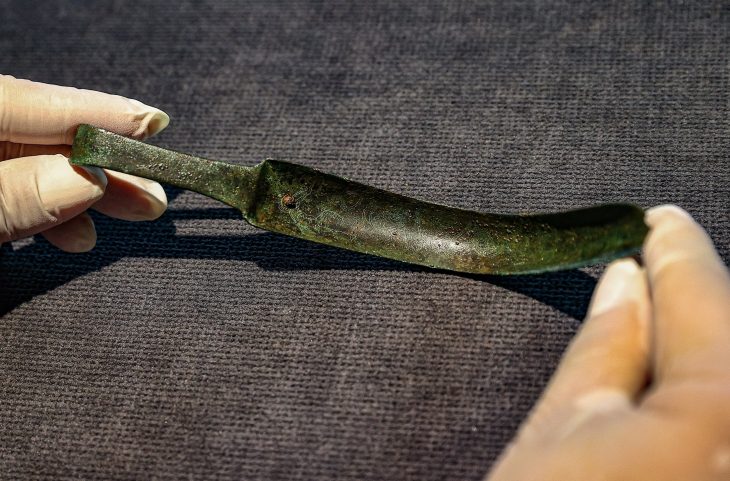
Chapurukha Kusimba, an anthropologist at the University of South Florida, has uncovered the first ancient DNA from the Swahili Civilization, prosperous trading states on the East African coast dating back to the 7th century.
From Kenya to Mozambique, Chapurukha Kusimba, a USF professor of anthropology, dedicated 40 years to studying the ancestry of those who built the civilizations.
The urban peoples of the Swahili coast traded across eastern Africa and the Indian Ocean and were among the first practitioners of Islam among sub-Saharan people.
A common language of African origin (Kiswahili), a shared dominant religion (Islam), and a geographic distribution in coastal towns and villages were the defining characteristics of the Swahili culture of eastern Africa during the Middle Ages and Early Modern Period beginning in the seventh century AD.
Published in Nature, this work examines the DNA of 80 individuals from as long as 800 years ago – making it the first ancient DNA uncovered from the Swahili Civilization.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

“This research has been my life’s work – this journey to recover the past of the Swahili and restore them to rightful citizenship,” Kusimba said. “These findings bring out the African contributions, and indeed, the Africanness of the Swahili, without marginalizing the Persian and Indian connection.”
As part of his decades-long research, Kusimba, a Kenya native, spent time with the people of Swahili to gain their trust before receiving their approval to complete cemetery excavations. To respect the remains, Kusimba finished the sampling and re-burial process all in one season.
Working alongside Harvard geneticists David Reich and Esther Brielle and corresponding authors, Jeff Fleisher from Rice University and Stephanie Wynne-Jones from University of York, Kusimba discovered the ancestry of the people analyzed was both African and Asian. The DNA revealed a pattern: the overwhelming majority of male-line ancestors came from Asia, while the female-line ancestors came from Africa.
Despite their intermarrying, descendants spoke an African language, not an Asian one. This led researchers to conclude that African women had great influence on the formation of the culture. So much so, the villages were established prior to the colonialism from Asia, making women the primary holders of economic and social power.
The findings challenge centuries-old narratives – constructed by other African natives – that suggest wealthier Swahilis did not have real ancestral connections to Asia and only claimed they did in order to minimize their African heritage to obtain higher social status and cultural affinities. Despite the vital role Swahilis played in trade between Africa and the rest of the Indian Ocean world for more than 2,500 years, Kusimba’s previous work from the 1990s documented the poor treatment of Swahili descent communities as a result of the narratives.

“I believe I was among many scholars who had worked on the Kenyan coast who did not think that the story from Persia was much more than that – a story,” said Dillon Mahoney, USF assistant professor and volunteer who works with recently resettled Swahili-speaking refugees.
“This research is not only significant for its scientific achievement, but it tells us that we must take non-Western and oral histories into full consideration, because our ancestry research is tending to support such stories, even if generations of academics have largely viewed such stories with skepticism.”
The results from this work prove Asians and African ancestors began intermarrying at least 1,000 years ago, but long after Africans had already established their villages.
“Our results do not provide simple validation for the narratives previously advanced in archaeological, historical or political circles,” Kusimba said. “Instead, they contradict and complicate those narratives.”
By challenging and overturning the narratives imposed from the outside for political and economic ends, this research brings peace and restores pride to the millions of people who identify as Swahili today. Up until now, it has been difficult to determine how people who identify as Swahili today relate to people of the early modern Swahili culture.