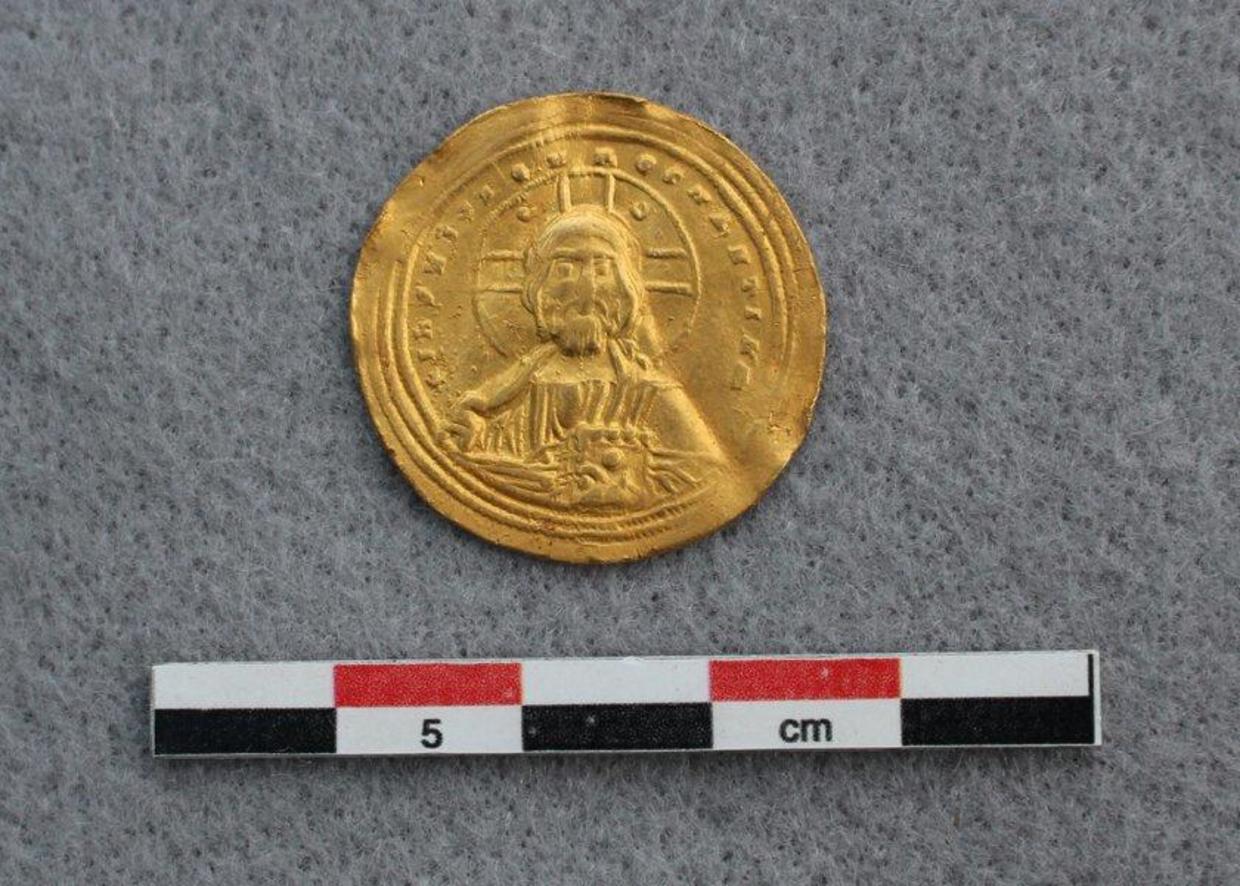
A metal detectorist exploring the mountains in the municipality of Vestre Slidre in southern Norway discovered a rare histamenon nomisma (literally standard coin), a Byzantine solid gold coin minted in Constantinople around 960 AD, depicting Jesus Christ.
The coin has been exceptionally well-preserved given its appearance. It is the only one of its kind ever found in Norway.
The Innlandet County Municipality said in a news release. “It has held up exceptionally well. The coin appears largely unchanged from when it was lost, perhaps a thousand years ago,”.
The ancient coin was introduced in the Byzantine Empire, also called the Eastern Roman Empire, and likely was minted in Constantinople, the Byzantine capital that is Istanbul today.
The coin was minted on one side, it depicts Christ holding the Bible, and on the other, probably the emperors Basil II (left) and Constantine VIII (right). Both were brothers and co-reigned. That means the artifact would have traveled more than 1,600 miles from its origin site to the spot where it was found.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
It was minted in the late reign of Basil II and Constantine VIII, sometime between 977 and 1025 AD, as indicated by the triple dotted border surrounding the coin.
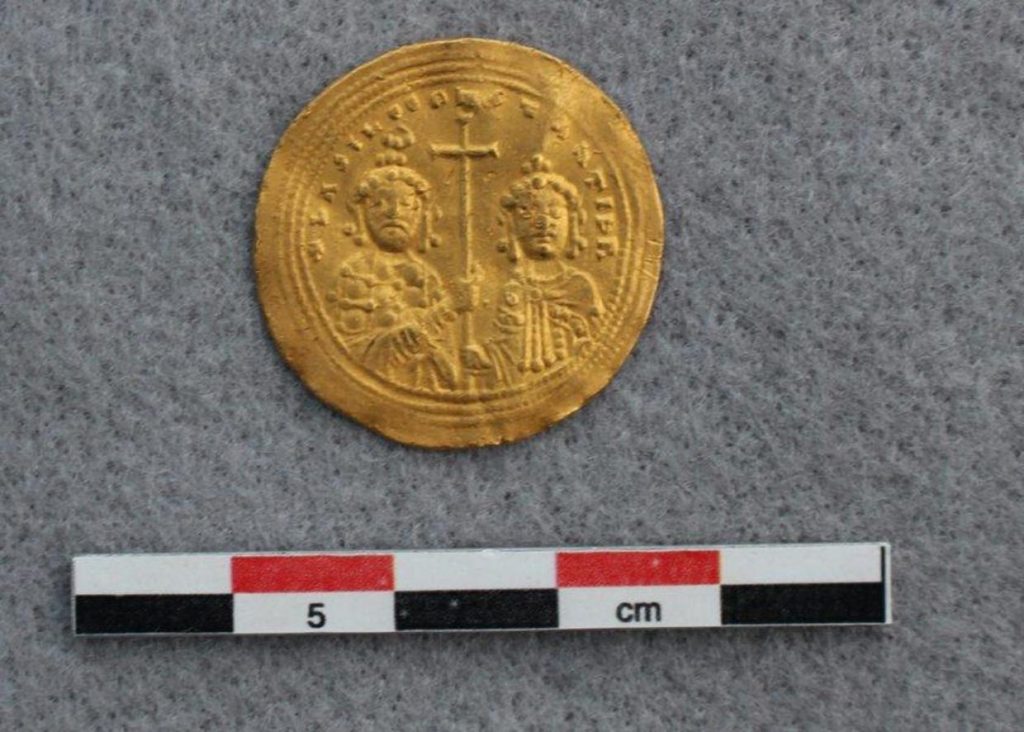

The gold coin has written inscriptions, too. One, written in Latin by the stamp of Christ, says, “Jesus Christ, King of those who reign.” The other, written in Greek on the coin’s opposite side, says, “Basil and Constantine, emperors of the Romans,” according to the county.
Archaeologists speculate that the rare and valuable coin might have made its way to Norway with the heavy booty the future King Harald III, aka Harald Hardrada, carried home with him after a decade spent in the Varangian Guard of the Byzantine Empire.
“At that time it was customary for the guards to be given the right to loot the palace and take all the valuables they could find when the emperor died. During Harald’s time in Byzantium, three emperors had died,” officials said. So, the former king could have acquired the gold coin in Constantinople and taken it back with him to Norway.
The gold coin could have also made its way into Norway’s early salt trade, which had transport routes that ran perpendicular from western Norway across the country.
Because the metal detectorist found the coin so late in the fall season, the spot where it was discovered will not be investigated further until next year.
Cover Photo: Christ is depicted on one side of the coin. MARTINE KASPERSEN/INNLANDET COUNTY MUNICIPALITY