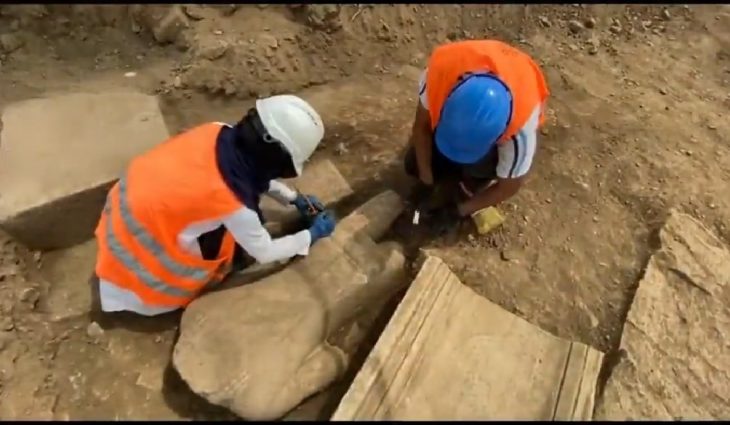
A recent archaeological find in El Salvador has unveiled a captivating glimpse into the rituals of the region’s Indigenous people, featuring a set of ancient puppets that challenge our understanding of Mesoamerican performances during the Middle Preclassic Period.
These intriguing puppets were unearthed by a team of researchers led by archaeologist Jan Szymański from the University of Warsaw, and they are believed to have played a significant role in public rituals, reflecting the cultural practices of the Indigenous people of the region.
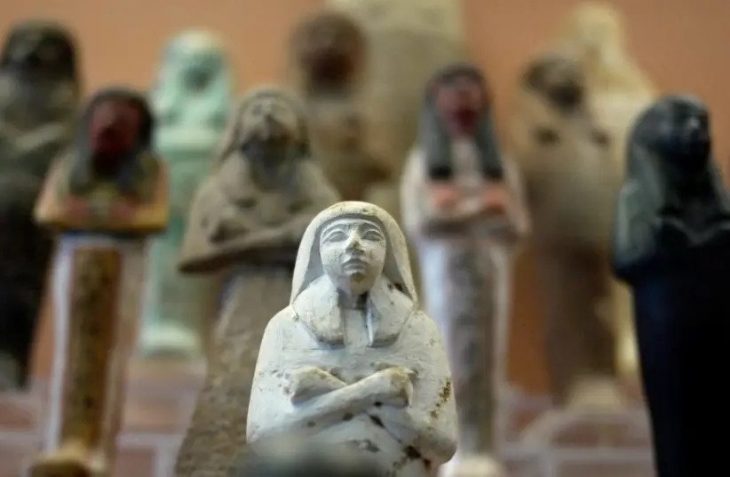
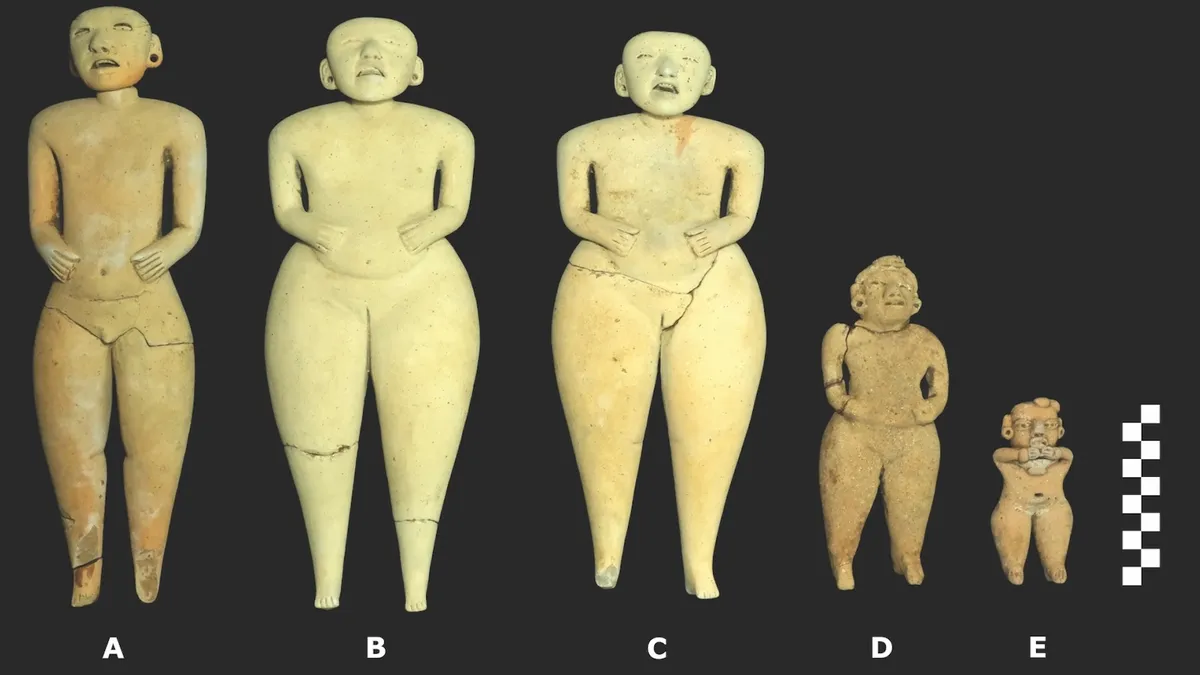
Three of the dolls are about a foot tall (30cm) while two others are about 10cm (0.3ft) and 18cm (0.6ft), researchers say.
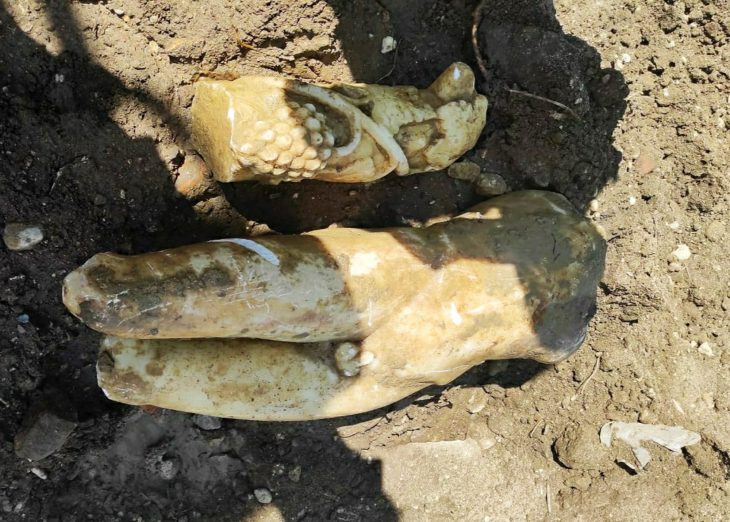
All of the discovered figurines feature open mouths, with some displaying visible tongues, while the three largest possess detachable heads with small holes in their necks and at the tops of their heads. Archaeologist Jan Szymański quickly realized that by running a string through these holes, the figurines could be manipulated to turn their heads from side to side, creating the illusion that they were singing, chanting, or talking. This suggests that they may have functioned as ancient marionette-like puppets, according to researchers who reported their findings this week in the journal Antiquity.
Art historian Julia Guernsey from the University of Texas at Austin has described the theory that the figurines functioned as puppets as “superprovocative.” Radiocarbon dating and ceramic analysis indicate that these intriguing objects were likely buried atop the pyramid around 400 B.C.E., during the Middle Preclassic period—a time when Mesoamerican cultures, including the nearby Maya, were on the verge of developing writing and establishing complex hierarchical societies. In contrast, Szymański suggests that the San Isidro site may have maintained a more egalitarian social structure during this transformative era.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
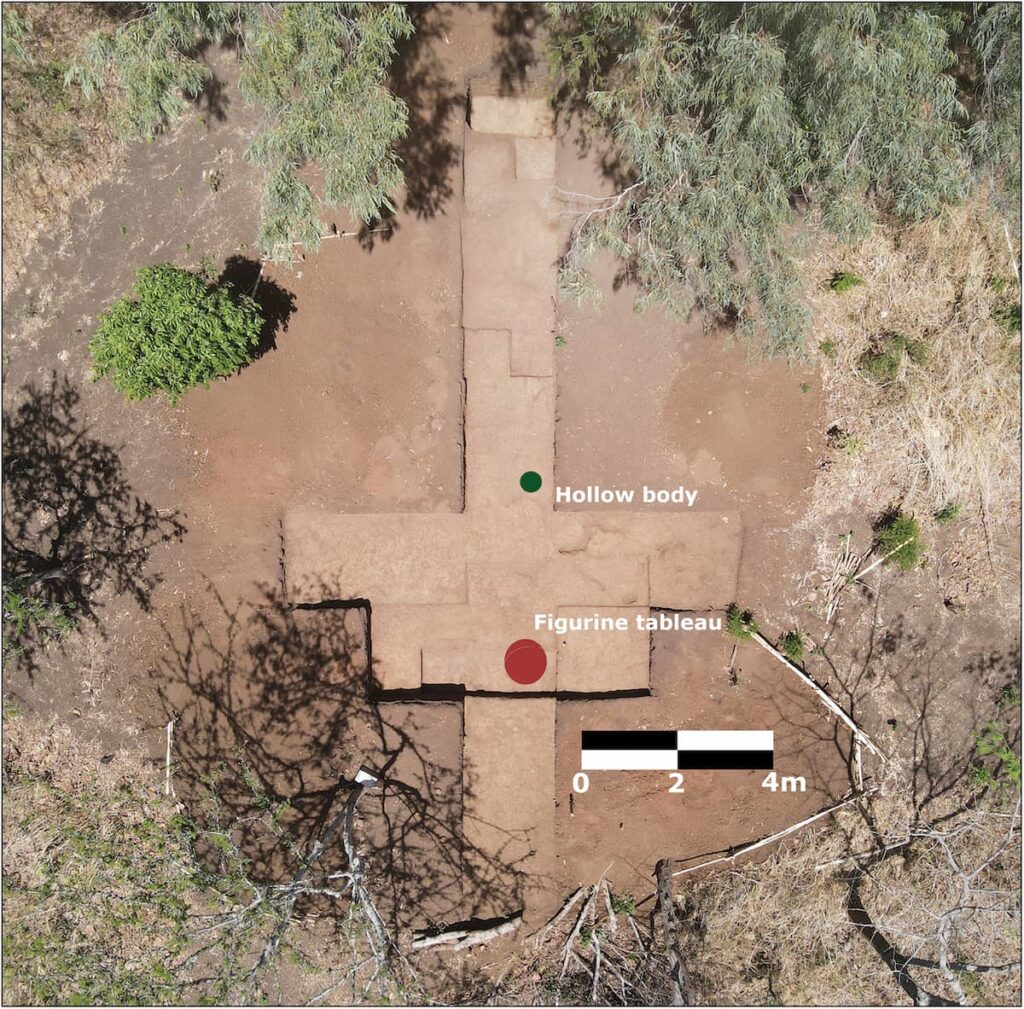

The figures are classified as “Bolinas figures,” a style that has been discovered at various archaeological sites, although most have been found fragmented or discarded in ancient refuse piles. A notable find of intact figures took place in 2012 at Tak’alik Ab’aj, a Maya site in Guatemala, where figurines with movable heads were unearthed as part of a funerary offering. This discovery implies that these figures may have served as symbolic representations of a journey to the underworld.
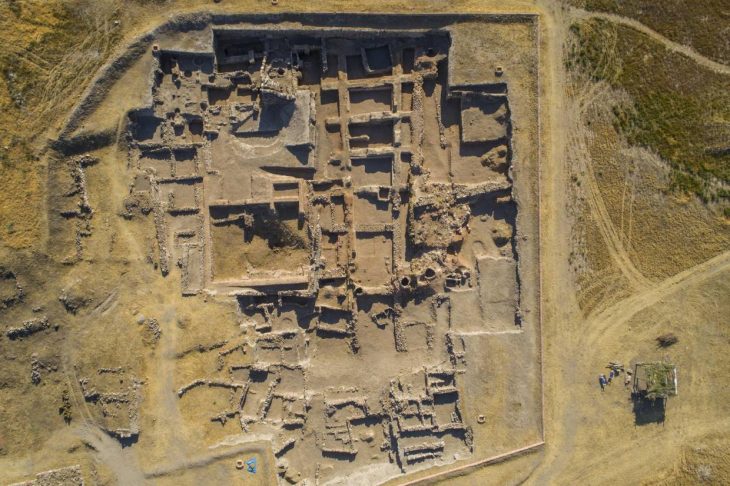
The figures were arranged in an apparent ritual configuration. Although time and the action of tree roots may have altered their original position, archaeologist Barbara Arroyo notes that their general westward orientation could link them to the symbolism of sunset and death in the Mesoamerican worldview.
The Bolinas figurines from Tak’alik Ab’aj and other archaeological sites feature intricate decorations, including skirts and hairstyles incised into the clay. Notably, one figurine from Tak’alik Ab’aj was adorned with a detachable jade earring fitted into a hole in its earlobe. These similarities lead Szymański and other archaeologists to speculate that the San Isidro puppets may have once been dressed in clothing made of cloth or straw, as well as adorned with miniature jewelry and even wigs.
Szymański proposes that altering the attire of these figures may have enabled them to portray different characters in various performances, effectively making them “clay actors.” He emphasizes the striking visual effect of the figurines’ expressions, which seem to come alive depending on the angle from which they are viewed. The archaeologist notes that when held in hand, the expressions can be so vivid that it appears as though the figures are on the verge of movement.
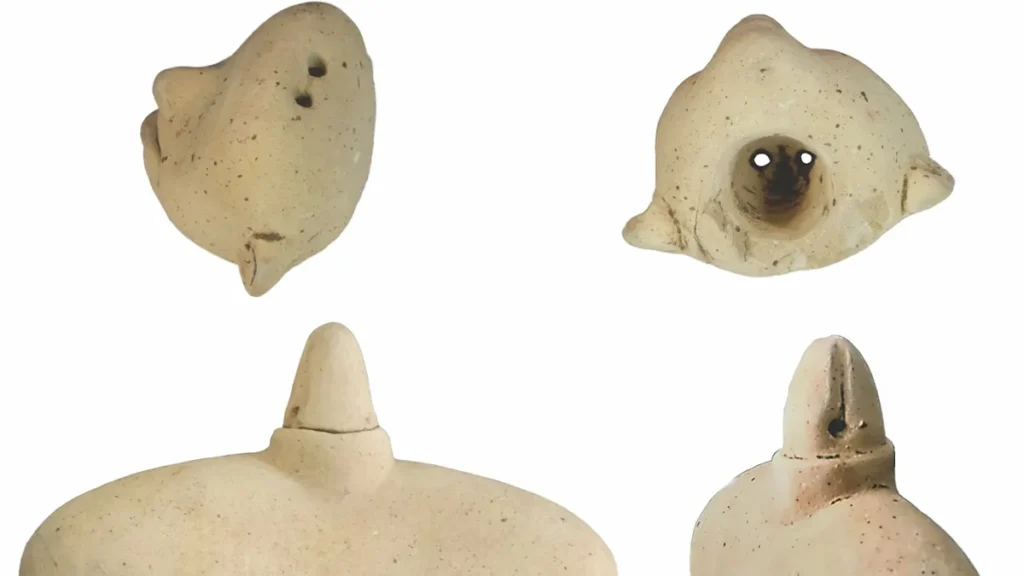

Although certain performances might have had educational or entertainment value similar to contemporary puppet theaters, the figures’ final positioning on top of a pyramid implies their vital role in religious rituals. Szymański believes these figures could have been involved in different performances before their deposition in this sacred setting.
To gain further insights into the performances and rituals associated with the puppets, as well as the puppeteers who operated them, Szymański’s team is actively continuing their excavation of the pyramid. He suggests that San Isidro may have functioned as a trading hub, facilitating the exchange of cultures, ideas, and languages from Central America and beyond.
In contrast to the nearby Maya societies that were establishing monarchies, San Isidro appears to have organized itself without a centralized ruler. Szymański speculates that the San Isidro puppets may have represented different languages in their various roles, highlighting the diversity of their egalitarian community, where multiple voices could be expressed.
Szymański, J., & Prejs, G. (2025). Of puppets and puppeteers: Preclassic clay figurines from San Isidro, El Salvador. Antiquity, 1–17. doi:10.15184/aqy.2025.37
Cover Image credit: J. Przedwojewska-Szymańska/PASI; Antiquity