Two sticks found in a cave in Australia show signs of processing that perfectly match Aboriginal sorcery and curse-making practices described in the 19th century. Approximately 11,000–12,000 years have been estimated for the sticks, making this the longest period of time that we have evidence for a cultural practice continuing anywhere in the world.
The discovery may represent the oldest known, culturally transmitted ritual—one that persisted among local people from the last ice age to colonial times, according to a study published today in Nature Human Behaviour.
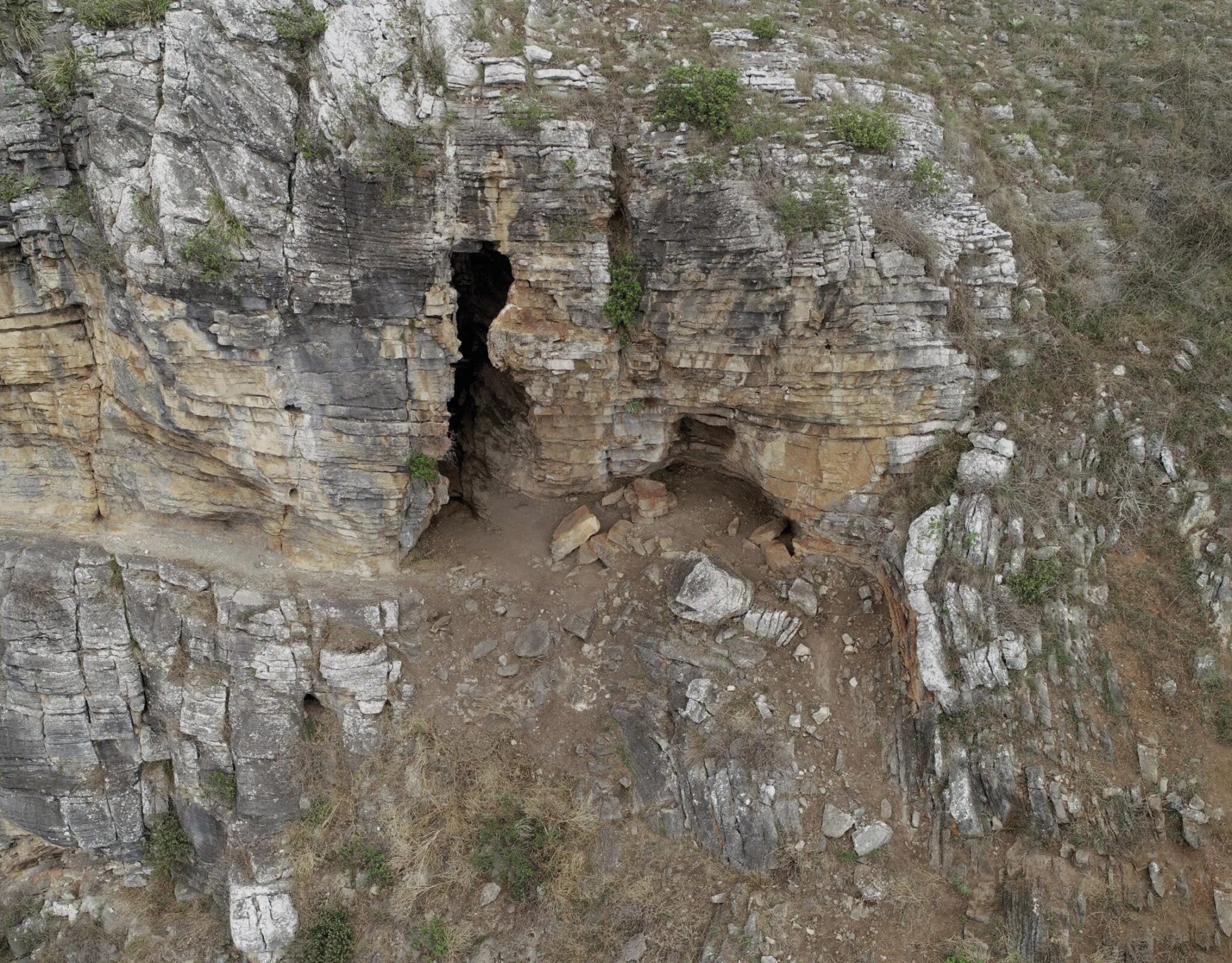
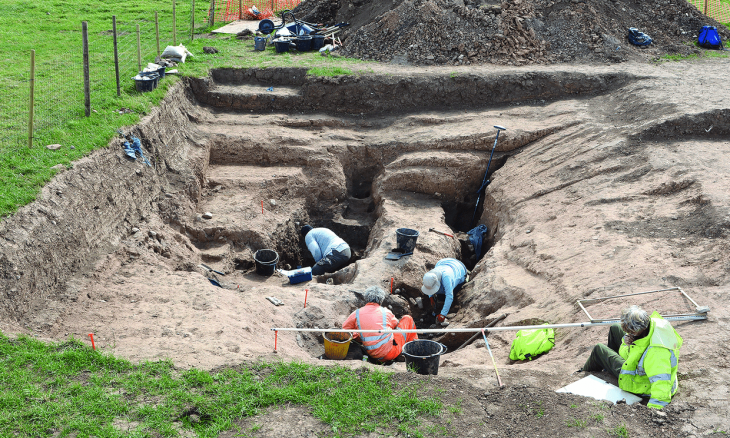
The finds were made in southeast Australia’s Cloggs Cave, a rich archeological site. Situated atop a limestone bluff with a view of the verdant Australian Alps foothills, the cavern descended approximately 12 meters below the surface, preserving an extensive legacy of Aboriginal culture. Human activity there dates back up to 25,000 years, according to earlier research.
Cloggs Cave, in Victoria’s Gippsland region, lies within the lands of the GunaiKurnai people. Representatives of the GunaiKurnai decided in 2009 that they wanted their history properly investigated and began working with anthropologists at Monash University.
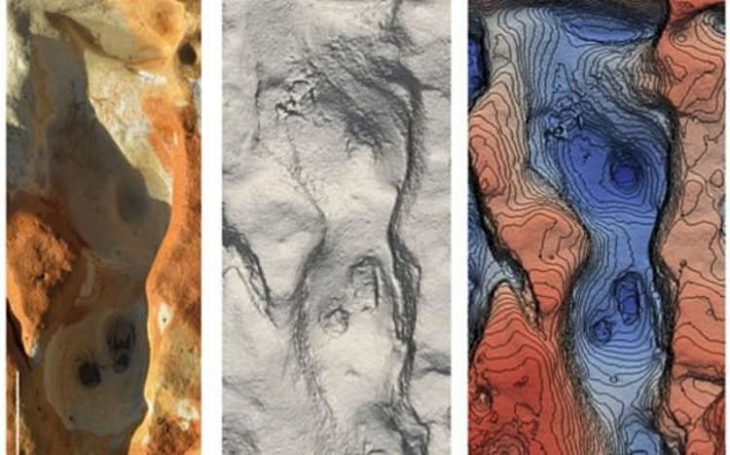
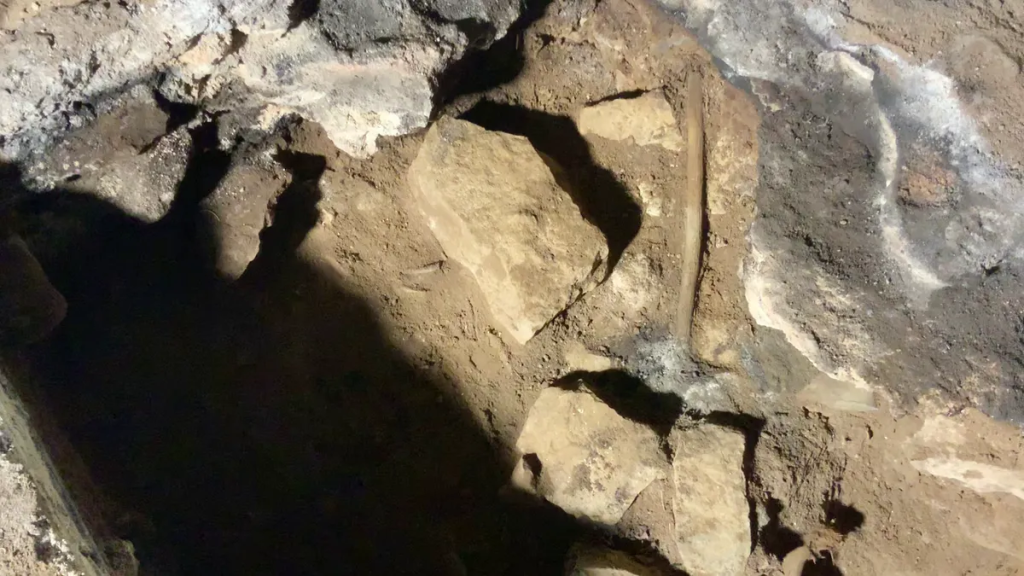
Around 6,000 years ago, a large portion of the cave turned into a sinkhole, which resulted in the juxtaposition of objects from wildly disparate ages. Professor Bruno David and associates decided to concentrate on a section of the cave that was not damaged in the collapse as a result. A 40-centimeter (16-inch) long, slightly burned Casuarina stick that was surrounded by limestone rocks emerged from a hand-sized fireplace. The stick was carbon-dated as approximately 12,000 years old, making it the oldest surviving wooden artifact found in Australia.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
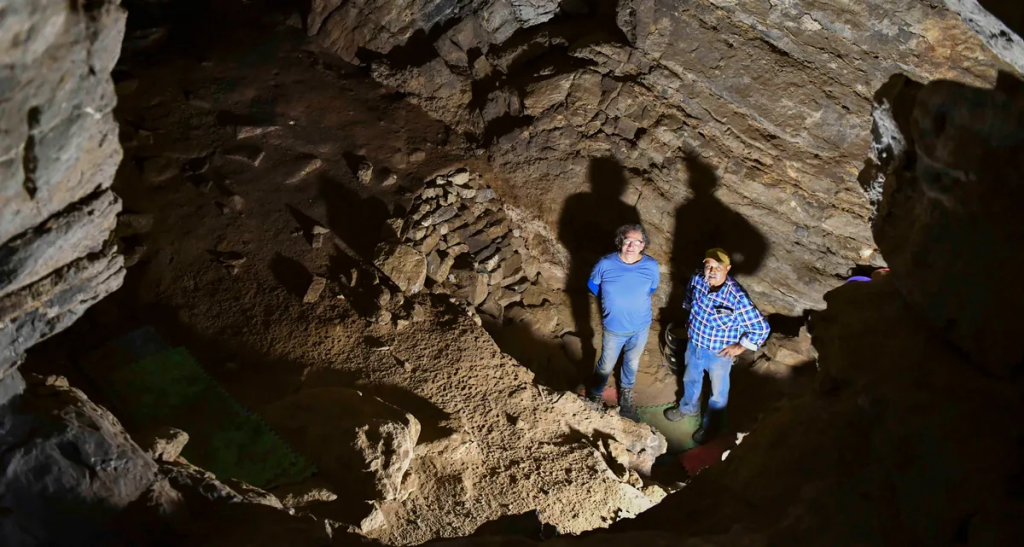

Anything wooden would rarely last that long, and the stick displayed even more remarkable qualities. Nothing like what is seen for something that was once part of a fire for warmth or food, the singeing at one end suggested it had been briefly placed in a cool fire. The stick carried lipids from human or animal fat, and twigs branching off had been carefully removed.
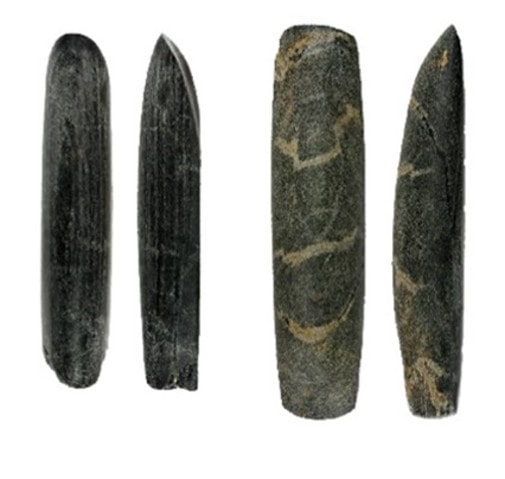
Further digging revealed a similar Casuarina stick, approximately a thousand years younger, but processed in the same way. Further research yielded a more comprehensive picture: Both sticks rested atop miniature fireplaces, which were little more than stone enclosures the size of palms filled with grass and twig ashes that seemed to have burned for a very short time. The sticks, the older one about 40 centimeters long and the younger one about half that length came from two species of Casuarina, flowering pine trees native to Australia with a long history of ceremonial use.
Surviving GunaiKurnai people had lost the cultural memory of what the sticks might have been used for. Researchers have therefore analyzed old ethnographic texts, which put everything in context as the evidence accumulated. In 1887, government geologist Alfred Howitt described rituals of the sorcerers who the local people called mulla-mullung. Other ethnographic texts associated Casuarina sticks with sorcery as well.
Howitt wrote in-depth accounts of mystical practices to cure the sick or curse enemies, drawing on both personal observations and accounts from Aboriginal people. One of these reports has a startling resemblance to the evidence found in the cave. A piece of clothing, a hairpiece, or a piece of food scrap was obtained by the sorcerer and attached to the end of a stick dipped in human or kangaroo fat in order to harm an enemy. The stick was then placed next to a small fire, and the mulla-mullung sung the name of the intended victim until the stick fell into the flames, enacting a fateful spell.

According to Bruno David, a lead author of the new paper and an archaeologist at Monash, the convergence of archaeological evidence and ethnographic accounts shows just how long Aboriginal traditions have survived.
“That’s 12,000 years of continuity, passing down knowledge from one generation to the next, of a cultural practice that has remained almost intact along 500 generations,” he says. “That’s absolutely remarkable.”
Rather than being a living space, the cave seems to have served mostly as a secluded den of ritual. In a series of discoveries spanning about 23,000 years, archaeologists have found ceremonial arrangements of stones, broken stalactites, a small grindstone, patches of calcite powder, and quartz crystals.
The discovery is published open access in Nature Human Behaviour.
Cover Photo: Jean-Jacques Delannoy 2019.