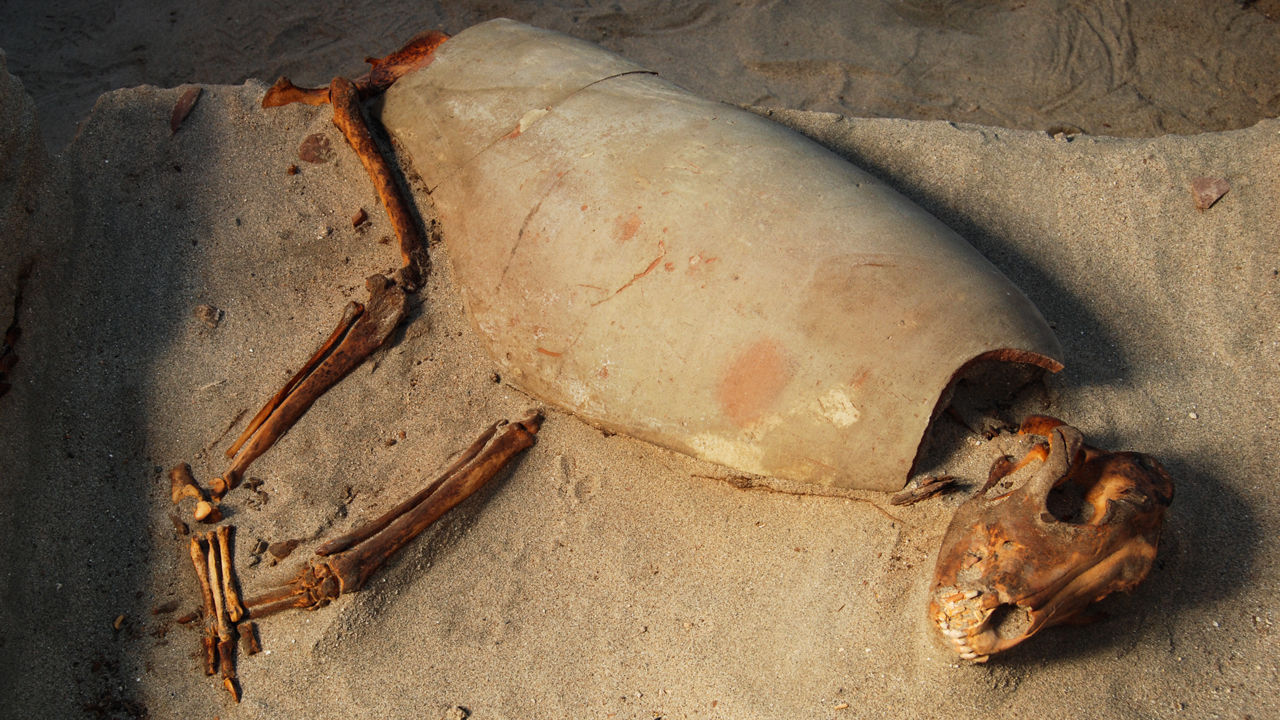
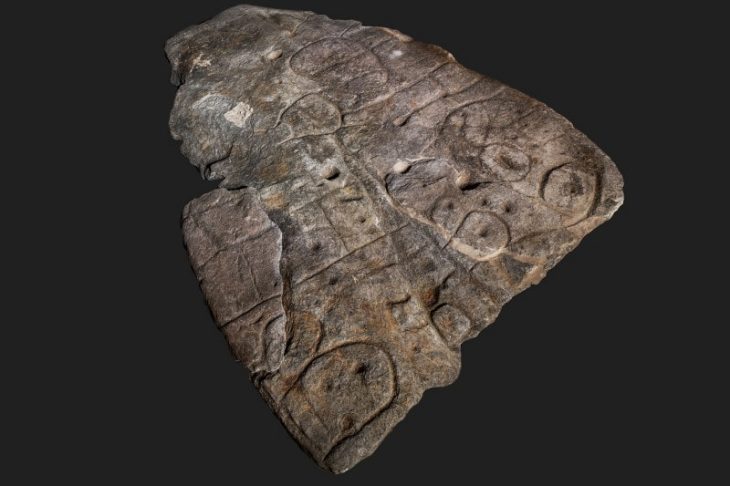
Hundreds of animal skeletons found in Berenice harbor in 2011 made researchers think that this place was used as a pet cemetery. The presence of collars and similar items around the necks of the animals shows that the animals here are special.
The site, located in the ancient Roman port of Berenice, was found 10 years ago, but its purpose was mysterious. Now a detailed excavation has uncovered the burials of nearly 600 cats and dogs, along with the strongest evidence yet that these animals were prized pets. That would make the site the oldest known pet cemetery, the authors argue, suggesting that the modern concept of pets was not alien to the ancient world.
Michael McKinnon, an animal archaeologist at the University of Winnipeg, said: “I have never encountered a cemetery like this.” He studied the role of animals in the Mediterranean throughout the past, but did not participate in this new work. . “The idea that pets are part of the family is hard to come by in ancient times, but I think they are here (family).”
Archaeozoologist Marta Osypinska and her colleagues from the Polish Academy of Sciences discovered a cemetery just outside the city walls, under a Roman rubbish dump, in 2011. It seems that the cemetery was in use between the first and second centuries AD when Berenice was a bustling town. A Roman port that traded ivory, textiles, and other luxury goods from India, Arabia, and Europe.
In 2017, Osypinska’s team reported the discovery of the remains of about 100 animals, most of which were cats, and they seemed to be cared for like pets. But the exact nature of the site is not yet clear. Salima Ikram, an ancient Egyptian animal expert at the American University in Cairo, said at the time that the bones may have been discarded.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
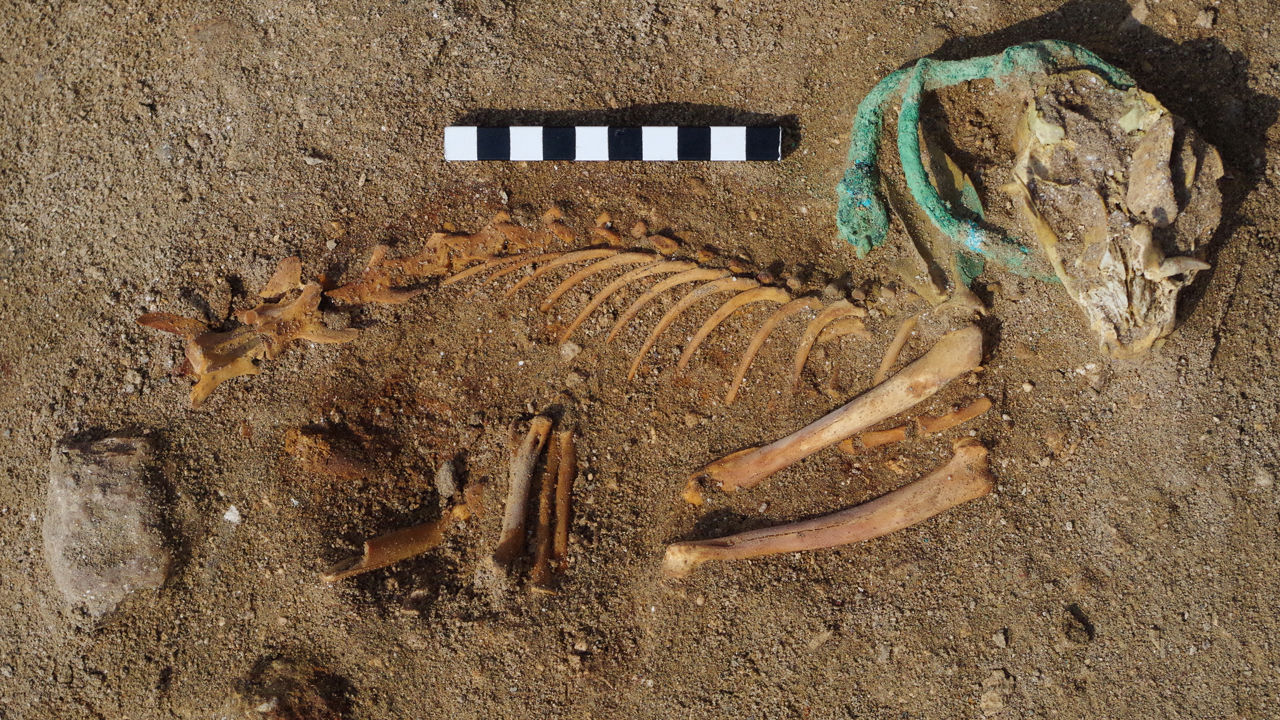

Osypinska and her colleagues have now excavated the remains of 585 animals from the site and analyzed the bones in detail. A veterinarian helped the team determine health, diet, and the cause of death.
These animals seem to have been gently placed in the prepared pit. Osipinska said that many were covered with textiles or pottery and “formed a kind of sarcophagus.” More than 90% of pets are cats and many cats wear iron collars or necklaces with glass and shells. A cat is placed on the wing of a big bird.
The team found no evidence of mummification, sacrifice, or other ritual practices observed at ancient animal burial sites, such as the site of Ashkelon in Israel. In Berenice, most of the animals appear to have died from injuries or diseases.
The dogs, which make up only about 5% of the burials (the rest are monkeys), tended to be older when they died. Many had lost most of their teeth or suffered periodontal disease and joint degeneration.
“We have individuals who have very limited mobility,” Osypinska says. Yet many lived long lives and their injuries healed. “Such animals had to be fed to survive,” she says, “sometimes with special foods in the case of the almost-toothless animals.”
The fact that humans took such good care of animals, especially in a rugged region where almost all resources had to be imported, and that they were so careful when burying them, as many modern owners do, suggests that the people of Berenice had a strong emotional bond with their cats and dogs, the team concluded last month in World Archeology. “They weren’t doing it for the gods or for any utilitarian benefit,” says Osypinska. Instead, she argues that the relationship between people and their pets was “surprisingly close” to what we see today.

Ikram is convinced. “This is a cemetery,” she says. “And it sheds an interesting light on the inhabitants of Berenice and their relationships with their animals.”
Archaeologist Wim Van Neer is also on board. “I’ve never seen a cat with a collar” from so long ago, says Van Neer, of the Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences, who has studied the relationship between people and animals in the ancient world, including at Berenice.
However, he said that the people of Berenice may cherish their cats and dogs for non-emotional reasons. He pointed out that the harbor should have been flooded with mice, making cats a precious working animal. Although some of the puppies in this location are small dogs similar to today’s toy breeds, and therefore have little use other than being kept in captivity, the larger dogs can guard the house and consume garbage. “I don’t think this is just a loving relationship.”
Osipinska hopes that this new work will convince other archaeologists that companion animals are worth studying. She said: “In the beginning, some experienced archaeologists made me reluctant to conduct this research.” She believes that pets have nothing to do with understanding the lives of ancient people. “I hope our research results prove that it is worthwhile.”