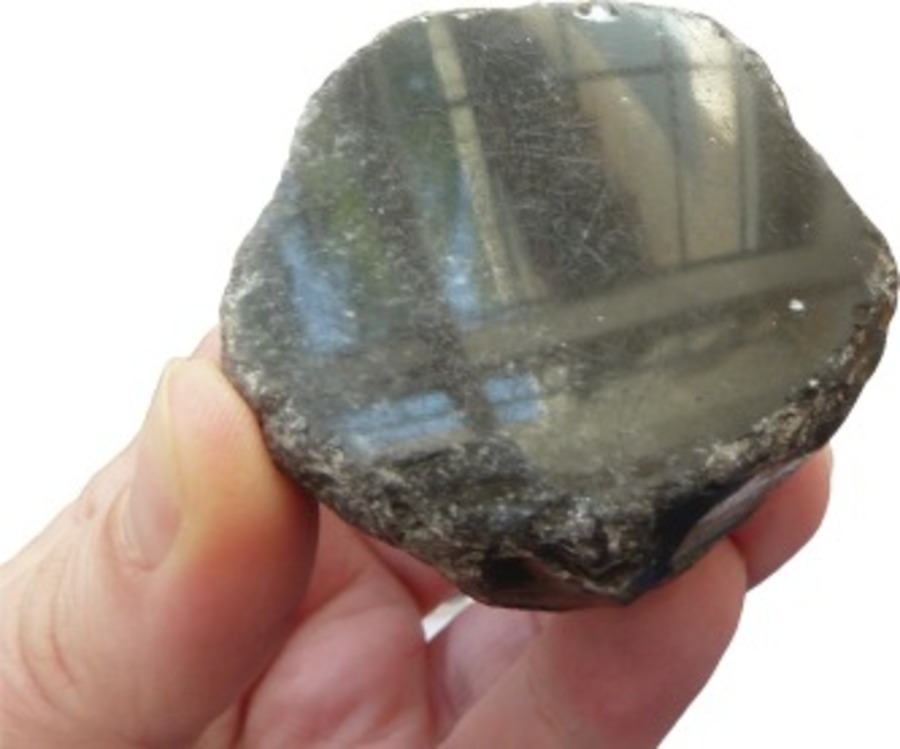
A recent study has applied a techno-functional approach to investigate the production and use of obsidian mirrors found at Tepecik Çiftlik, a significant archaeological site in Anatolia. Obsidian has been utilized in the region since the 8th millennium for creating both functional tools and non-utilitarian artifacts, such as mirrors and ornaments.
The mirrors, distinguished by their elegant circular shape and mesmerizing reflective surfaces, are exceptionally rare treasures, with a mere 56 known obsidian specimens unearthed across six archaeological sites in Central Anatolia and one in the Levant. These mirrors were not practical tools but rather objects imbued with symbolic meaning.
The contexts in which these mirrors have been found—often in funerary and ritual settings—suggest that they served purposes beyond mere reflection. They may have acted as status symbols, ceremonial tools, or even held spiritual significance.
Tepecik Çiftlik emerges as a crucial site for understanding the production of these mirrors. Situated in the Melendiz Plain of Cappadocia, this settlement was inhabited from the Neolithic to the Early Chalcolithic period, approximately between 7000 and 6000 BCE. Its close proximity to natural obsidian sources, such as the Nenezidağ and Göllüdağ deposits, facilitated the development of a specialized industry focused on cutting and polishing this volcanic material.
Excavations at Tepecik Çiftlik have revealed not only finished mirrors but also preforms at various stages of production, enabling researchers to reconstruct the manufacturing process in detail. This makes Tepecik Çiftlik the only site where local production of obsidian mirrors has been definitively documented, while other sites have primarily yielded finished products, suggesting they may have been imported.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The research focused on understanding how these mirrors were made and used by employing technological analysis, which identifies knapping scars on cores and products to characterize the knapping techniques and manufacturing processes. This analysis aims to reconstruct the complete chaîne opératoire, or production sequence, of the mirrors. Additionally, use-wear analysis was conducted to identify the technical activities in which the tools were engaged, examining traces left on the tools during their use.
The production of these mirrors involved a complex process. Archaeologists have identified at least eight distinct stages based on the analysis of the artifacts. Initially, a piece of obsidian with a relatively flat surface and subcircular shape was selected. Sharp edges and ridges were then removed, and the contours were polished. A coarse-grained stone was used to begin smoothing the surface, followed by finer abrasives like sand or ash mixed with water, fat, and leather to refine the texture. It is believed that some mirrors were further polished with fat and soft fabrics to enhance their shine.
The end result was a portable object with a reflective surface capable of mirroring the observer’s image. However, it appears that these mirrors were not used solely for reflection, leaving their precise function shrouded in mystery.
The discovery of these mirrors in diverse contexts suggests their use went beyond mere practicality. At Çatalhöyük, a prominent Neolithic site, mirrors were found in tombs alongside vibrant pigments, indicating their potential role in rituals for beautifying the deceased.
Some researchers speculate that mirrors may have served as signaling devices or tools for redirecting light. However, the dominant theory posits that they were status symbols for elite individuals, supported by their intricate production and limited distribution, indicating they were reserved for special occasions.
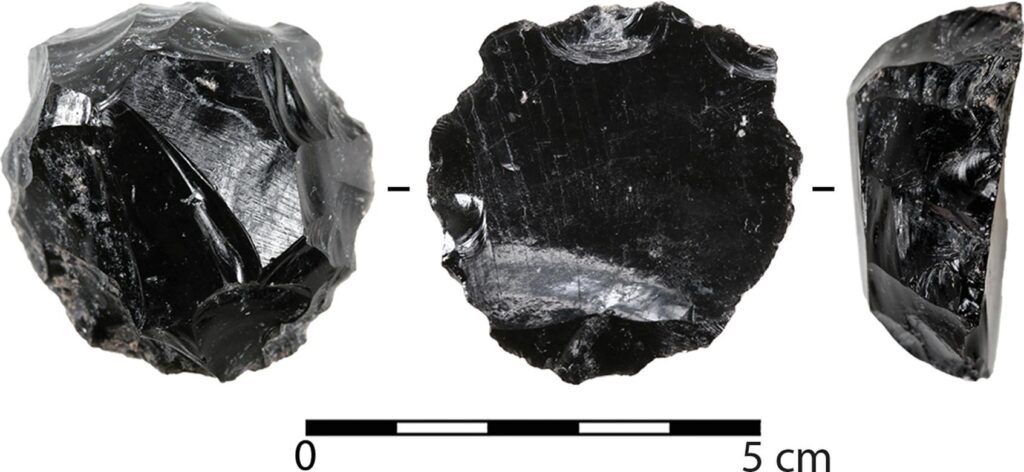

The distribution patterns of Neolithic obsidian mirrors raise questions about their movement across regions. Most mirrors in Anatolia were likely produced at Tepecik Çiftlik and transported to other settlements like Çatalhöyük and Akarçay Tepe, as evidenced by the absence of preforms at these sites.
In the case of mirrors found at Domuztepe and Tel Kabri, located far from obsidian sources, the situation is more complex. Domuztepe has yielded other obsidian artifacts, suggesting access to exotic materials and advanced polishing techniques, though the mirrors’ exact origin remains unclear. Tel Kabri, in the Levant, is notable for its distance from natural obsidian sources, with the single mirror found there likely imported from Anatolia, indicating these objects traveled significant distances as luxury items in early trade networks.
The mirrors were studied using stereoscopic and metallographic microscopes at various magnifications, ranging from 10x to 500x. The interpretation of the traces was based on comparisons of archaeological and experimental traces, allowing researchers to recognize the activities in which the tools were involved. A reference collection from the Laboratory of Technological and Functional Analyses of Prehistoric Artefacts in Rome was consulted, which includes experimental tools made from various raw materials.
At Tepecik Çiftlik, the study found that nearly 70% of the tools from the Early Chalcolithic assemblage exhibited significant surface damage due to post-depositional surface modifications (PDSM). These modifications were caused by various taphonomic processes and improper storage conditions, including bright spots, intersecting striations, and micro pitting. Despite these challenges, the main PDSM observed on the mirror assemblage were striations and micro pitting, which were distinguishable from use-wear.
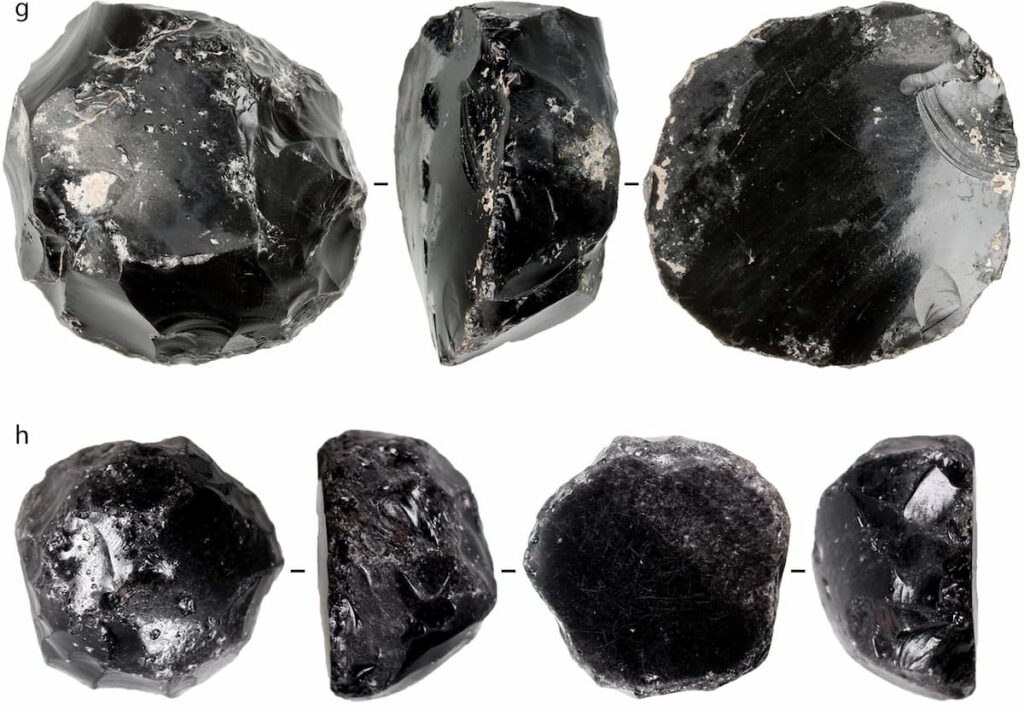

The research successfully identified and documented every step of the production sequence for the mirrors at Tepecik Çiftlik. The findings contribute to a better understanding of the manufacturing techniques and usage of obsidian mirrors in ancient Anatolia, providing valuable insights for future studies in this field. This work represents a significant advancement in the analysis of prehistoric artifacts and highlights the importance of interdisciplinary approaches in archaeological research.
In conclusion, the comprehensive analysis of obsidian mirrors from Tepecik Çiftlik not only illuminates the intricate manufacturing techniques and cultural significance of these rare artifacts but also underscores the complex trade networks and social hierarchies of Neolithic societies, paving the way for further exploration into the interplay between material culture and identity in ancient Anatolia.
Alice Vinet, Neolithic obsidian mirrors from Southwest Asia: A reflection on their diffusion and manufacture. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, Volume 62, April 2025, 105047. doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2025.105047
Cover Image Credit: The finished mirror discovered at Tepecik Çiftlik in 2012 in a Ceramic Neolithic level with a highly reflective surface. Credits: A. Vinet.