Archaeologists have uncovered an almost circular adobe building with six towers, built in the 6th century BC, near Birjand in South Khorasan.
Excavations in the largely unexplored Khorasan began in 2009 and are one of the few excavations that have continued to the present day. In the east of Iran, only two archaeological sites had previously been excavated: Dahane-i Gholaman in Sistan to the south of Khorasan and Tappe Rivi in the north of Khorasan.
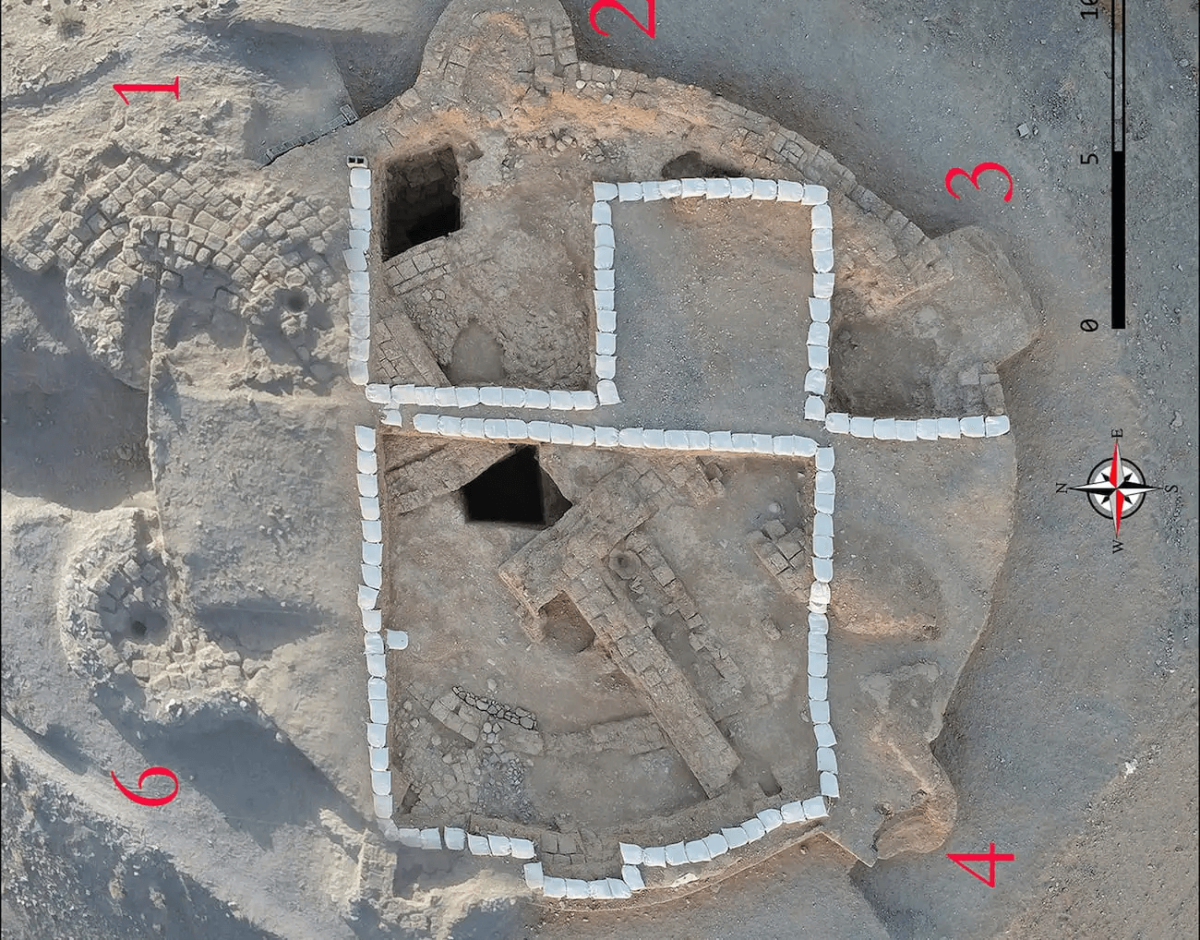
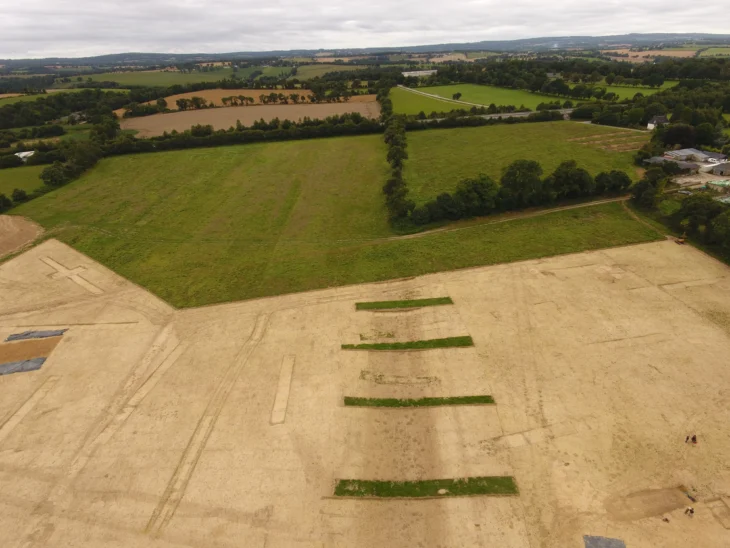
The site, called Tappe Takhchar-Abad is located near Birjand and on the edge of a barren plain; no contemporaneous and related sites have been identified. Since 2009, there have been four excavation seasons.
Tappe Takhchar-Abad sits on a semiconical hill, with a base diameter of 42 meters and a height of 4 meters, around which is a trench about 11 meters wide, with a canal to the northeast that supplied it with water.
After four seasons of excavation, the remnants of an almost circular building made of adobe and pisé (Chineh/pakhsa) with a diameter of eighteen meters, six solid towers, and walls as high as three meters were exposed.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
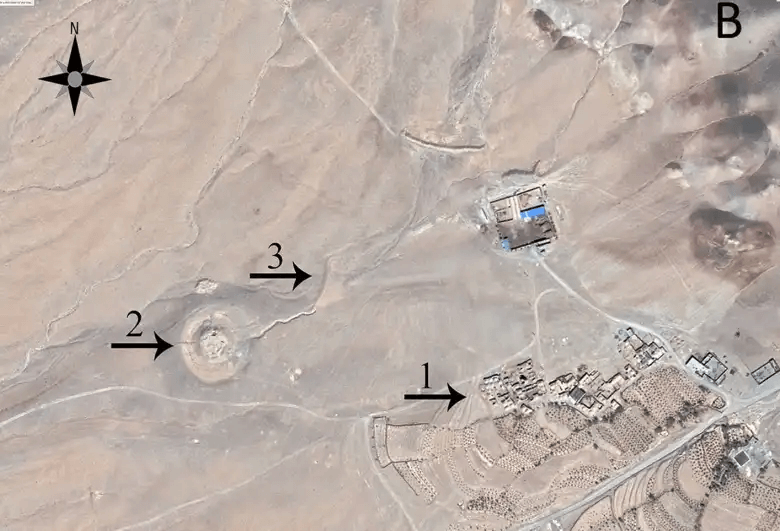
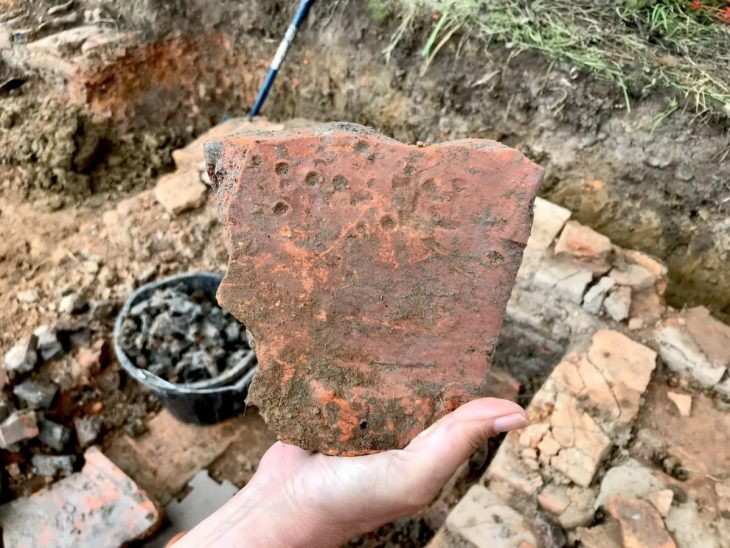
This building was completely covered and intentionally filled with sand. Additionally, it was indicated by two soundings that this building was filled in two stages.Tests revealed that it was intentionally filled to a height of nearly 2 meters with alternating layers of broken or intact brick, sand, and stones.
The archaeologists wrote that the evidence shows that after the building was filled, some structures were built on top of it during the Parthian period.
Traditionally, circular sites have been attributed to the Parthian period, but recent evidence suggests that the construction of these buildings began in Greater Khorasan during the Achaemenid period, and that about 10 such sites were first identified and excavated in Bactria, east of Greater Khorasan.
The authors were able to divide and date the pottery found at Takhchar Abad into two periods. The Late Iron Age/Achaemenid period (seventh-sixth centuries BC) and the Parthian period (third-fourth centuries AD).
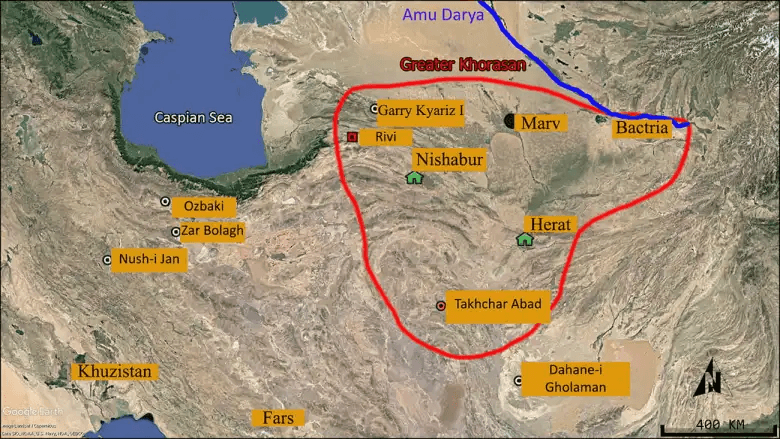
Takhchar Abad is similar to Garry Kyariz I, which is located 67 kilometers northwest of Ashgabat, Turkmenistan. It is a circular structure with eight semi-oval towers that was used from the Iron Age to the Achaemenid period.
The Achaemenid period lasted approximately 200 years (550–330 BC). The Achaemenid Empire ruled over the largest imperial region in antiquity, stretching from the river Syr Darya (in central Asia) to Egypt.
In terms of cultural materials, it is difficult to identify Achaemenid sites using surface materials such as pottery because the cultural materials of the Achaemenid period are very similar to those of previous periods.
These excavations in south Khorasan are expected to play an important role in the identification of Achaemenid-era buildings and shed new light on the history of this period.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2024.42
Cover Photo: Mohsen Dana et al. / Antiquity
















