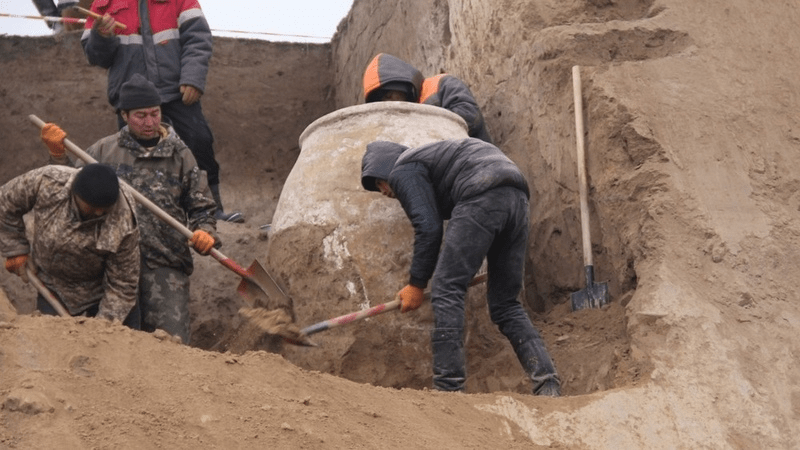
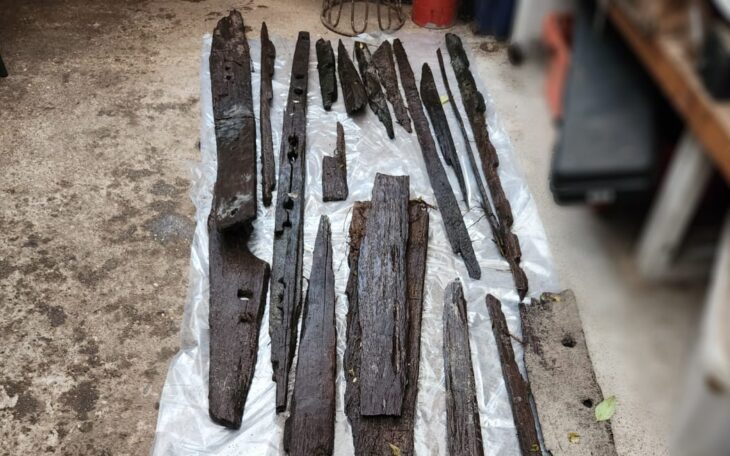
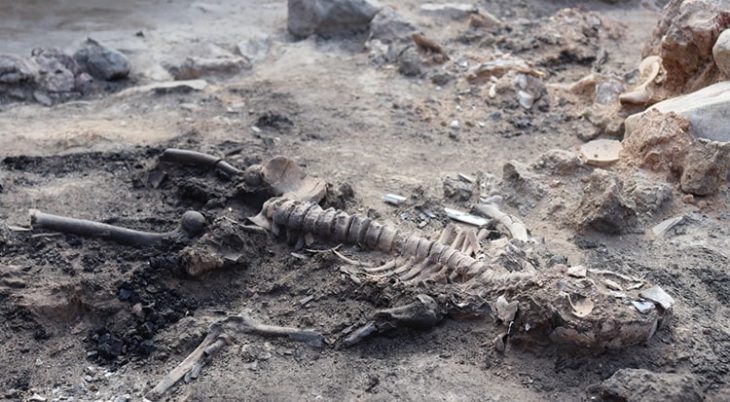
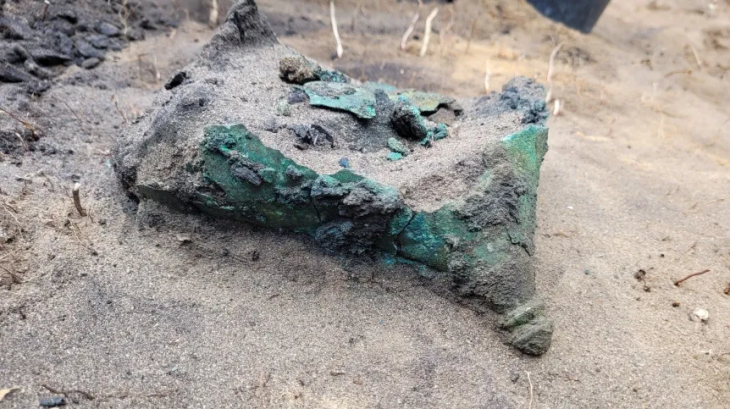
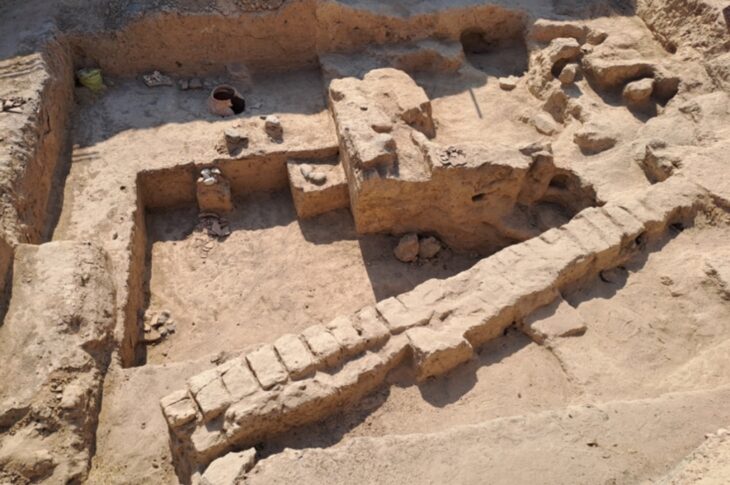
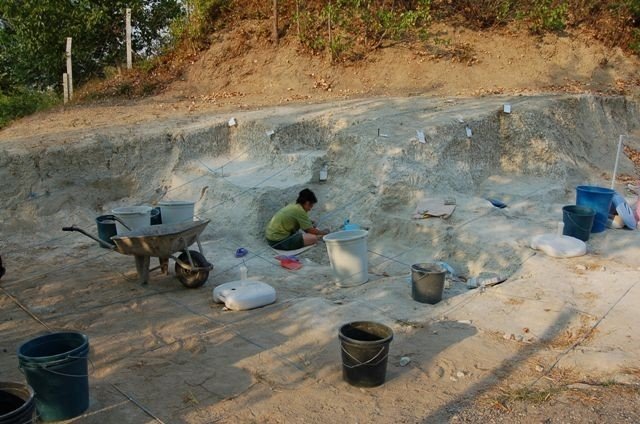
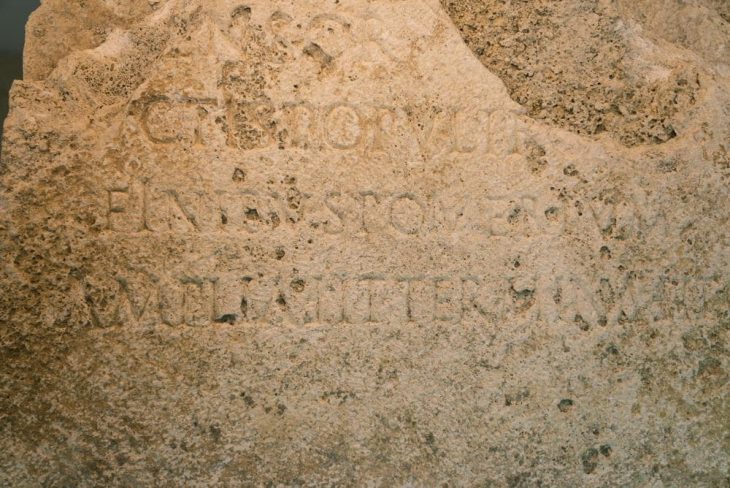During recent archaeological excavations in the town of Uzgen in the Osh province of Kyrgyzstan, a 1.75-meter-high clay vessel known as a ‘hum’ was unearthed.
The ancient settlement of Uzgen is the center of the oasis rich of monuments of settled and nomadic people, dating in a wide chronological range. It belongs to a zone of early contacts on the Silk Road, being the most eastern city center of Davan, as the city of Ju-Chen known on Chinese sources is traditionally localized here in the context of military expeditions of 104-99 BC. The main period of development is IV-I centuries BC.
However, the town flourished under the rule of the Qarakhanid state in the 10th century AD. It was one of the capitals of the Karakhanids, who called it Mavarannahr and left three well-preserved mausolea.
This amazing discovery was announced by Turarbek Abdyrahmanov, an archaeologist from the Kyrgyz Republic’s National Academy of Sciences.
The excavations, led by Mars Boranbaev, had begun 10 days ago when on March 1 a ‘Hum’ was discovered 2.5 meters below ground level. The artifact, believed to have been built between the 7th and 4th centuries BC, was carefully removed unharmed and transferred to the Uzgen Museum of Architecture and Archaeology.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“After meticulous cleaning, the ‘hum’ now awaits further examination as part of our ongoing research endeavors,” Abdyrahmanov elaborated. “Already, fragments of clay pottery indicative of the Shoro-Bashat culture have been unearthed, signaling the rich historical tapestry of the region.”
By the end of the Bronze and Early Iron Ages, began to form, Shorobashat culture in the Ferghana Valley. The era of the Late Bronze and the Early Iron Age in the Fergana Valley parallel there were nomadic (Kairakkum and Eilatan, 11th-3rd century BC) and sedental (Chust and Shorobashat, 14th-1st centuries BC) cultures. Shorobashat culture is a sedentary agricultural culture.
The excavation site is located close to the Kyzyl-Oktiabr area, where plans are in the works for a bypass road. It has great historical potential. Abdyrahmanov noted that increased archaeological research has been conducted in the hopes of finding more ancient artifacts because of the busy activity around the old city.
The ‘hum,’ towering at 1.75 meters in height and spanning 1.30 meters in width, serves as a testament to the ancient civilizations that once thrived in these lands.