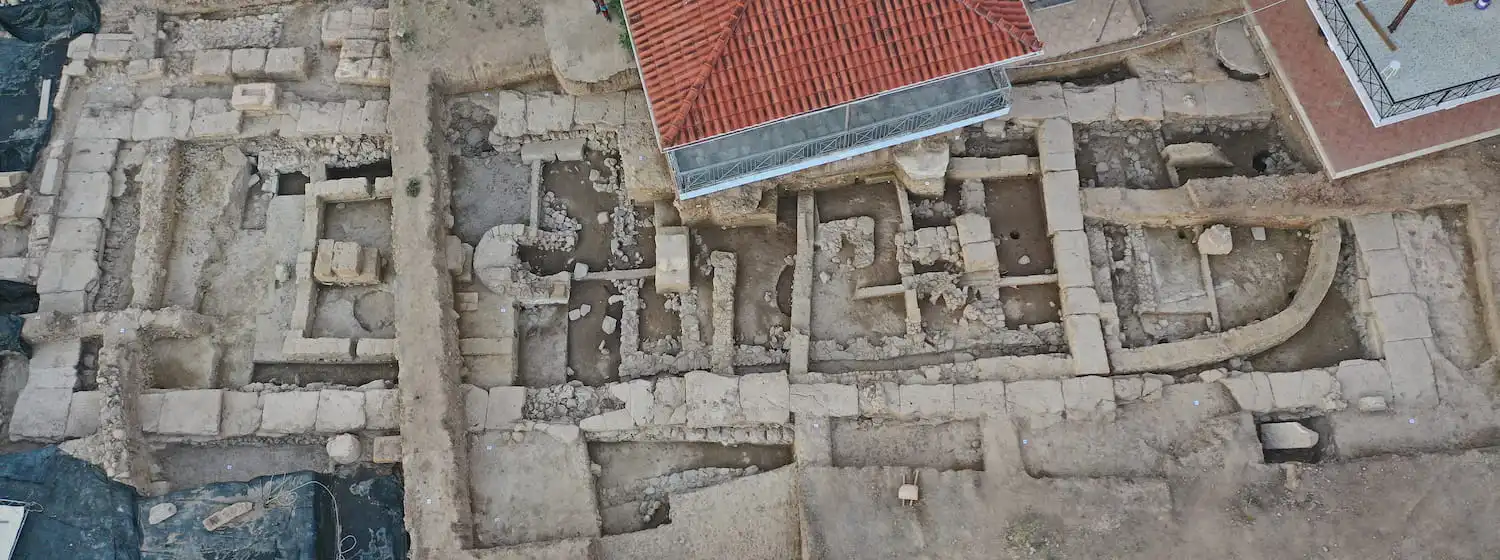
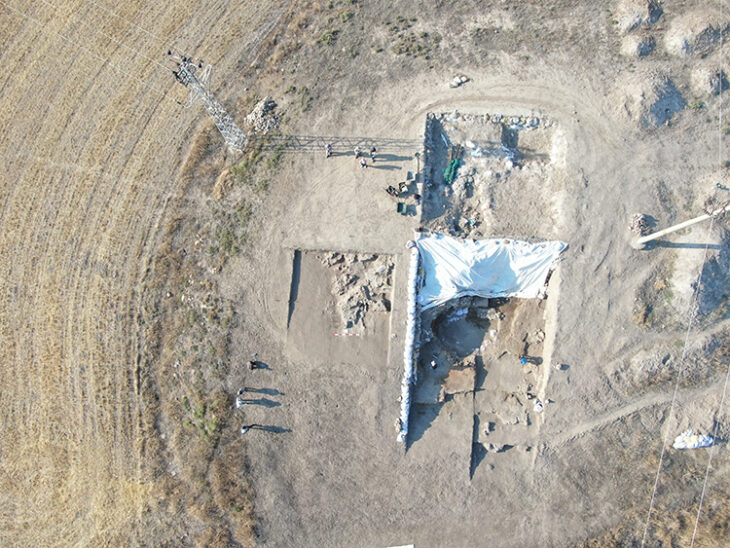
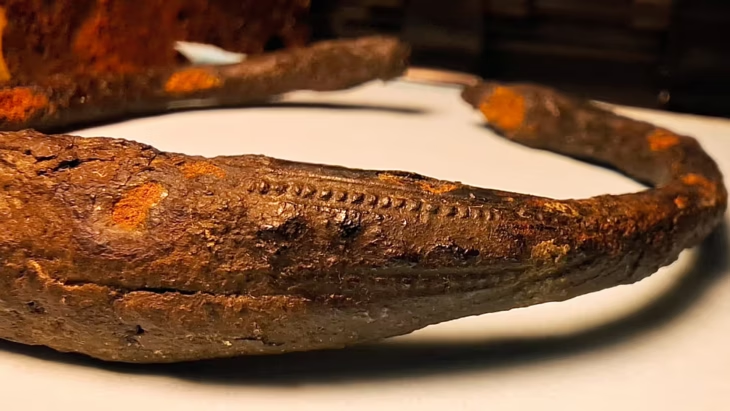Archaeologists excavating at the Artemis Amarysia sanctuary in Amarynthos on the Greek island of Euboea have revealed new insight into the temple configuration.
Constructed circa 700 BC, the temple’s length—more than 100 feet in Greek metric units—was larger than anticipated. According to archaeologists, this “perfect” measurement is encountered on other monuments of the same period.
Archaeologists were surprised when they discovered that the temple’s floorplan was apsidal (with a semicircle apse at one end), which was unusual for the time period.
During antiquity, the sanctuary was the center of worship in dedication to Artemis (the goddess of the hunt, wild animals, and nature). Archaeologists found hearths or altars where animals were sacrificed to honor Artemis, in addition to layers of ash and calcined animal bones.
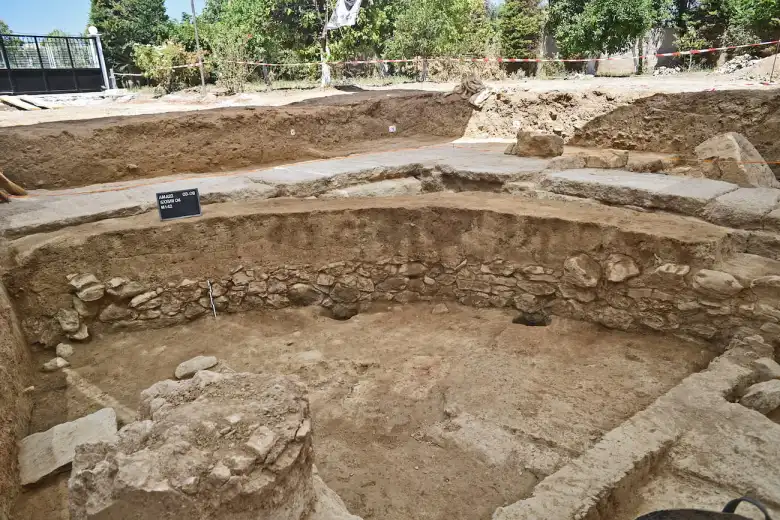

Temple inside, stone platforms discovered were likely where animals were sacrificed by burning parts of them as offerings to Artemis. Holes in the roof allowed smoke from the fires to escape.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
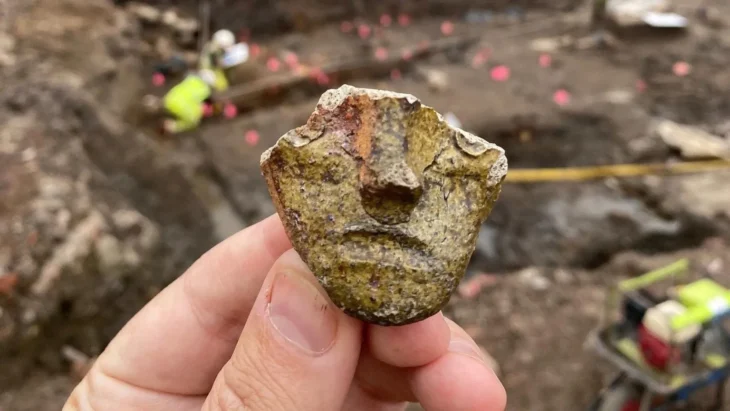
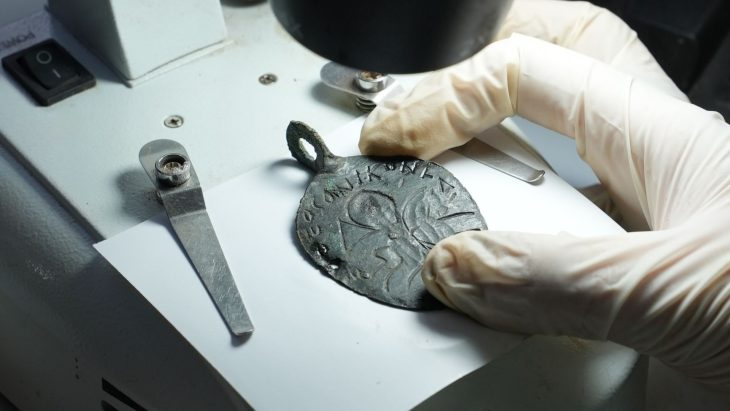
Archaeologists have discovered numerous ancient artifacts, including jewelry, tools, and pots, which were once offerings left by previous visitors, while excavating in the soil close to the temple. An ivory sculpture of an Egyptian person, illustrating how people from distant lands brought exotic gifts, was one particularly unusual discovery.

Evidence suggests the first temple was later partly burned down, then rebuilt smaller using mud bricks before an even bigger replacement was constructed around 500 BC.
The temple sits at the bottom of a hill occupied since Bronze Age times over 3,000 years ago. Deep holes dug by the archaeologists found older remains from 900-800 BC and even Bronze Age items like a terra cotta bull head dated to around 1200 BC, proving people had honored Artemis on this spot for thousands of years.

Documents retrieved from an old palace attest to the existence of a town named Amarynthos in the vicinity of the temple between 1500 and 1100 BC (Mycenaean period). Seeing landmarks from long ago probably increased the area’s religious significance.
After lots of digging and discoveries, archaeologists are now poring over their findings in labs.