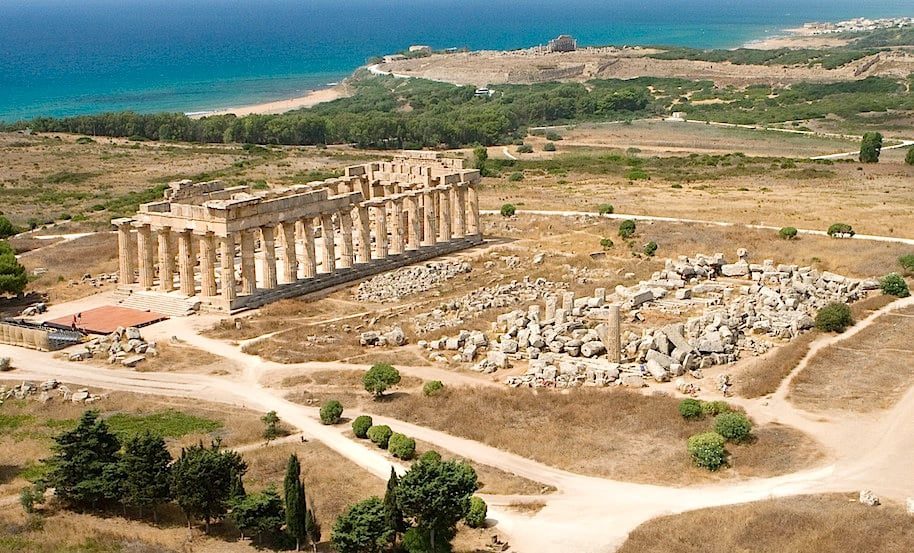
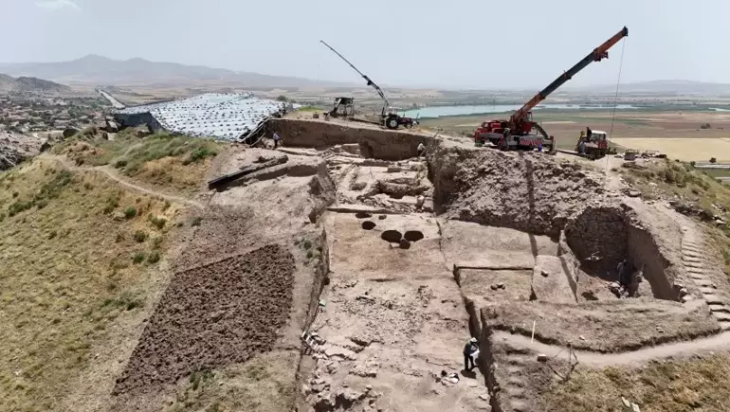
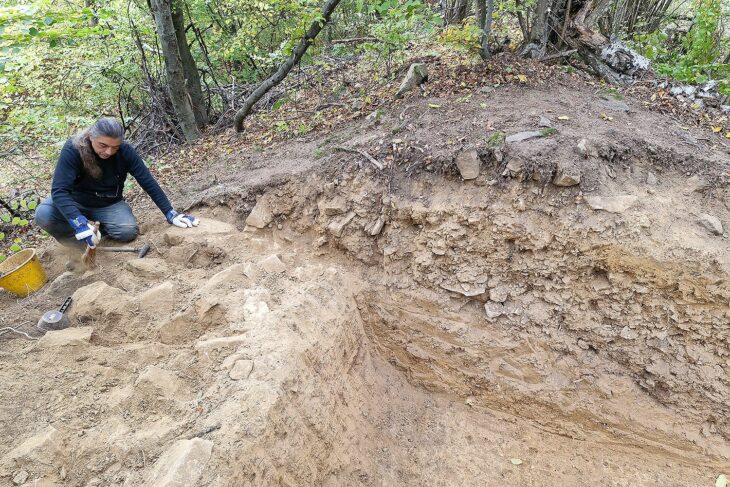
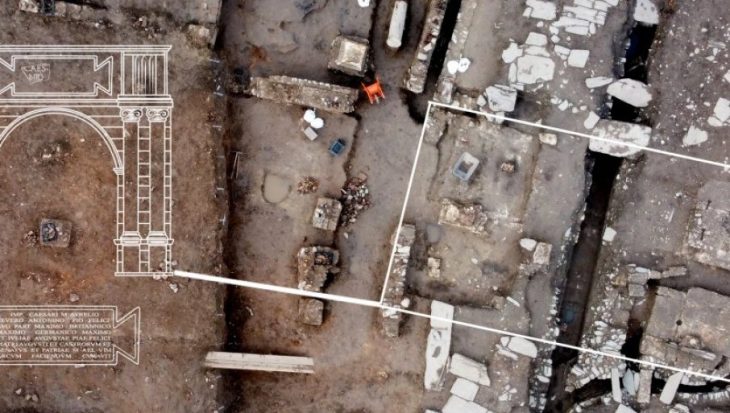
Recent excavations in the ancient Magna Graecia city of Selinunte in southwestern Sicily have revealed the presence of a new small temple in the sanctuary of this ancient Sicilian city, located behind the well-known Temple C.
Magna Graecia (Megalē Hellas) refers to southern Italy’s coastal areas, which were colonized by various ancient Greek city-states from the 8th to 5th centuries BCE. It is, in fact, a herb, wild parsley, in Greek sèlinon, that gives its name to this city built in the VII century BC.
Selinunte was rich and powerful enough even to found a colony, Eraclea Minoa though its glory was short-lived, only 240 years. Founded in 650 BC, it fell in 409 BC defeated by an alliance between Segesta – a long time rival – and Carthage.
The ancient city, one of southern Italy’s biggest and most important ancient Greek cities, boasts several magnificent temples, the earliest dating to 500 BC. It has a remarkable archaeological heritage, characterized by temples of impressive Doric architecture.
The new discovery has been described as of “great value” by the advisor for Cultural Heritage and Sicilian Identity, Francesco Paolo Scarpinato.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
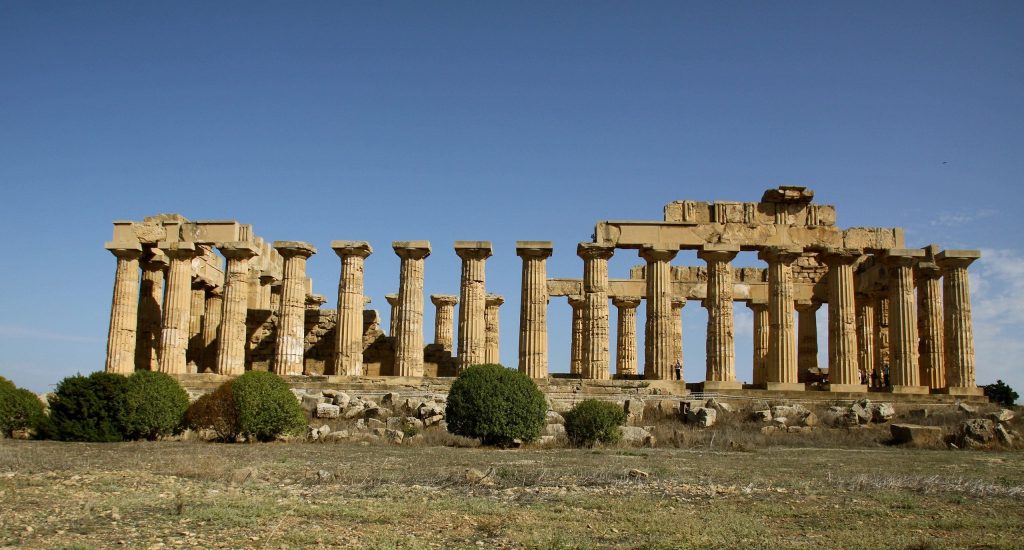

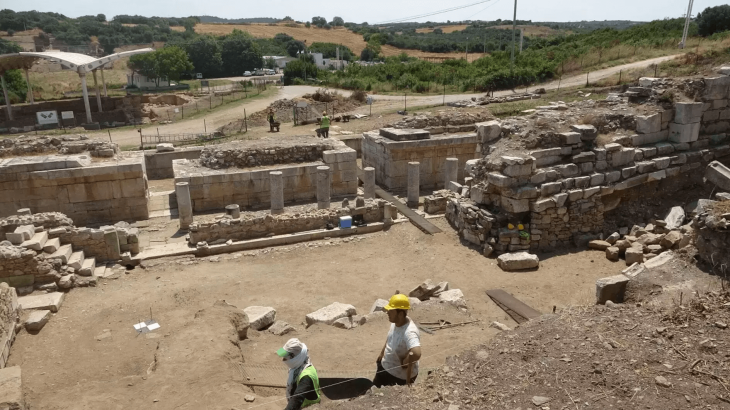
An archaeology team from the University of Milan and the Institute of Fine Arts at New York University has been excavating at Selinunte for more than ten years. Works in the ancient city this year, archaeologists have focused on the urban sanctuaries within the large peribolos wall on the Acropolis, where they have uncovered portions of settlements and numerous artifacts of great interest.
The Selinunte Archaeological Park excavations have revealed new constructions within the holy region, including what appears to be a small temple that was previously undiscovered based on its features.
The official said that new buildings had been found linked to the sacred area between the Archaic and Classical periods and a structure that at the moment would appear to be a small temple, about two-thirds the size of Temple R.
The director of the Archaeological Park, Felice Crescente, and the archaeologist, Clemente Marconi, who leads a group of sixty collaborators and students engaged in the investigations at Selinunte, will present the findings of the recent excavation work to the public next Sunday, August 11, at Baglio Florio.
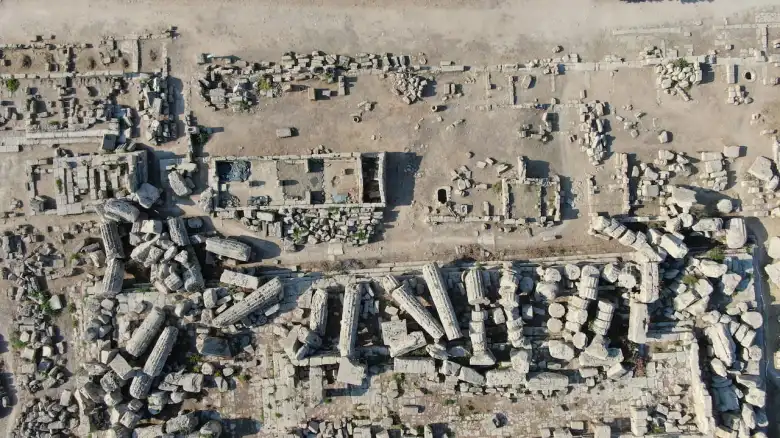

Recent explorations have covered several areas of the large urban sanctuary on the Acropolis, one of the most significant cult sites in the Greek world during the Archaic and Classical periods. The large monumental entrance to the northwest and the area containing a circular well and various objects, including coins and a valuable gold jewel, has been precisely identified by the archaeological mission in this context.
However, the most notable discovery is the identification of a structure that appears to lead to a previously unknown small temple with no columns and modest dimensions.
The archaeologists hope that these new discoveries will provide a better understanding of the evolution of Selinunte, a city that was once one of the most prosperous and advanced centers of the Greek world in Sicily. The new temple, along with other discoveries, could provide important information about religious practices and the spatial organization of the city, leading to a reinterpretation of Selinunte’s history, the only Greek city of antiquity that has been preserved in its entirety, and its place in the larger context of the ancient Mediterranean.