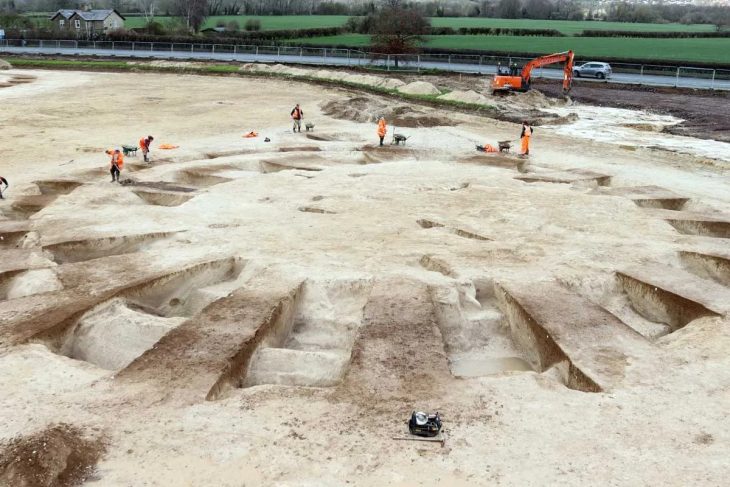
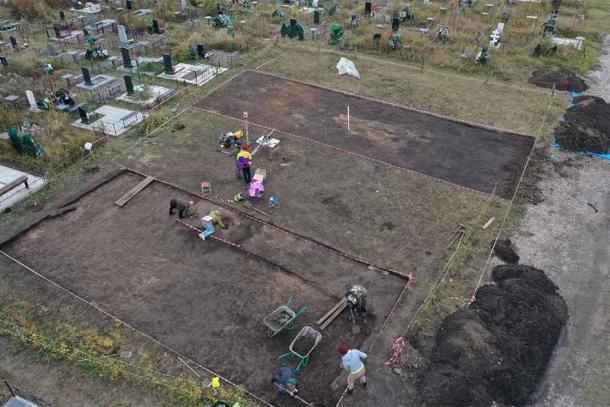
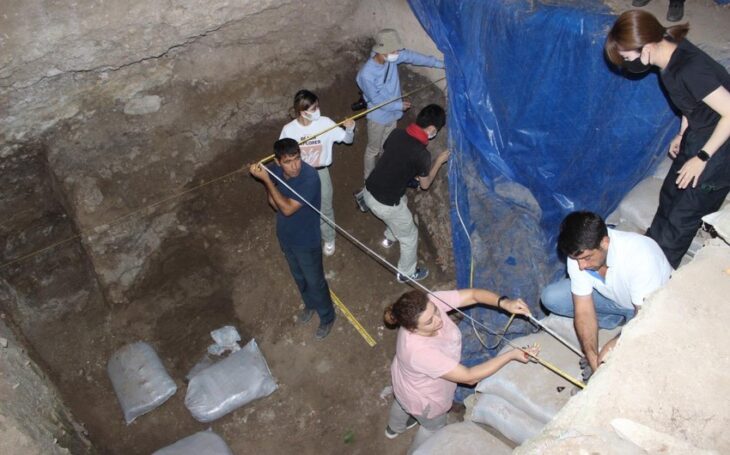
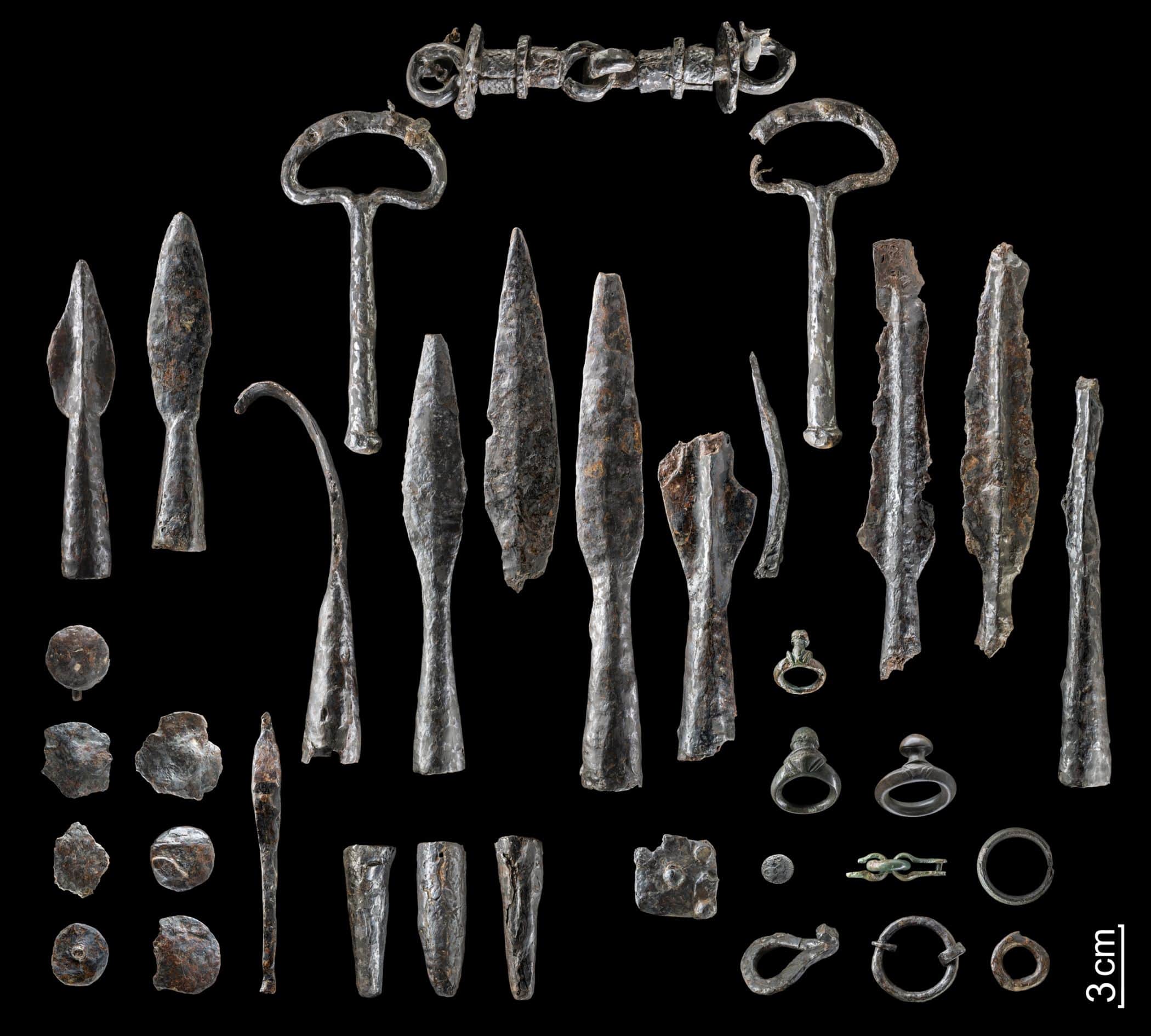
Archaeologists from the Westphalia-Lippe Regional Association (LWL) announced that a metal detector has discovered “one of the largest Iron Age weapon stacks in West Germany”.
LWL archaeologist Prof. Dr. Michael Baales, head of the Olpe branch, reported the find. The finds are of paramount importance to archeology in the country and shed light on the cult actions of Iron Age warriors after a military conflict.
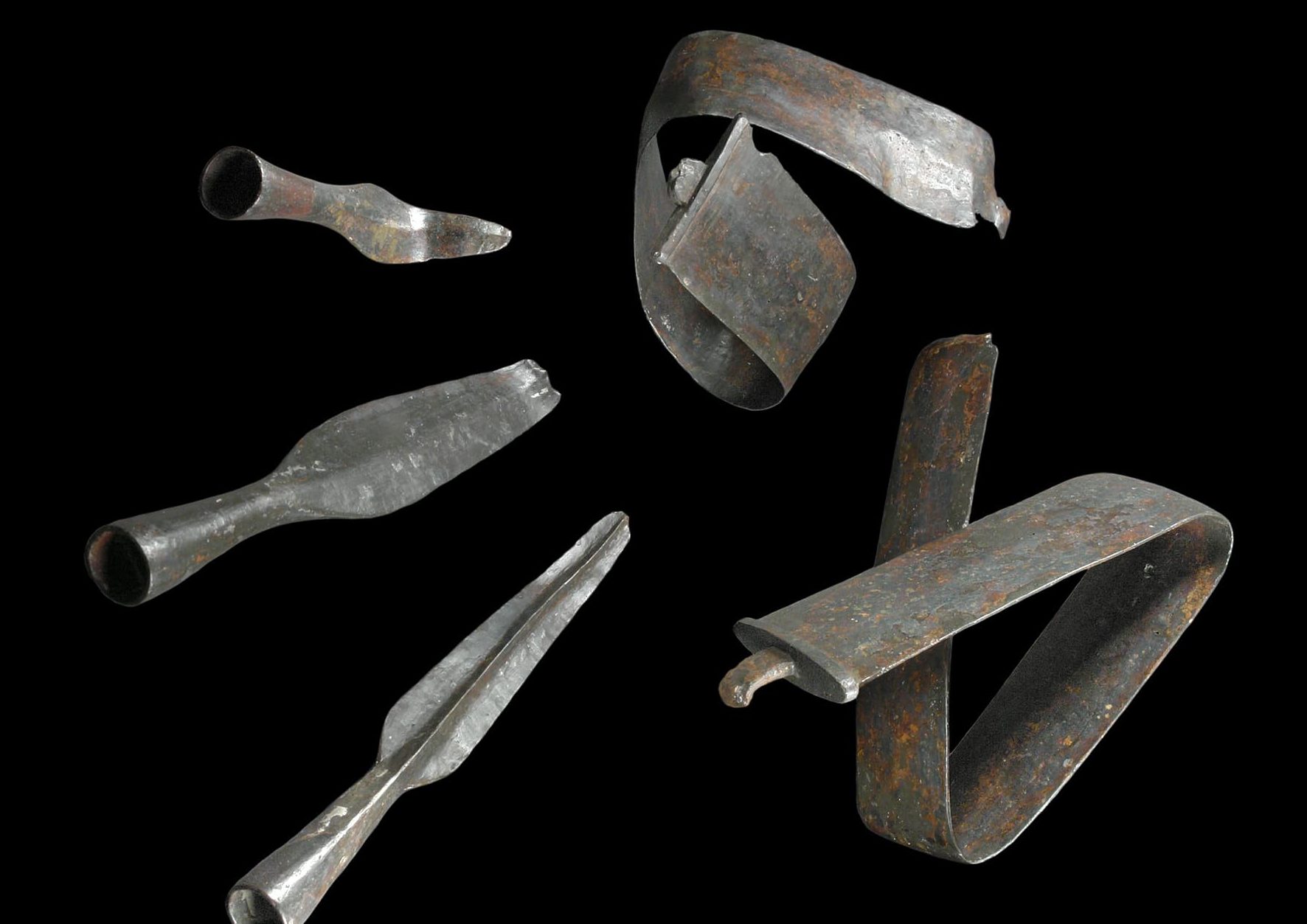
According to Manuel Zeiler, an archaeologist at LWL, the hoard includes more than 150 items, including intentionally bent arms such as 40 spearhead and lancehead tips, knives, and pieces of shield bosses (round structures at the center of a shield); tools; belt hooks; horse gear; three silver coins; bronze jewelry; and one fibula, or lower leg bone, told Live Science.
“The arsenal is the largest in [the German state of] North Rhine-Westphalia and also links the [state’s region of] Sauerland with complex processes in Iron Age Europe,” Michael Baales, an LWL archaeologist and head of the Olpe branch in North Rhine-Westphalia, said in a translated statement, released March 31.
Moreover, the damaged weapons — which ancient people would have purposefully destroyed by bending them — shed light on how victorious Iron Age warriors treated the losing side’s arsenal, Baales said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The finds are not new in Wilzenberg, earlier in the 1950s, two swords wrapped in two spearheads and two lanceheads were found by chance. Not only were the swords bent, but their ends were deliberately deformed.

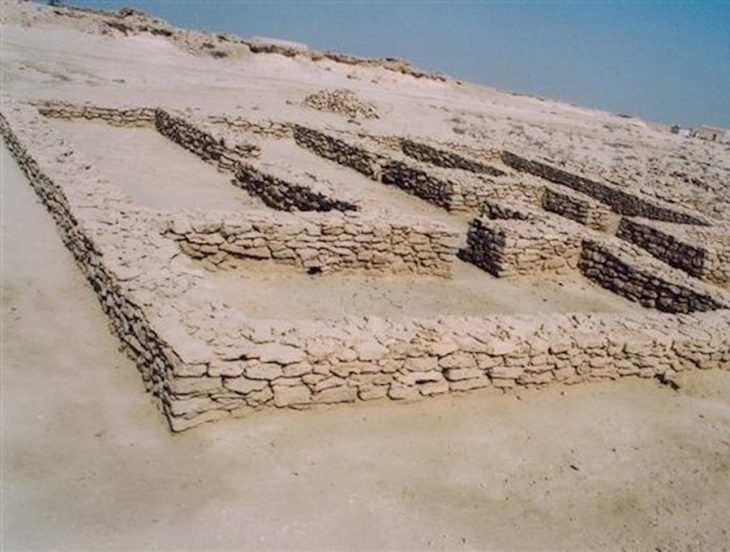
The hillfort, according to Zeiler, is situated on the Wilzenberg range, which stands at 2,158 feet (658 meters). The ancient hillfort, known as the Wallburg, was visited by people during the Iron Age, roughly from 300 B.C. to the birth of Christ, and the walls of the ancient hillfort are still visible today, often by tourists and hikers who frequent the mountain.
Most of the artifacts from the hoard date to about 300 B.C. to the first century B.C., although the coins and the swords had a more narrow window of only the first century B.C., Zeiler said.
Although the hillfort at Wilzenberg is far from Celtic cultural centers in other parts of continental Europe, its architecture and the hoard’s bent objects are “comparable with Celtic culture,” according to Zeiler. Celtic and other Iron Age cultures are known to have bent defeated enemy weapons in a manner similar to the newfound hoard.
The new analysis of the hoard shows that “far away from the Celtic civilization, people celebrated a triumph after battle similar to the Celtic world,” Zeiler told Live Science.
Despite the many weapons and parts of horse gear found at the hillfort, there’s no evidence of an epic battle there, Zeiler noted. “The damage was clearly not caused during a fight, and consequently the Wilzenberg is not a battlefield,” Zeiler said in the LWL statement. Many of the weapons cannot be precisely dated, so it’s not clear whether they were damaged and laid down over the centuries, or whether they were deliberately twisted at a single event, he said.
Photo: LWL-Archäologie für Westfalen / Hermann Menne