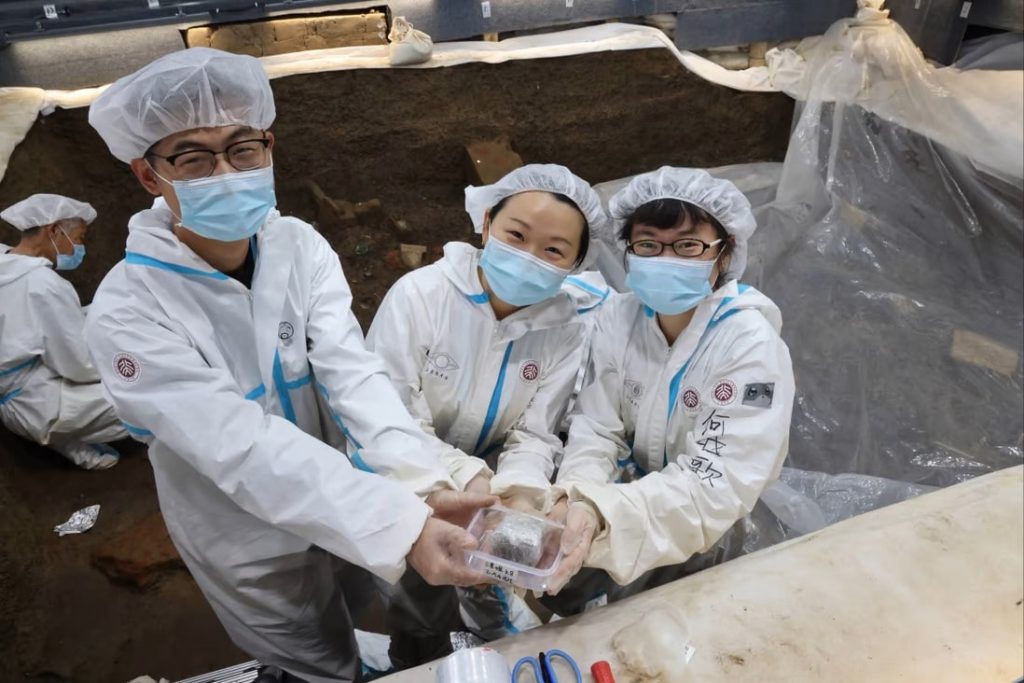
According to the South China Morning Post, researchers in China believe a skeleton discovered in a tomb in the country’s northwest is the first documented case of foot amputation (Yue) as a punishment for a crime.
According to the Peking University researchers, a biological investigation of the woman’s bones ruled out medical or other grounds for the amputation, and the victim survived for at least five years after the punishment was carried out.
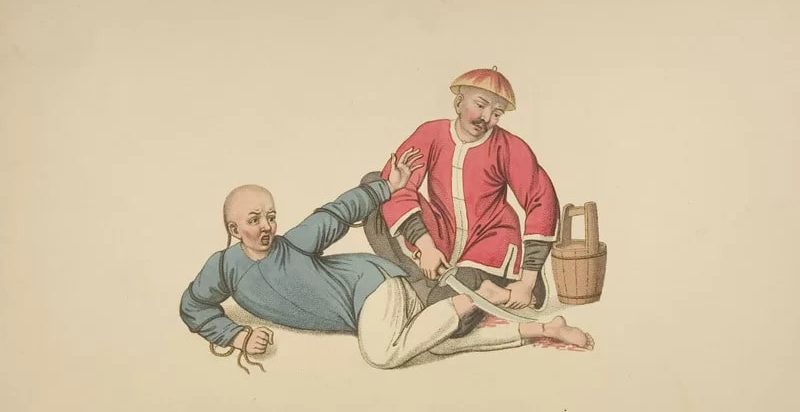
In ancient China, amputating one or both feet was a practice known as the Yue and was one of the five punishments of ancient China. The “Five Penalties” system, was in place for at least a thousand years till about 200 BC.

The so-called Five Punishments (wuxing) were the capital punishments in ancient China. According to legend, either the Yellow Emperor or the Xia dynasty (17th – 15th cent. BCE) adopted these as they were common penalties used by the southern Miao tribes.
The Confucian Classic Shangshu” Book of Documents” (chapter Lüxing) says that when Chi You brought chaos onto the earth, the Miao tribes created the five punishments: “They made the five punishments engines of oppression, calling them the laws. They slaughtered the innocent, and were the first also to go to excess in cutting off the nose, cutting off the ears, castration, and branding.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
In historical archives and artwork, there is plenty of proof supporting the practices. For instance, in the earliest Chinese written records, the Shang dynasty’s (circa 1600-1050 BC) bone inscriptions seem to show some images of a foot being cut off with a saw, which is the earliest form of the character for Yue.
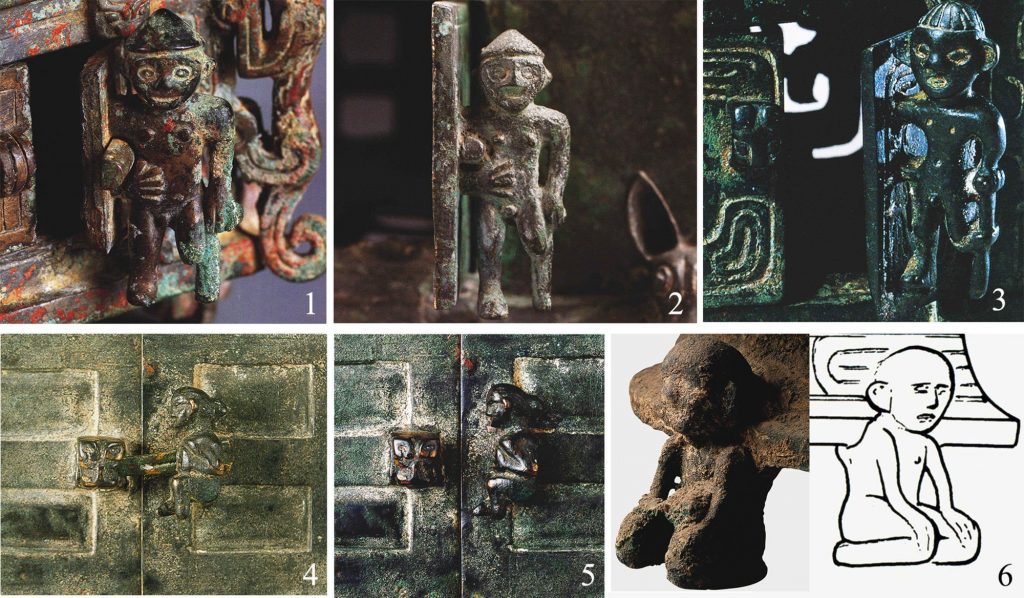

Western Zhou (from around 1046 to 771 BC) bronze vessels have some engravings showing people with one or both legs missing acting as gatekeepers. In the Spring and Autumn period (770-476 BC), foot amputation became such a common form of punishment that demand and prices for special shoes shot up.
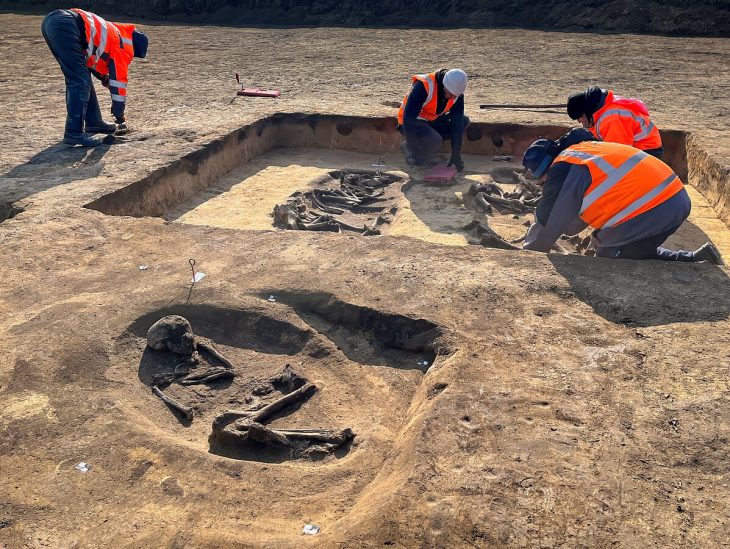
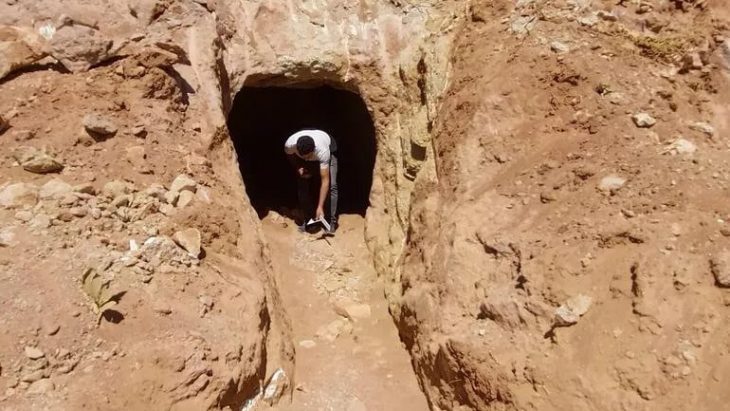
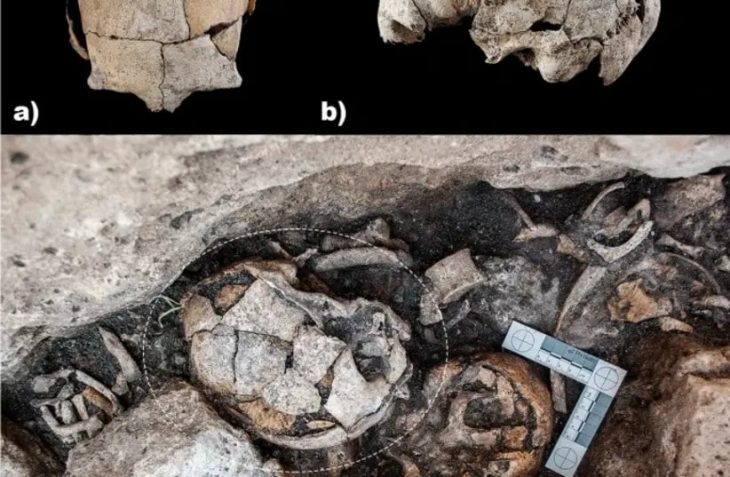
The skeleton of the woman who is thought to be the earliest known punitive foot amputation case was found in a tomb at a cemetery at the site of Zhouyan near Baoji in China’s northwestern province of Shaanxi.
The amputee’s corpse was discovered during excavations that began in 1999, but it was pushed aside without any in-depth investigation because archaeologists were more interested in locating artifacts, of which there were few discovered at the site.
The location, which was the cradle of the Zhou civilization, is renowned as the “hometown of bronzes” because of the huge quantity of containers, oracle bones, and tombs that have been discovered there. Oracle bones and tombs have also been discovered at the site.
Li Nan, a postdoctoral researcher at Peking University, studied the bones. She said recent scientific and technological developments had made a further study of the remains worthwhile.
“People only regarded this human bone as an incomplete bone before, but when I had a certain knowledge reserve, I thought at first sight that it might be a case of amputation,” she said.
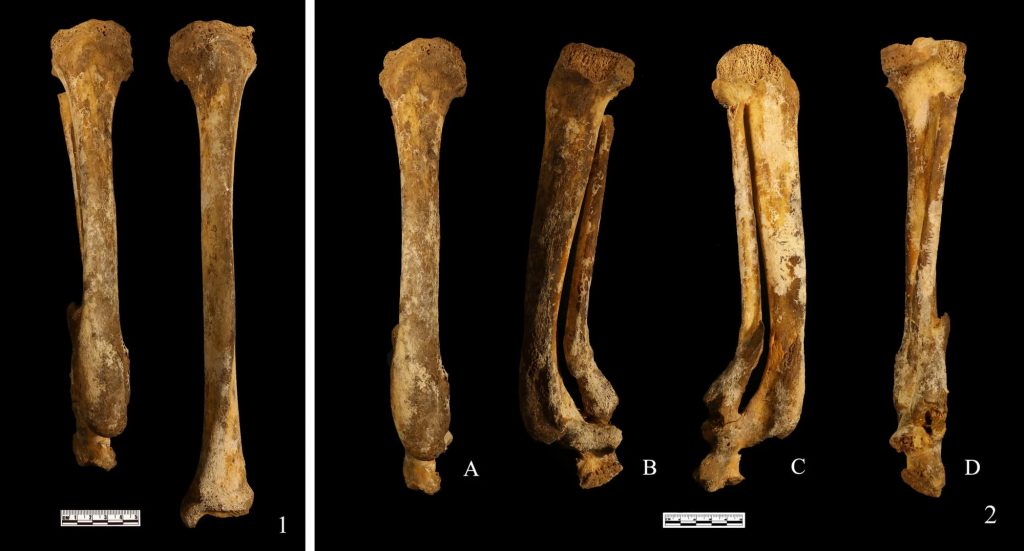
An X-ray study revealed that the bones belonged to a lady in her 30s or 35s who had her right foot amputated.
Sometimes patients with diseases such as diabetes, leprosy, and cancer, who had suffered frostbite or burns, had their limbs removed.
But a study of the bone density and structure of other parts of the skeleton ruled out disease.
The amputation had also caused serious deformities to the tibia and fibula – something that suggested it was not a medical operation because those leaves wounds that are relatively flat and smooth.
“Combining the biomedical analysis of the tomb occupier and the Yue amputees images engraved on bronze vessels unearthed from nearby tombs, it can be basically determined that this is an example of the Yue penalty and is the earliest known example,” Li said.
The team of researchers from Peking University, led by postdoctoral researcher Li Nan, has published a paper in Acta Anthropologica Sinica on the findings of their study.
Cover Pic: China Underground