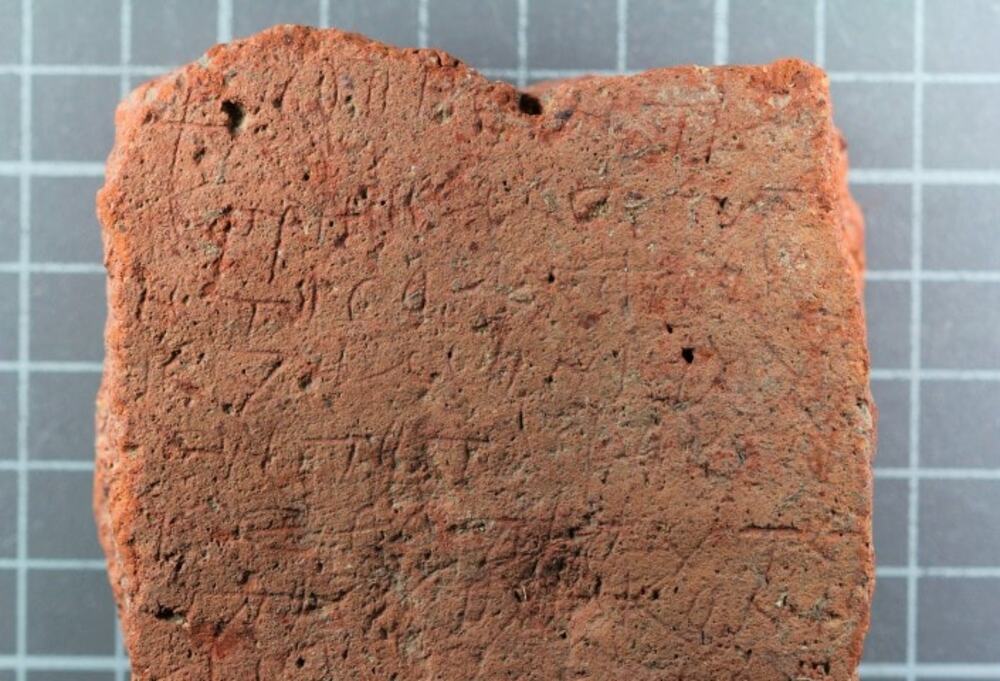
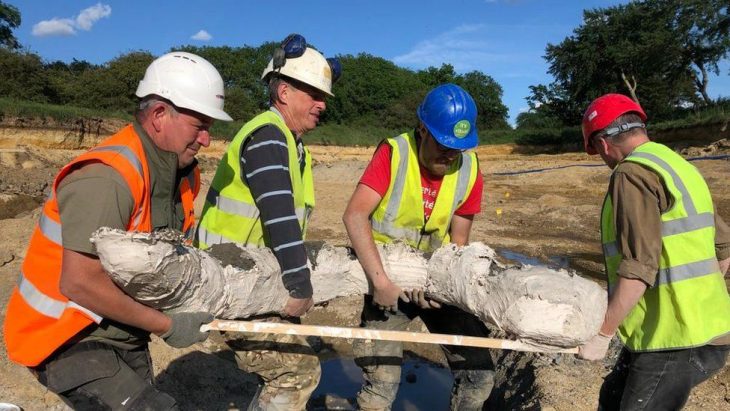
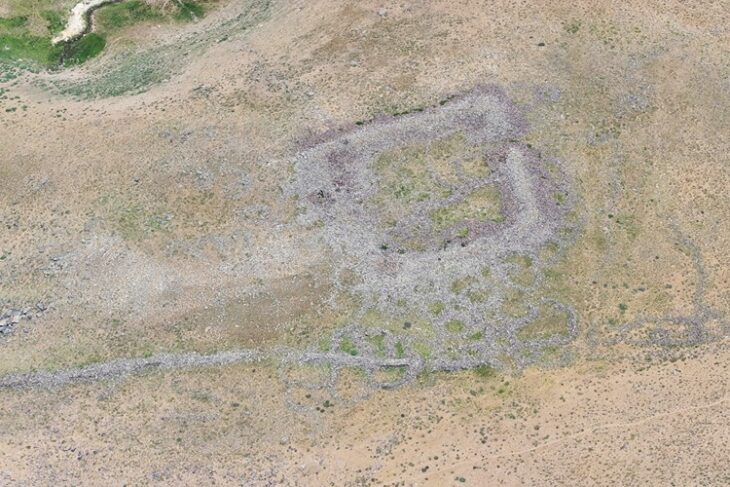
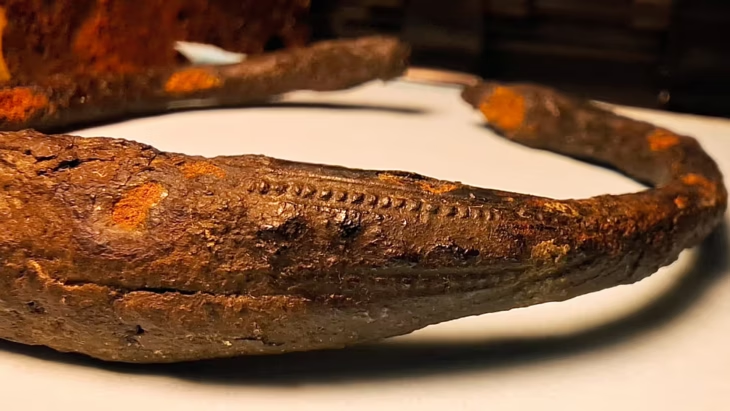During excavations in the Silifke castle located on lies on a hill in the town with the same name in the province of Mersin in south Türkiye, a mysterious burial tablet believed to belong to the Byzantine period and believed to protect from evil was unearthed.
The “talismanic grave tablet,” unearthed at the 185-meter-high hilltop castle in Silifke adds a fascinating layer to our understanding of the region’s history.
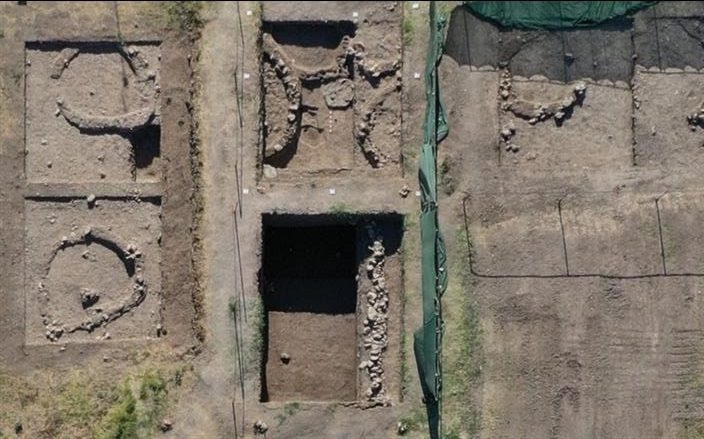
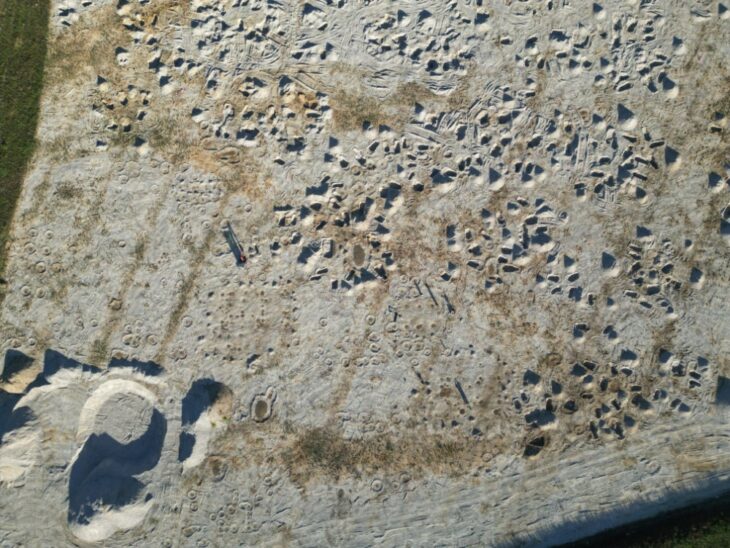
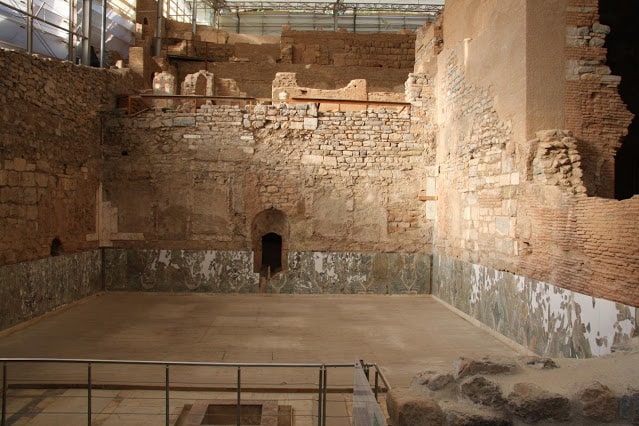
This Byzantine hilltop fortress, with its moat, two dozen towers, and vaulted underground chambers, was once Silifke’s command center. It was originally built by the Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire during the 7th-century Arab raids, though the present structure dates from 500 years later.
This discovery is part of ongoing excavation and restoration efforts led by the Ministry of Culture and Tourism. The 13th phase of these excavations, overseen by Professor Ali Boran from Ankara Haci Bayram Veli University, has brought to light this intriguing artifact.
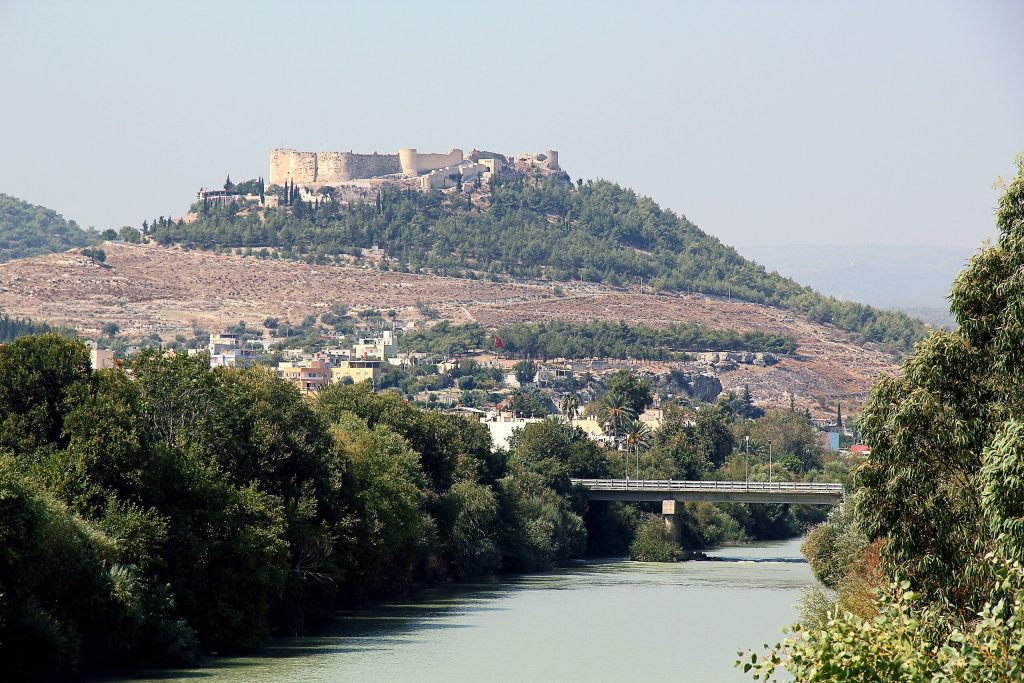

Work on the tablet continues. However, initial studies suggest that it was made to protect buildings or tombs from evil and enemies.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Excavation leader Professor Ali Boran told AA that the current season’s excavations revealed important findings that will provide new identities for ancient architectural structures.
‘As far as we understand from the inscriptions inside, this is a magic, talismanic tablet that was made to protect that building or tomb from all kinds of evil and enemies. Its full analysis continues with our epigraphy professors, but we see that this place is not only a city but also has different features,” Boran said.

“We have not found a grave structure inside the castle so far. The tablet indicates that there was a grave structure here at that time. It is understood that this is an important tablet for the history of the region and Anatolia in the context of revealing the data.’”
“This tablet was unearthed in a place west of the mosque. The tablet is not of a very large size, but when we look at its content and writing style, it is a find that can give a lot.”
“Similar to how some people today view a ‘nazar boncugu’ as protective, such items have been used since antiquity to ward off harm. The presence of this tablet at Silifke Castle is a crucial historical insight,” Boran added.
This finding underscores the castle’s role beyond its architectural and urban features, revealing a deeper layer of cultural and historical context.