A recently published study suggests that a woman buried in the upper reaches of the Tigris River in south-eastern Türkiye around 12,000 years ago may have been a shaman believed to have had a spiritual connection with wild animals.
According to researchers, the burial may represent one of the earliest known examples of its kind in an Anatolian Neolithic context.
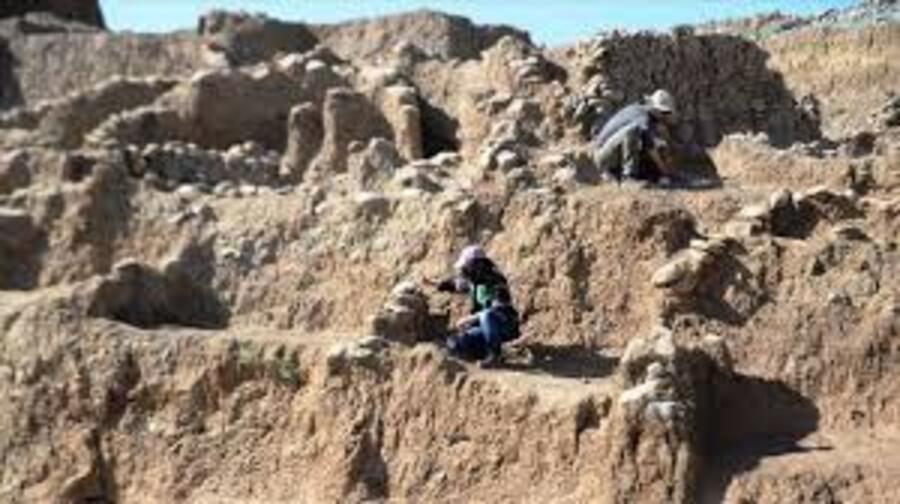
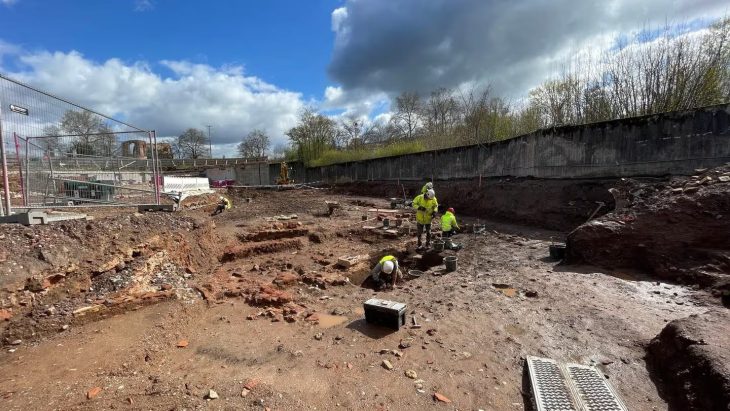
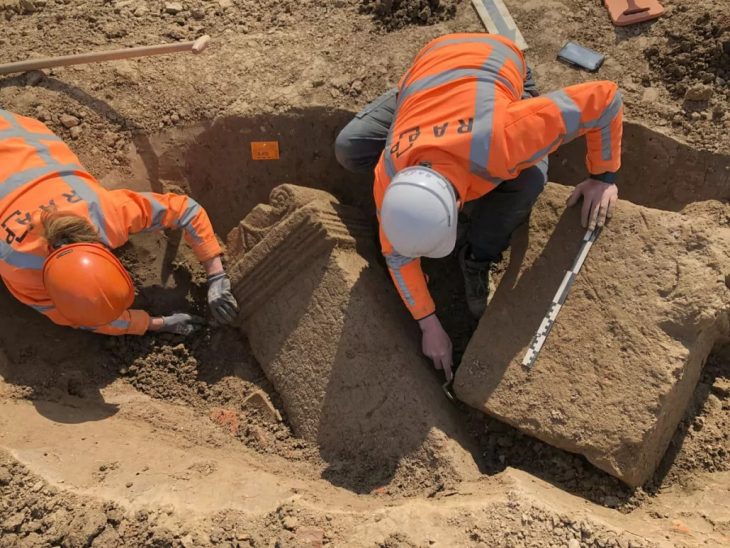
A new archaeological discovery at Çemka Höyük (meaning the “mound by the water”) in the Dargeçit district of Mardin province has revealed that a woman dating back to 12,000 years ago with unusual grave finds offers important clues about the spiritual and shamanic rituals of the period. These findings suggest that the woman may have been a shaman.
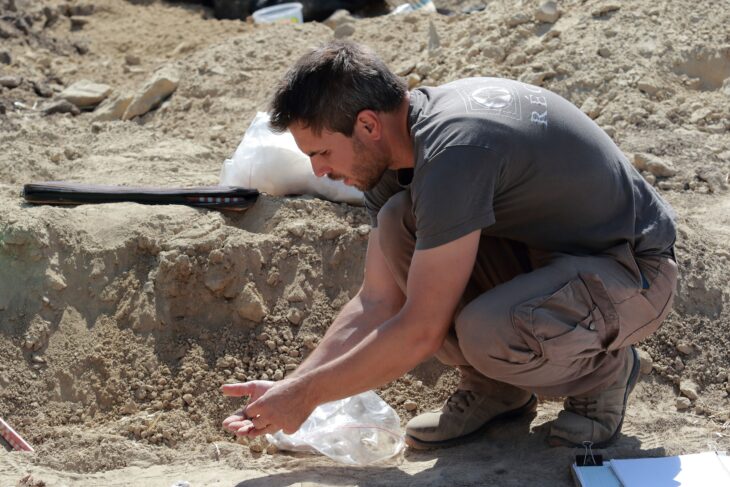
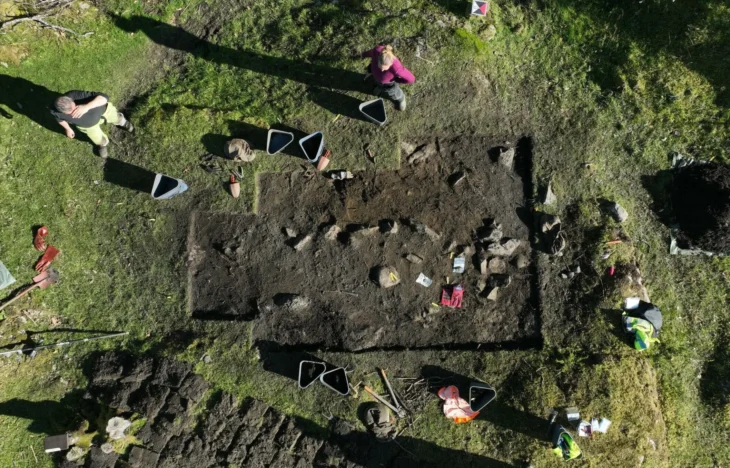
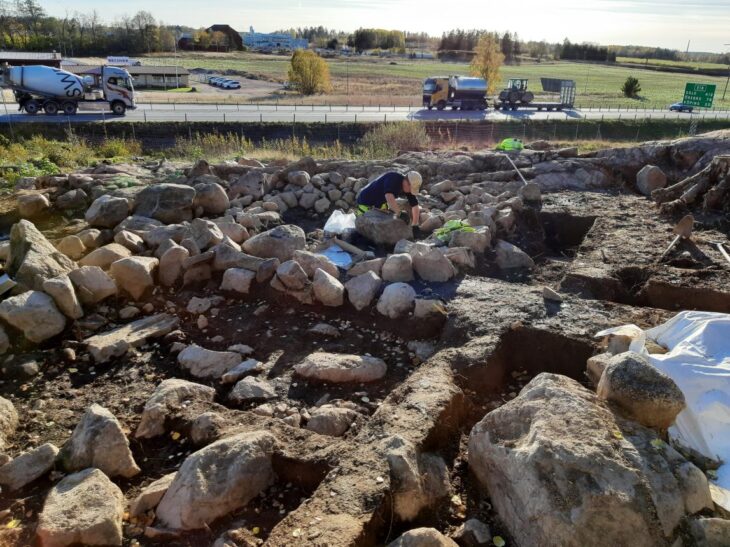
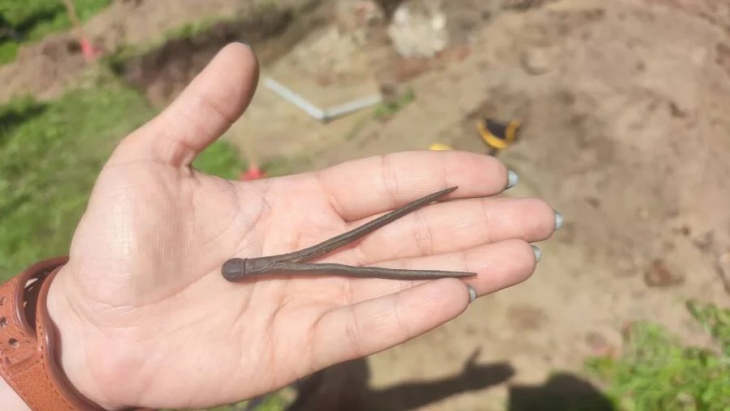
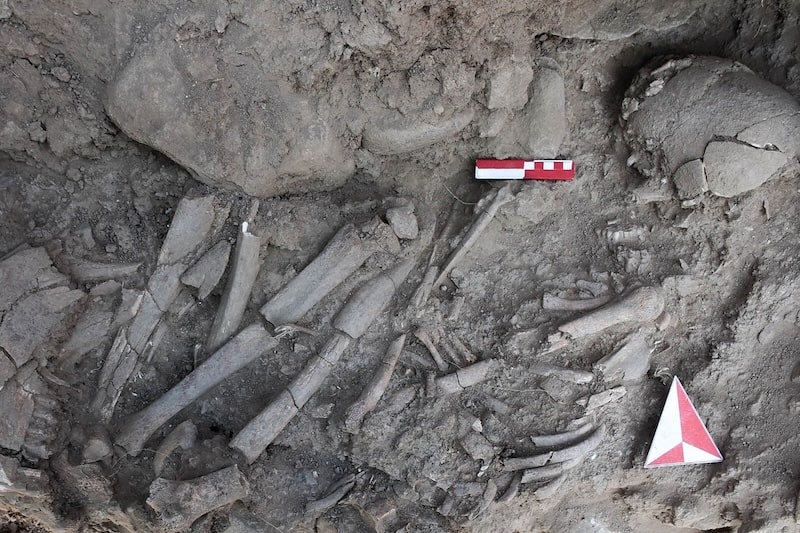
In the grave of the woman, who died at the age of about 25-30, the skull of an aurochs, partridge wings, marten legs, and the remains of sheep or goats were found. The woman was buried under the grave pit and the grave was sealed with a large limestone block. This is noteworthy as a practice contrary to the burial traditions of the period.
The woman, who died from natural causes was buried under the floor of a mudbrick building at Çemka Höyük, while another 14 people were buried under other nearby buildings. The burials took place during what archaeologists call the Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA) period, a transitional phase of human society between 10,000 and 8,800 BC, just before the development of agriculture. It was common during the PPNA to bury the dead under the floor of a house, but it was unusual to cover it with a limestone block.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
People at this time were still hunter-gatherers, like their Mesolithic ancestors, and pottery hadn’t yet been invented. However, it appears that they had already established settlements, at least for parts of the year, in locations such as Göbekli Tepe, an archaeological site in Turkey 150 miles west of Çemka Höyük, and Jericho in the Palestinian Territories.
The situation after the excavation of the tomb surprised the archaeologists even more: the skull of an aurochs (a primitive ox) was placed above the woman’s body, with its jaw separated and resting at her feet. Other animal bones appeared to be dispersed throughout the burial pit, including the remains of a sheep or goat, a partridge’s wing, and a marten’s leg.
The animals must have been wild because the woman was buried before farm animals were domesticated, according to lead study author and archaeologist Ergül Kodaş of Turkey’s Mardin Artuklu University. He points out that the fact that there are so many aurochs bones suggests the significance of wild cattle, which were already a major source of food even though they wouldn’t be domesticated for thousands of years.
This tomb provides important information about the ritual and social life of hunter-gatherer societies before the development of agriculture. British archaeologist Kathleen Kenyon has emphasized the complexity and sophisticated ritual practices of this period. This discovery at Çemka Höyük helps us better understand this complexity and spiritual beliefs.

Archaeologist Bill Finlayson of Oxford University notes that the term ‘shaman’ was coined in the 18th century to describe indigenous practices in Siberia, so their role in the Neolithic period may not be fully determined. However, when the female grave at Çemka Höyük is compared to similar shamanic burials, it is thought to be a spiritual leader.
Archaeologist Steve Mithen of the University of Reading says that social and environmental changes during the PPNA period may have increased the importance of people who could communicate with unseen forces. In this context, the discoveries at Çemka Höyük provide new insights into the development of ritual beliefs in early societies.
The 12,000-year-old female grave found at Çemka Höyük makes an important contribution to our understanding of shamanic practices and ritual beliefs in the Neolithic period.
This peculiar burial suggests that women were heavily involved in the ritual belief that archaeologists now believe played a significant role in the development of early societies. Archaeological findings allow for a deeper understanding of the spiritual and social structures of early societies.
The study was published in the journal L’Anthropologie.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anthro.2024.103277
Cover Photo: AA
















