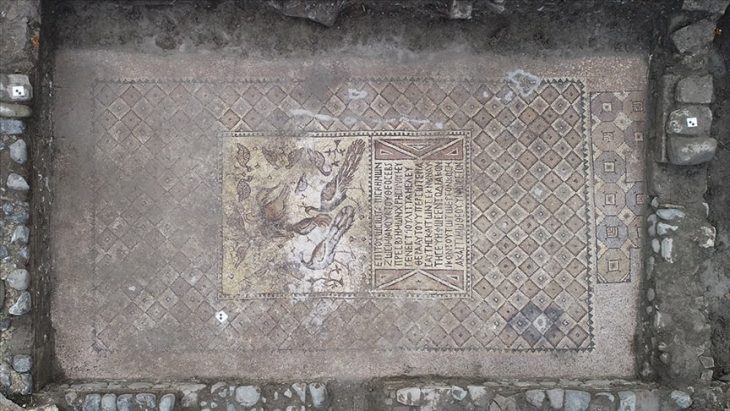
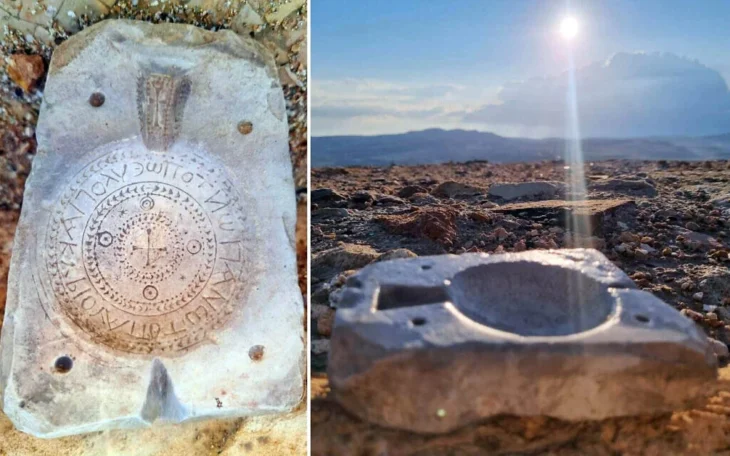
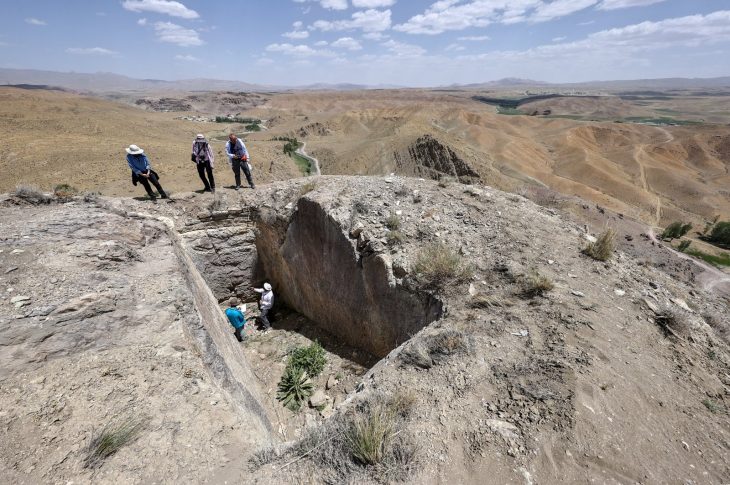
Phrygian Valley, 10 meters high monument with Phrygian scriptures inscriptions on it discovered. The unearthed Maltaş monument is actually the facade of a temple with a triangular roof and niches.
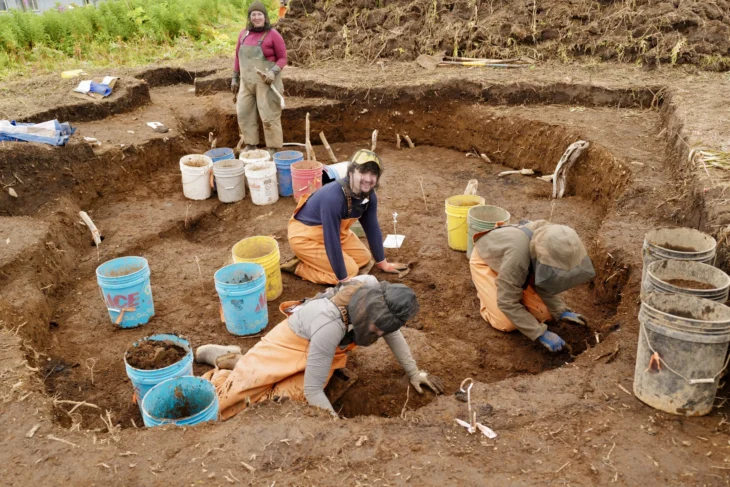
Rescue excavation, which started in late June, continues at the Maltaş Monument, which dates back to the 7th century BC, in the historical Phrygian Valley in the İhsaniye district of Afyonkarahisar.
While just a 3-meter-long section of the monument is visible above ground, recent digs revealed 7 meters of the monument, which dates back to 7th century B.C., in recent excavations.
The Maltaş monument, according to Afyonkarahisar Governor Gökmen Çiçek, is one of Phrygia’s best accomplishments. Çiçek described the monument as an “incredible structure,” saying, “Maltaş was built 3,000 years ago and is still standing intact today. Only a certain part of this structure was above ground. When we reached its underground section during our rescue excavation, we came across an enormous artifact,” he said.
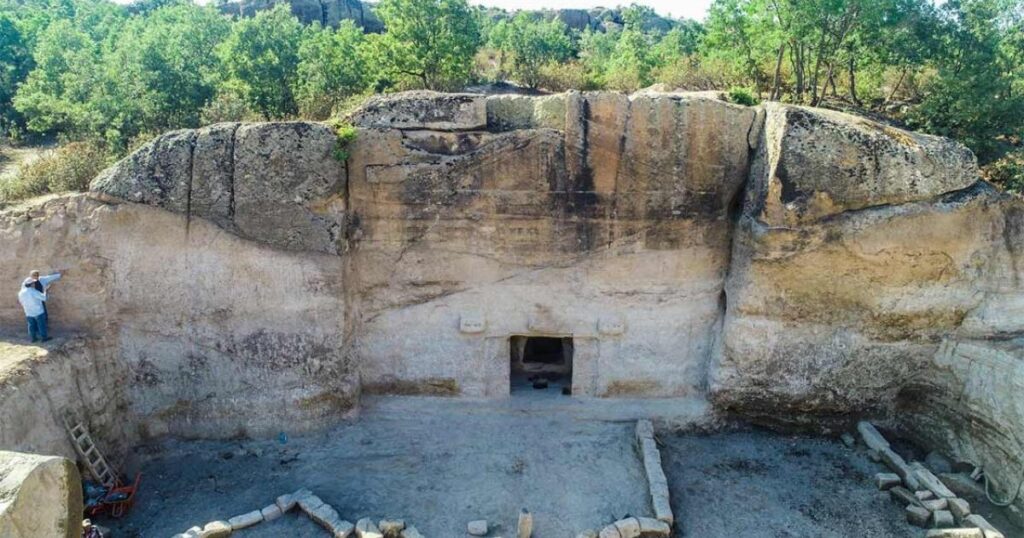

The governor said that experts have been working on this area recently, noting that they are still attempting to find out what the newly revealed niche inside the monument is.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Maltaş (Malkaya) Monument
The monument is situated atop one of the Akkuşyuvası rocks, which form the western boundary of the valley. It’s around 750 meters south of the Aslantaş tomb. Maltaş, like Değirmen Yeri, Bahşayiş, and Deliklitaş, is a shaft monument.

The monument is mostly buried under the earth. In the year 1881, W. M. Ramsay discovered the monument nearly totally hidden in the dirt and dug it out only to a certain level with the aid of workmen.
Although the earth in front of the monument was removed during the excavations of Gabriel (1936), Haspels (1950), and Brixhe (1970), it was replaced with soil to preserve the monument from water damage after each interaction with groundwater. Despite this, the researchers claim that the moisture in the soil has worn out the subterranean portions.
On it, there are two inscriptions. The first inscription is on the left frame’s outside border, which surrounds the façade wall. Over the ground level, the upper half of this inscription may still be seen today. The second inscription is inscribed on the upper frame of the niche portion, which is fully underground, from left to right. With a depth of 9 meters, its shaft is the deepest of the Phrygian shaft monuments.