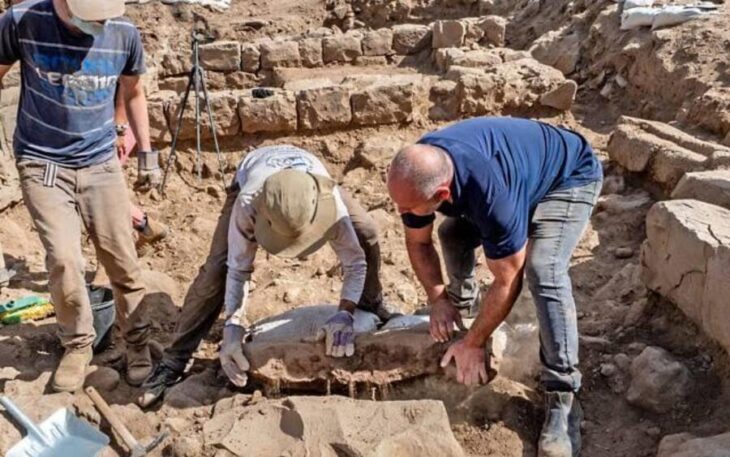
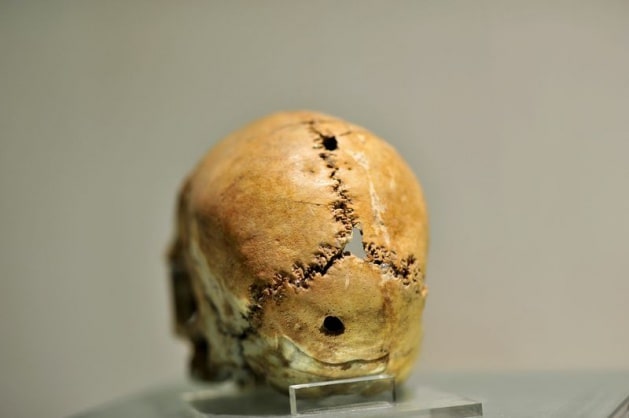
A “revival” effort is underway on a woman’s skull unearthed in 1989 during archaeological digs at the Aşıklı Mound in the Central Anatolian province of Aksaray and believed to have undergone the first brain surgery in history.
It is thought that it was the skull of a nearly 25-year-old woman and that she lived for about 10 days following the procedure. The 10,400-year-old Aşıklı mound, located in Gülağaç district’s Kızılkaya hamlet, is recognized as the earliest village of Central Anatolia and Cappadocia. Many historical firsts have occurred on the mound. There, for example, were the earliest agricultural experiments, as well as the domestication of sheep and goats.
The skull, on which the first brain surgery was conducted, is of immense historical significance and is on display in the Aksaray Museum.
Speaking to the state-run Anadolu Agency, Aksaray Museum Director Yusuf Altın stated that there were two holes in the skull and that they believed they were the remnants of history’s first skull surgery.

Altın stated that 9,500 years ago, the average age of individuals was between 30 and 35 and added, “The studies carried out on the skull by scientists revealed that the woman who had the surgery lived about 10 days after the operation. The Aksaray Municipality started a project on the skull exhibited in the Aksaray Museum. We had a 3D scan of the skull done. We will portray a 25-year-old woman from 9,500 years ago, and two 3D copies of it will be made. One will be exhibited at the Aksaray Science Center and the other will be in our museum. These studies are being carried out in Germany. After they are finished, we will present the copies to visitors. They will be made of beeswax.”
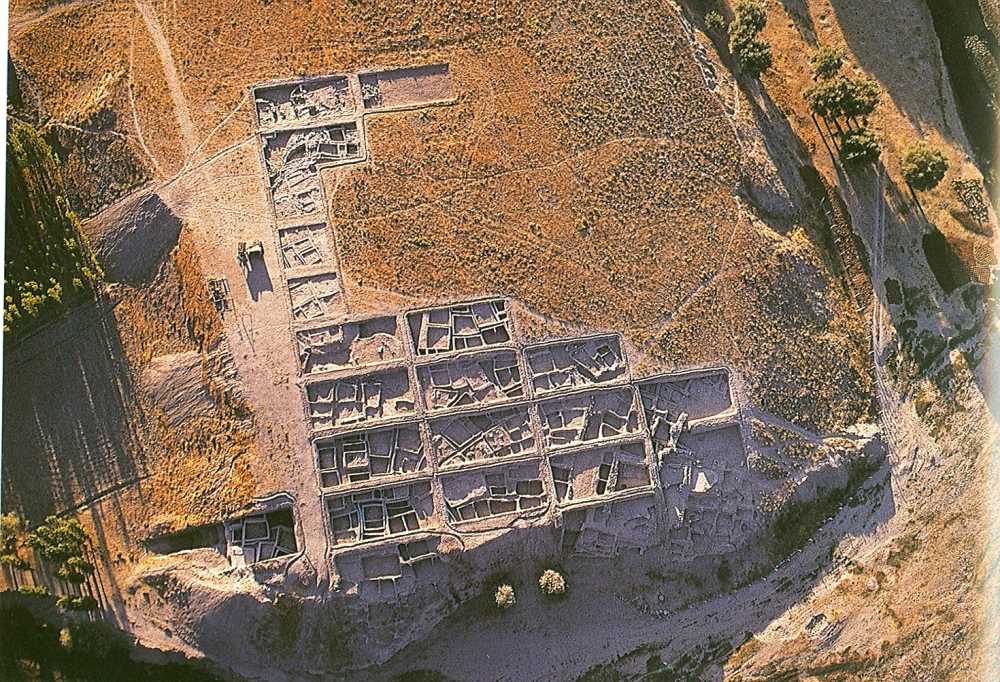
The excavations at Aşıklı Mound began in 1989, according to Mihriban Özbaşaran, professor at Istanbul University’s Prehistoric Archaeology Department and the head of the Aşkl mound excavations.
“Excavations have continued uninterruptedly since then. There is agriculture and animal husbandry in Central Anatolia today. We see it in the mound, too, namely the first people who were engaged in agriculture and animal husbandry. The first settlement began there in 8,400 B.C. Aşıklı mound was a place of the first village settlement, the first agricultural experiments and the place where the first sheep and goats were domesticated,” she said.
Özbaşaran said that the woman of the skull was buried with her baby and they found it that way.
“In the examinations at Hacettepe University, it was revealed that this skull was especially pierced and the operation was performed very sensitively. It was revealed that this was an operation performed using obsidian drillers. Then there was regeneration in the cells in the skull. So it seems that the woman lived for some time after the operation. When the project is finished, we will meet the woman of Aşıklı.”