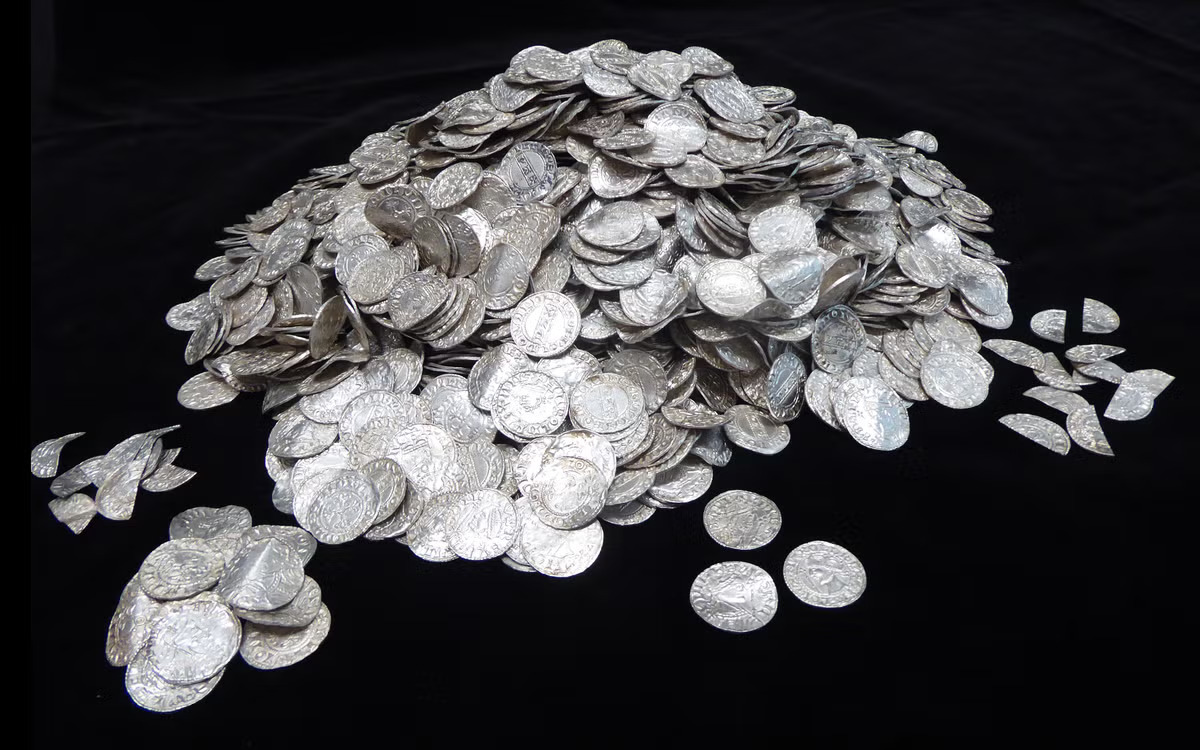
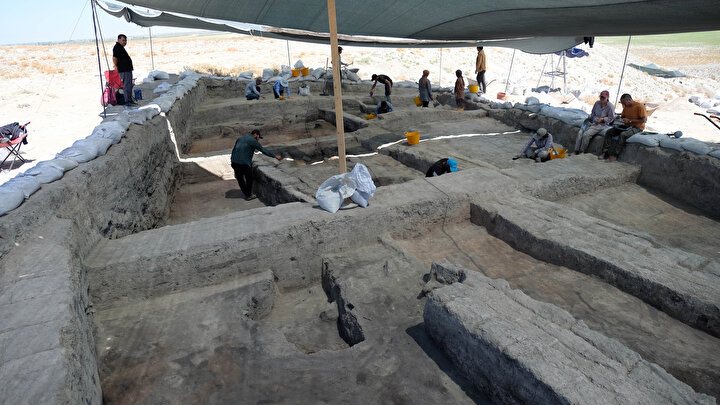
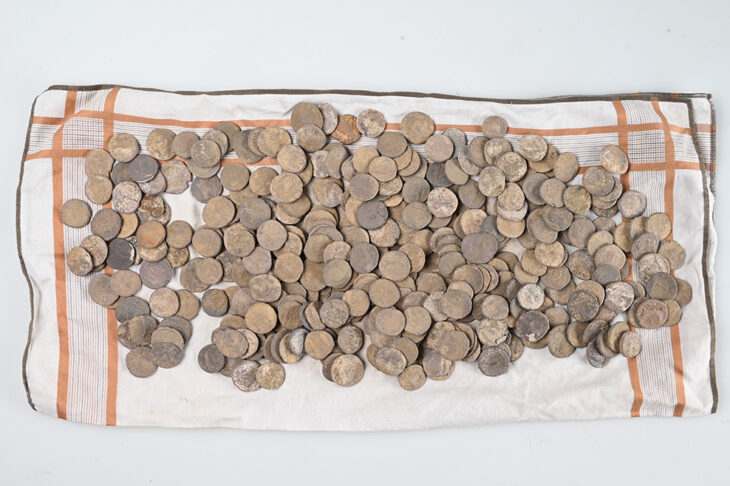
In early 2019, seven metal detectorists found a cache of 2,584 silver coins dating to the Norman Conquest that had lain in the ground for almost 1,000 years in a field in the Chew Valley in southern England. Now, the silver pennies have sold for $5.6 million—making them the most expensive treasure ever found in the United Kingdom.
Adam Staples and the other detectorists reported their “unprecedented” discovery to officials using the British Museum’s Portable Antiquities Scheme, a record of archaeological finds made by members of the public, according to a statement from the museum.
“It’s fantastic, unbelievable,” said Staples. “It has definitely changed my life. It was like holding history in your hand. And, obviously, the financial side of it is brilliant as well.”
The coins are a mix of Saxon and Norman currency, showing a turning point in English history and covering the transition from Saxon to Norman rule (between 1066 and 1068). Experts believe that the coins were likely buried for safekeeping during the turmoil of the conquest.
Michael Lewis, head of the Portable Antiquities Scheme, said in the statement that the find is “incredible.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Lewis said the coin hoard will help deepen understanding of the most famous date in English history: 1066, the year William, Duke of Normandy, defeated King Harold at the Battle of Hastings, replacing England’s Saxon monarchs with Norman French rulers.
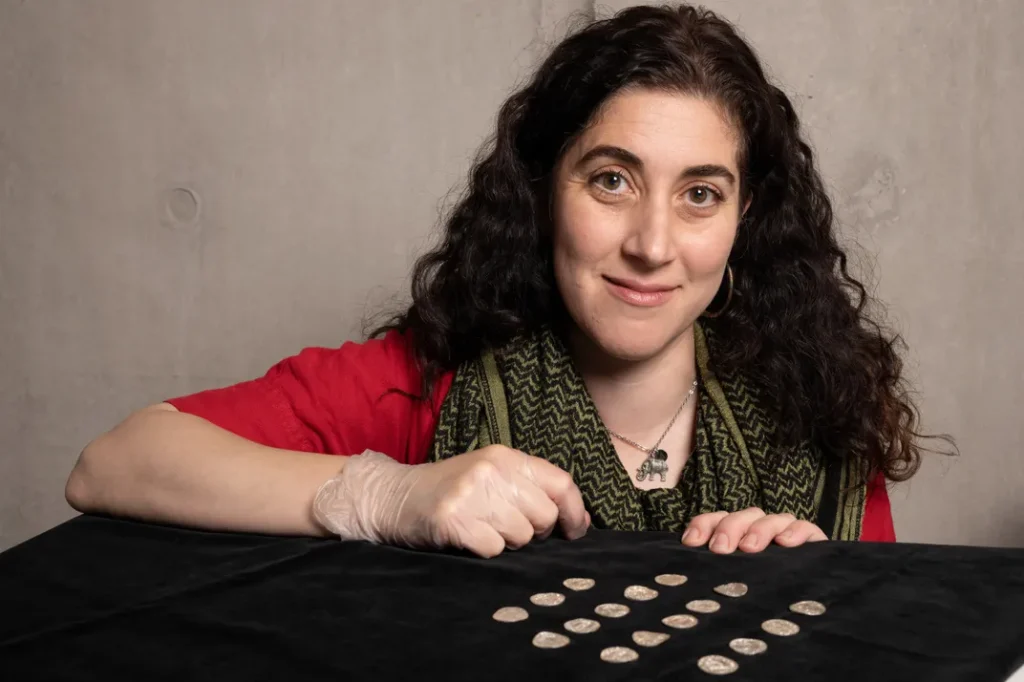

Though the invasion marked a historic schism, the coins in the hoard are remarkably similar whether they were minted before or after the conquest.
Just under half the coins depict Harold II of 1066, the last crowned Saxon king of England. Just over half feature William I (also known as William the Conqueror), the first Norman king. Other than the ruler they depict, the two types of coins are quite similar.
The AP notes that each has an emblem on one side and a picture of a king’s head in profile on the other, while Harold’s has the word “peace,” which is written as “pax,” and William’s has an ornate cross.
“The hoard symbolizes a pivotal moment in English history, and we are delighted to have made this acquisition so that it may be enjoyed by generations to come,” Sam Astill, chief executive of the South West Heritage Trust, said in the statement.
Named for the rural region in which it was discovered, the Chew Valley Hoard was purchased for the country using funds from the charitable division of the British National Lottery. It will have a permanent home at the Museum of Somerset in Taunton, 130 miles southwest of London, after being on exhibit at the British Museum and other museums across the United Kingdom.
Cover Image Credit: British Museum