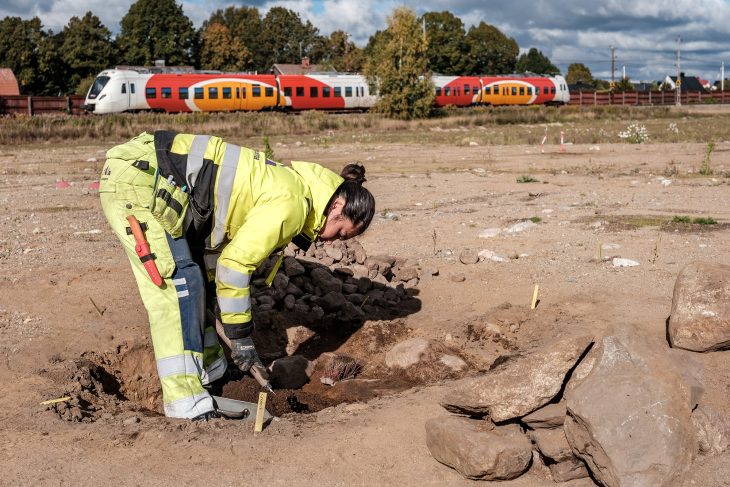
An approximately 2,700-year-old Pre-Roman necropolis was discovered by archaeologists during excavations conducted in advance of a planned electric power plant construction project, roughly 31 miles (50 kilometers) northeast of Naples, Italy.
The remarkable discovery of a pre-Roman necropolis in Amorosi (Benevento), in the Telesina Valley, is announced by the Superintendency of Archaeology, Fine Arts, and Landscape for the provinces of Caserta and Benevento. The necropolis is distinguished by a rich collection of burial goods.
While several layers of activity from prehistory to late antiquity were discovered during the site excavation, the best-preserved archaeological evidence concerns a sizable burial area that was observed between the end of the Iron Age and the advanced Orientalizing period (from the third quarter of the 8th century BCE to the second half/end of the 7th century BCE).
It’s interesting to note that the large cemetery was established and put to use around the same time that Rome was founded, which is said to have happened in 753 BC. However, the Iron Age society that built this burial site had no direct connection with Rome, which was situated 200 kilometers (about 120 miles) away.
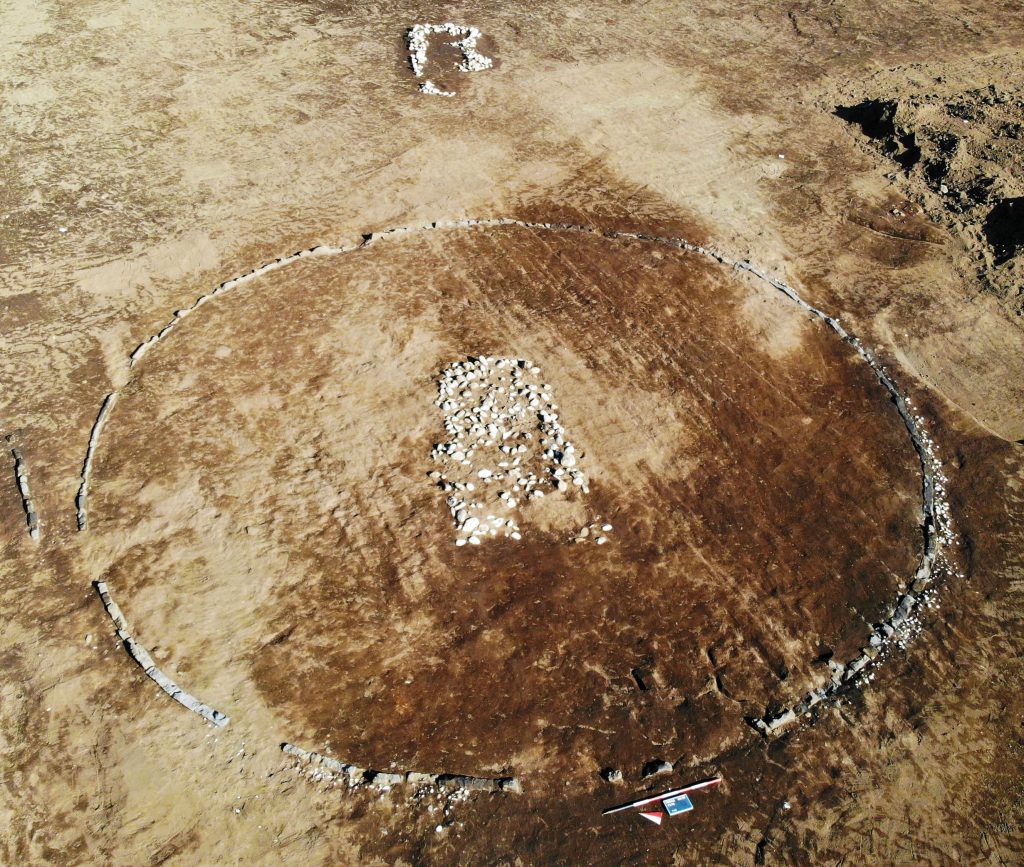

This large Iron Age cemetery is spread across 140,000 square feet, or 13,000 square meters, of open space. It was unearthed in the Telesina Valley, not far from the banks of the Volturno River, in an area that was just outside the village of Amorosi (Benevento).
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
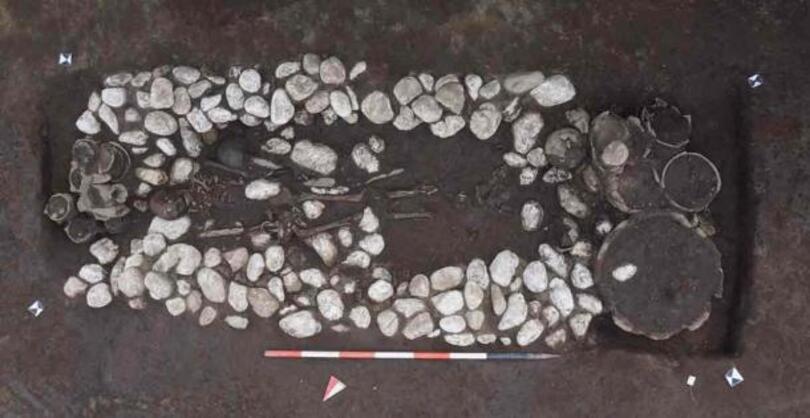
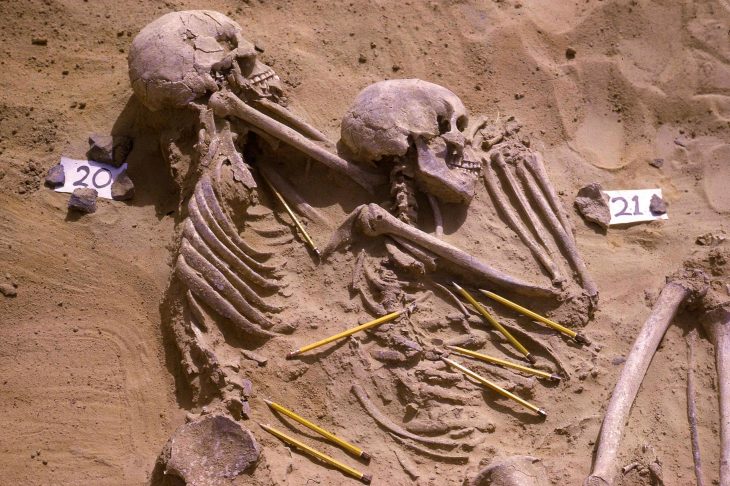
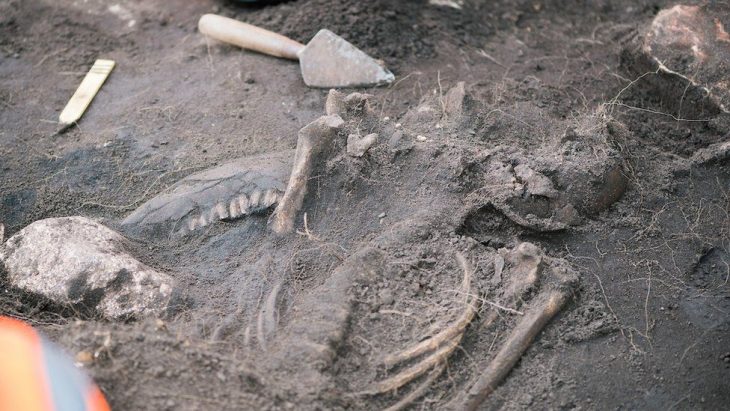
A total of 88 cinerary and inhumation tombs, complete with grave goods that identified the occupants as members of the pre-Samnite Culture of the Pit Tombs—a people who lived in the interior of what is now known as Campania—were unearthed by archaeologists.
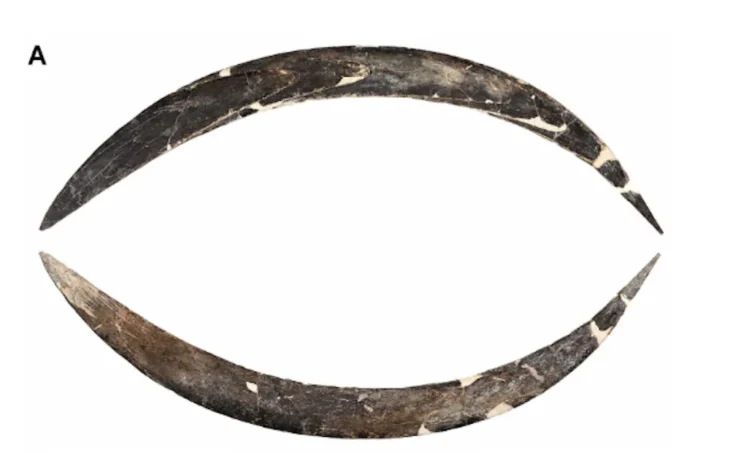
The grave goods evince distinct gender differences. The men’s tombs contained weapons, while the women’s tombs were richly adorned with bronze decorations such as fibulae, bracelets, pendants, amber elements, and worked bone pieces.
Both men and women were buried with pottery of various shapes and sizes, usually placed at the feet of the deceased. Some burials were notable for the exceptional objects, for example, a large, richly decorated bronze belt found in one grave.
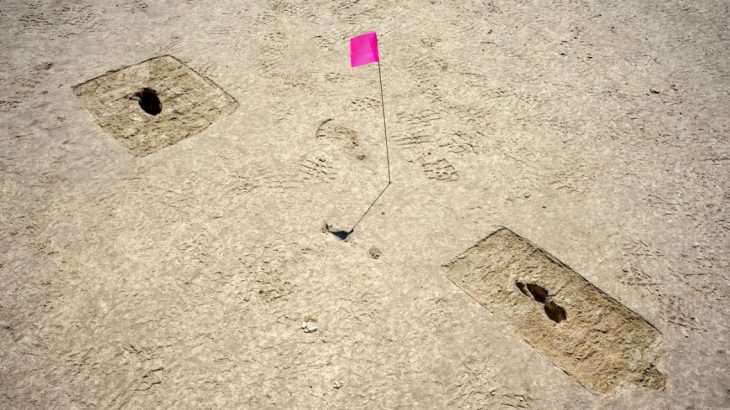
In addition to the pit tombs, two stand-out graves in the literal sense were large mound burials 50 feet (15 meters) in diameter that must have belonged to the highest-ranking elites of the community at that time.
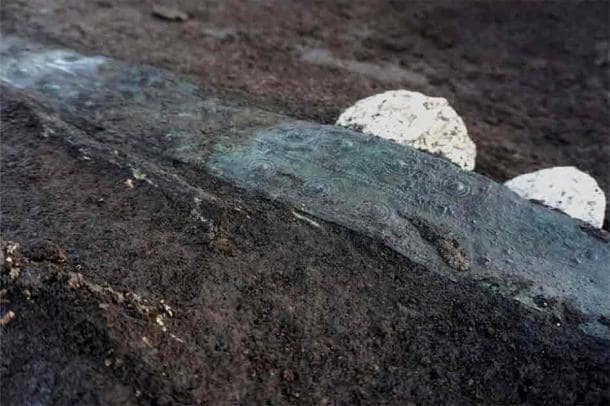

The Superintendency of Caserta, in partnership with Terna Spa and the Municipality of Amorosi, initiated a comprehensive research project during the excavation phase.
With the assistance of multiple experts, the project involved micro-excavations of the soil inside recovered containers, preliminary material restoration, anthropological analysis of the bone remains, and archaeobotanical analysis of the soil in a specially designated warehouse-laboratory in spaces provided by the Municipality of Amorosi.
Also, the municipality of Amorosi has begun to plan a museum to exhibit the archaeological treasures found in the excavation (and future ones) in the hope of attracting cultural heritage tourism.
Cover Photo: One of the burials at the site. Superintendency of Archaeology, Fine Arts and Landscape