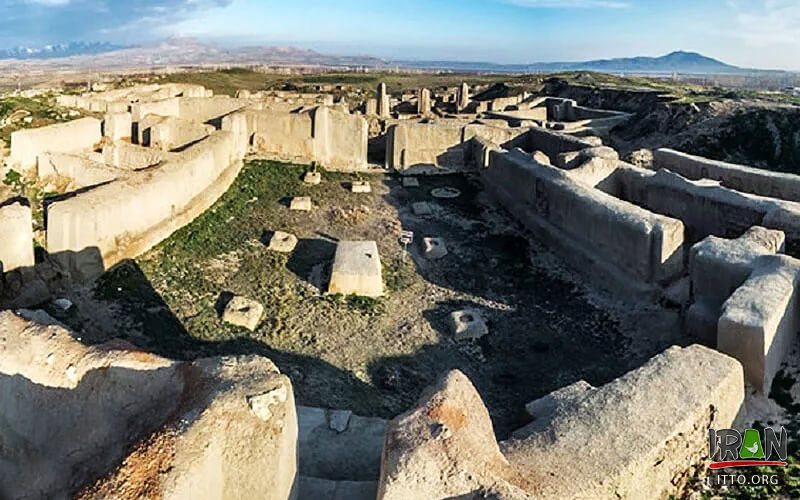
Hasanlu Teppe dominates the plain known as Solduz in Iran and was one of the largest settlements in the Qadar River valley. The ancient city, also known as Teppe Hasanlu or Tappeh Hassanlou, is located in the south of Lake Urmia, in the West Azerbaijan Province, in the northwest of Iran.
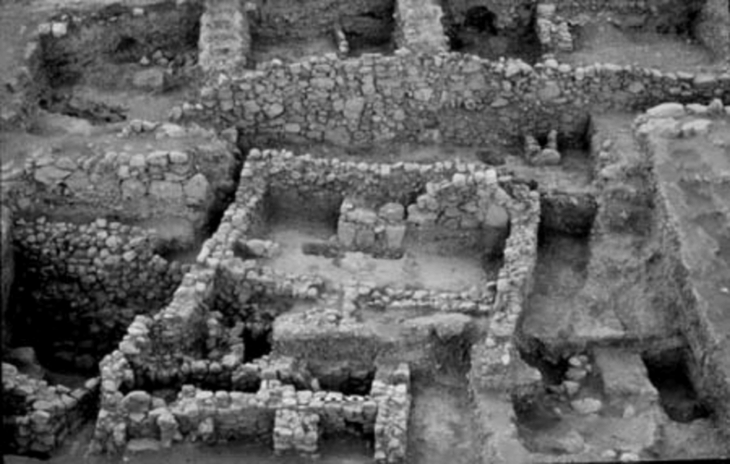
The once much larger site has shrunk due to agriculture and construction activities, now it is about 600 m in diameter, and the Citadel has a diameter of about 200 m. The site consists of a 25-m high central “Citadel” mound surrounded by a low Outer Town, 8 m above the surrounding plain.
The settlement was looted and burned in 800 BC. Much of the turmoil and devastation caused by that catastrophe was long frozen in time until archaeologists discovered well-preserved structures, artifacts, and even human remains while trying to piece together the destiny of the ill-fated community.
Although it seems like an old story so far, the artifacts found here became the main source of questions that archaeologists still cannot answer even after years.

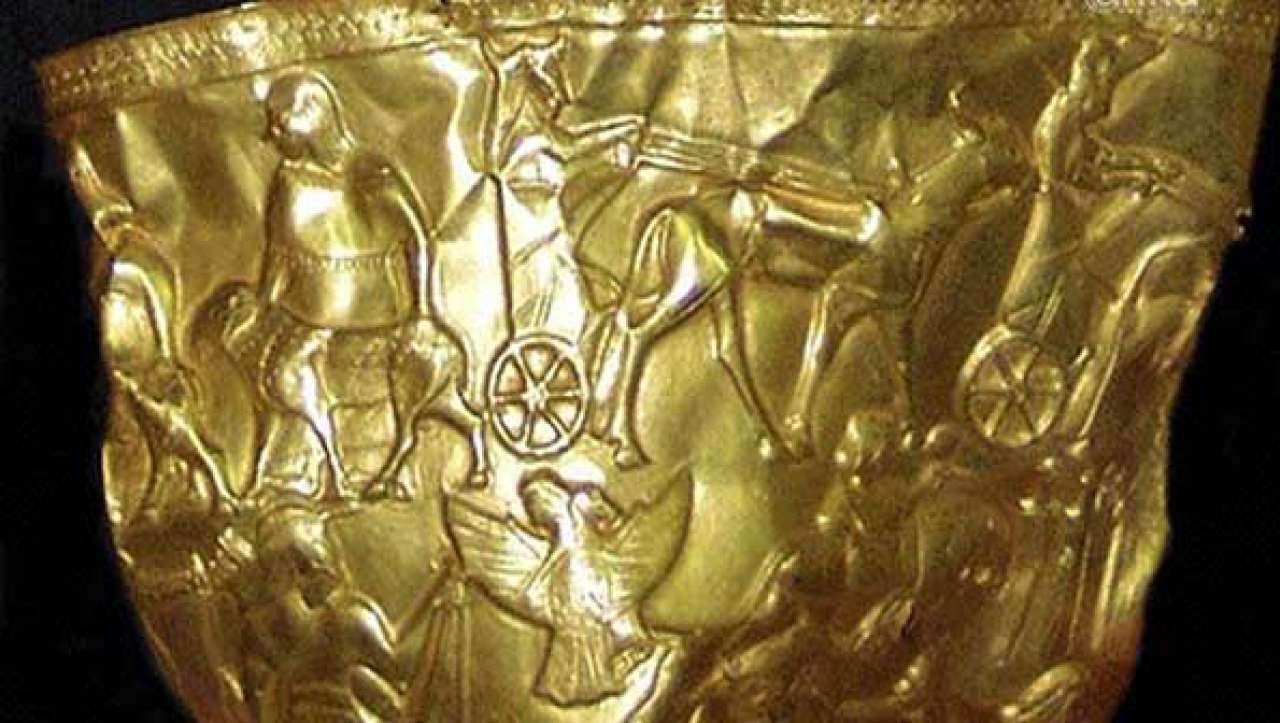
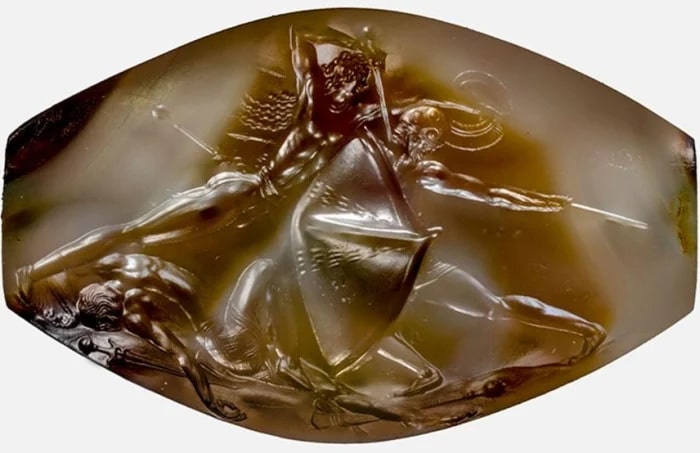
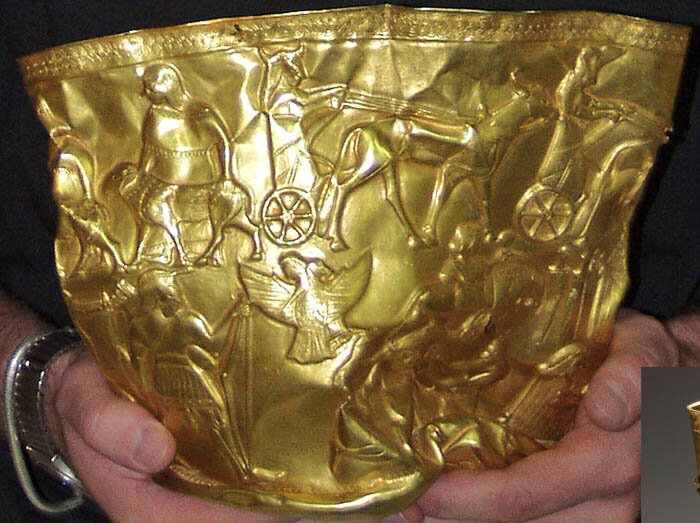
Engraved with images of gods and rituals, a stone cylinder with gold caps, a figurine of laminated ivory, and a sword-hilt with a bronze guard, the Gold Bowl of Hasanlu is named after the man who discovered it.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The ‘gold bowl of Ḥasanlu’ was found in the debris of Burned Building I West on the Citadel Mound at Ḥasanlu in 1958.
As written in Iranicaonline, It had fallen into room 9 in the southeastern corner of the building where, at the end of the 9th century B.C.E., it was buried under the collapsed mud-brick walls of the second story along with the bodies of three men. One of these men was carrying the bowl. Although badly crushed, it could be determined that the man had fallen on his right shoulder, with his head facing the north wall. His lower right arm lay upright against the wall face, his hand bent at the wrist. This arm, from wrist to shoulder, was protected by a gauntlet made perhaps of leather.

Probably The three soldiers were in the process of plundering a wealthy, multistory complex as the citadel burned. They located the bowl and other valuables in a second-story storeroom. As they fled with their prize, the mud-brick building suddenly collapsed.
More importantly, In no time, it became evident that the bowl epitomized a unique and significant example of the ancient goldsmith’s expertise, demonstrating a high degree of technical mastery and a wide range of ornamental motifs that were deemed to provide a key to the religious and mythological traditions of its time.
Over the years, the bowl has been discussed in countless scholarly books and articles including an analysis by Marie-Therese Barrelet (1911-1996) as one of the greatest finds of the decade.
Little is known about the residents of Hasanlu and their invaders due to a lack of written documents. There is no written documentation from Hasanlu attesting to the residents’ identities.” “We know neither the historic name of the location nor the state to which it may have belonged, much alone the linguistic and/or racial connections of its inhabitants – neither before nor during the era in question,” says Irene J. Winter in her essay “The Hasanlu Gold Bowl: Thirty Years Later.”
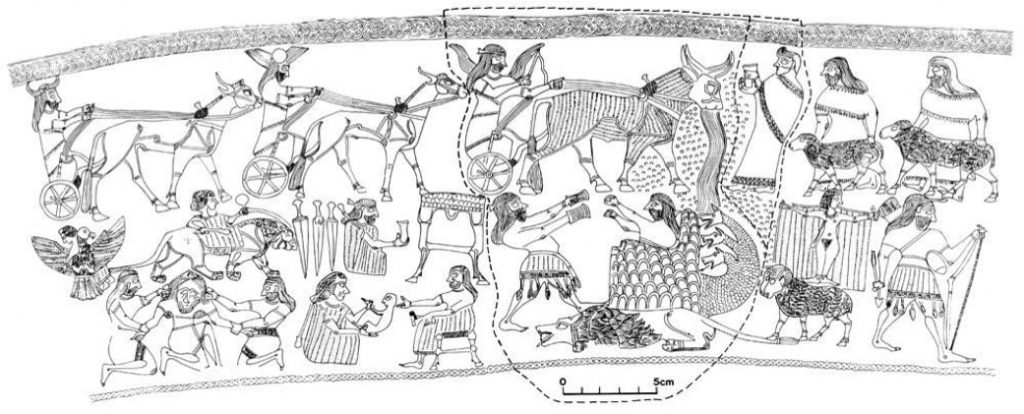
The Ḥasanlu bowl weighs 33 3/8 ounces and is decorated by repousé work and chasing. The bowl is about 20 cm in height, with a base of about 15 cm and a rim of about 18 cm.
Although its mysteries and civilization cannot be determined, the Hasanlu bowl is crumpled but still remains dazzling.
According to the Britannica Encyclopedia, Hasanlu was inhabited from about 2100 to about 825 BC, but the richest period yet excavated dates to the 10th and 9th centuries BC. The period, often called “Mannaean” after the name of the people who lived in the area, is characterized by gray pottery accompanied by black and red varieties, the black ware being of a much finer quality and probably made in imitation of metal vessels.
The Gold Bowl of Hasanlu is being kept at the National Museum of Iran in downtown Tehran.