Scandinavian genes were present on the British Isles several centuries earlier than previously thought, including evidence from a man buried in York. Using ancient DNA, researchers have linked genetic evidence to historical accounts of Germanic, Roman, and Viking movements, revealing complex migrations patterns that shaped early medieval Europe.
Researchers describe a novel data analysis technique called Twigstats in a study published in Nature. This technique makes it possible to measure the differences between genetically similar groups more precisely, exposing hitherto undiscovered aspects of global migration.
This innovative approach has unveiled previously unknown details about European migrations, offering a clearer view of the movements that shaped the continent’s history.
They applied the new method to over 1500 European genomes (a person’s complete set of DNA) from people who lived primarily during the first millennium AD (year 1 to 1000), encompassing the Iron Age, the fall of the Roman Empire, the early medieval ‘Migration Period’ and the Viking Age.
The researchers employed a novel approach that focuses on genome mutations that occurred within the last 30,000 years, rather than taking into account all genetic differences between populations. This allowed for a more thorough examination of the relationships between genetically similar groups. They were able to compare genetically similar populations more precisely by focusing on these relatively recent mutations.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The Romans – whose empire was flourishing at the start of the first millennium – wrote about conflict with Germanic groups outside of the Empire’s frontiers. Groups from Scandinavia and northern Germany migrated southward during the early Iron Age, as confirmed by genetic evidence. These migrations brought Scandinavian ancestry to southern Germany, Italy, Poland, Slovakia, and southern Britain.

Interestingly, one person from southern Europe was discovered to be wholly Scandinavian. This lends credence to the notion that the spread of Germanic languages and genetic mixing had a significant impact on Roman European populations.
One of the most remarkable finds is the discovery of a man with 25% Scandinavian ancestry who was buried in Roman York between the second and fourth centuries CE. He may have been a gladiator or enslaved soldier, according to researchers, demonstrating that Scandinavians lived in Britain for centuries prior to the Viking invasions. This casts doubt on the widely held belief that Scandinavian influence didn’t start until the Anglo-Saxon or Viking eras.
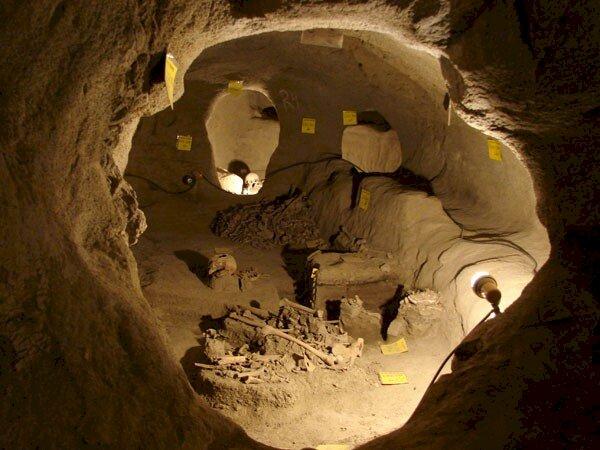
The second wave of migration occurred between 300 and 800 CE, but this time it was from Central Europe into Scandinavia. The combination of local and Central European ancestry found in DNA from Viking-era remains in southern Scandinavia suggests a major genetic influx shortly before the Viking Age.
This is corroborated by archeological evidence; discoveries in Sweden indicate that migrants from Central Europe settled and raised locally. This migration represented a long-term change in Scandinavian ancestry rather than an isolated incident. Scholars hypothesize that ongoing conflicts in the area might have prompted these movements.
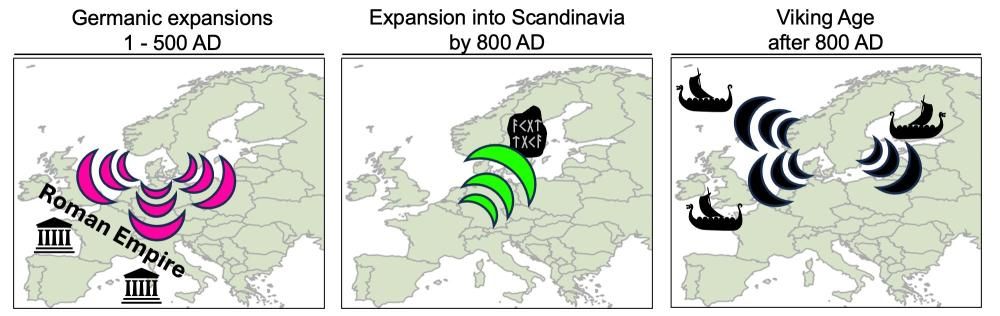
Europe was the scene of numerous raids and settlements during the Viking Age (c. 800–1050 CE). According to genetic evidence that supports historical records, Viking-era people in Britain, Ukraine, and Russia have Scandinavian ancestry. Due to their involvement in raids or military expeditions, some Viking remains found in British mass graves had direct genetic ties to Scandinavia.
Leo Speidel, lead author of the study, emphasizes that Twigstats provides an unprecedented ability to analyze subtle genetic shifts over time. “Twigstats allows us to see what we couldn’t before, in this case migrations all across Europe originating in the north of Europe in the Iron Age, and then back into Scandinavia before the Viking Age. Our new method can be applied to other populations across the world and hopefully reveal more missing pieces of the puzzle.”
Peter Heather, a co-author and medieval historian, notes that historical texts often hinted at migration-driven transformations in Europe.
“Historical sources indicate that migration played some role in the massive restructuring of the human landscape of western Eurasia in the second half of the first millennium AD which first created the outlines of a politically and culturally recognizable Europe, but the nature, scale and even the trajectories of the movements have always been hotly disputed. Twigstats opens up the exciting possibility of finally resolving these crucial questions.”
Speidel, L., Silva, M., Booth, T. et al. High-resolution genomic history of early medieval Europe. Nature 637, 118–126 (2025). doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-08275-2
Cover Image Credit: Part of the Zliten mosaic from the 2nd century AD showing gladiators. Photo: Wikipedia