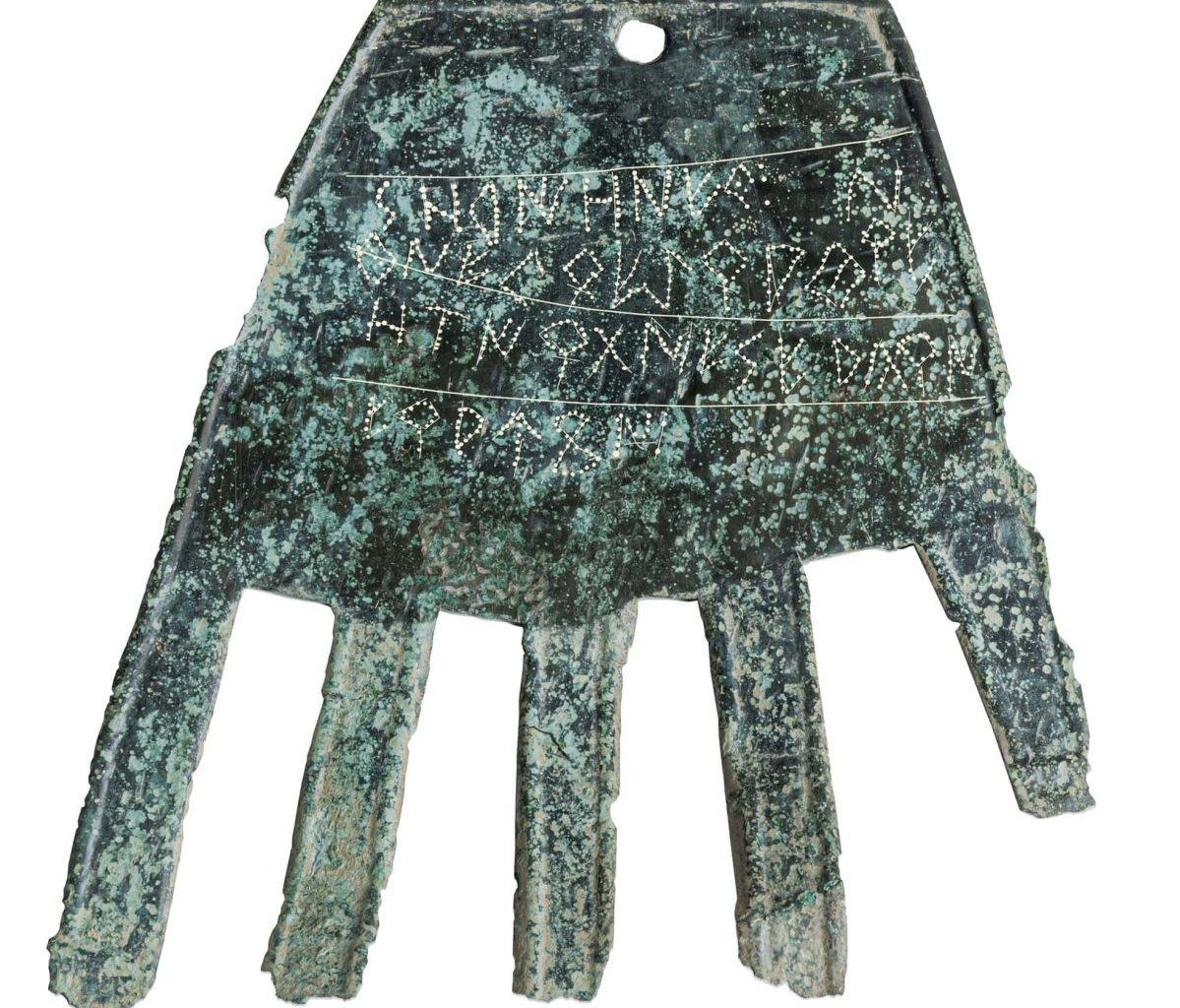
Researchers have discovered rare evidence of an enigmatic ancient language on a 2,000-year-old bronze hand. The inscription on the hand is the oldest and longest known example of Vasconic.
Its detailed linguistic analysis suggests that the script represents a graphic subsystem of Palaeohispanic that has roots in the modern Basque language and is the first example of Vasconic epigraphy.
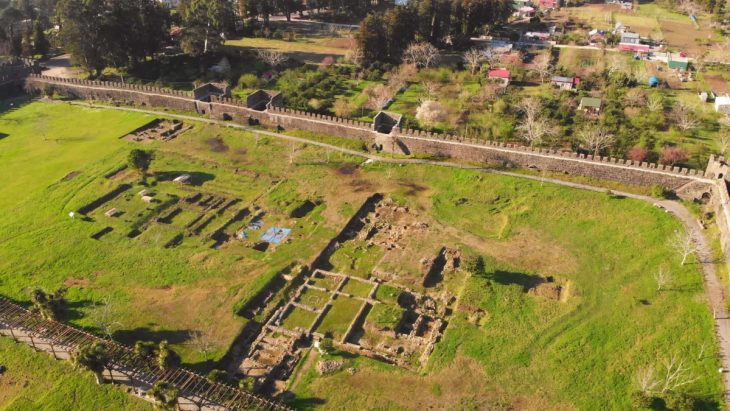
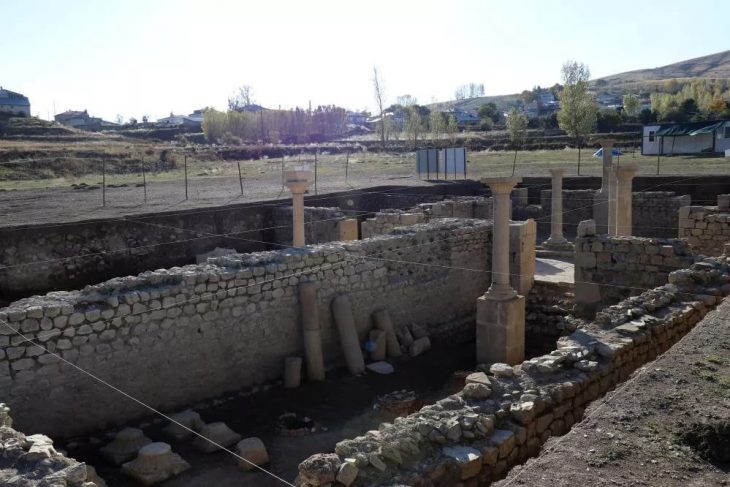
Archaeologists discovered the bronze hand in 2021 at the Irulegi archaeological site near the Aranguren Valley in Spain’s northern Navarre region, about 8 km from modern-day Pamplona.
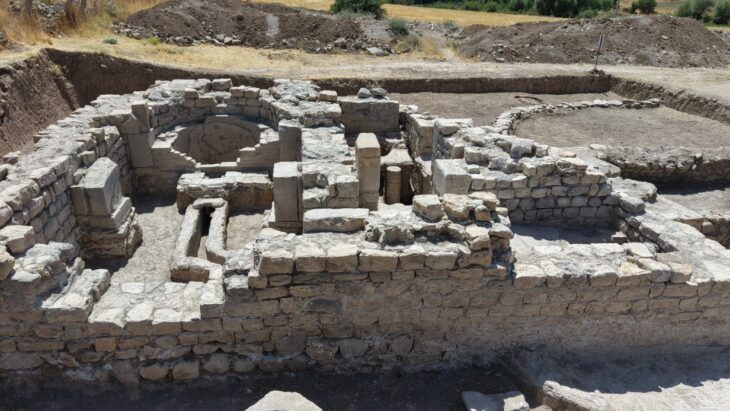
Researchers got to work excavating the hillock, on which the walls of a medieval castle also stand. At the foot of the fortification, the remains of a 2,000-year-old settlement were uncovered.
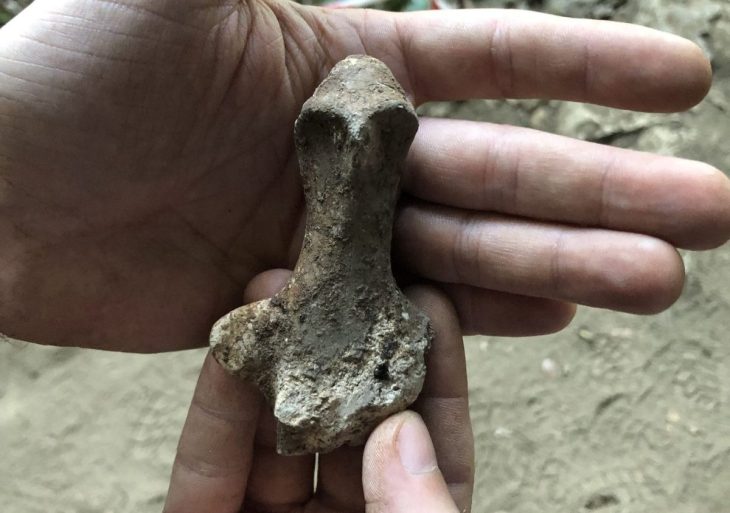
On the threshold of one of the homes destroyed during the Sertorian Wars, workers found a bronze slab in 2021 that was roughly 14.5 centimeters (5.7 in) long and shaped like a hand. Laboratory analysis revealed that strange inscriptions were engraved on its fingers, in the form of 40 symbols distributed across four lines. It consisted of a sheet of bronze, cut to represent the shape of a life-sized right hand.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The text inscribed on this artifact, which was found at the entrance of a domestic building, is interpreted as apotropaic, a token entreating good fortune.
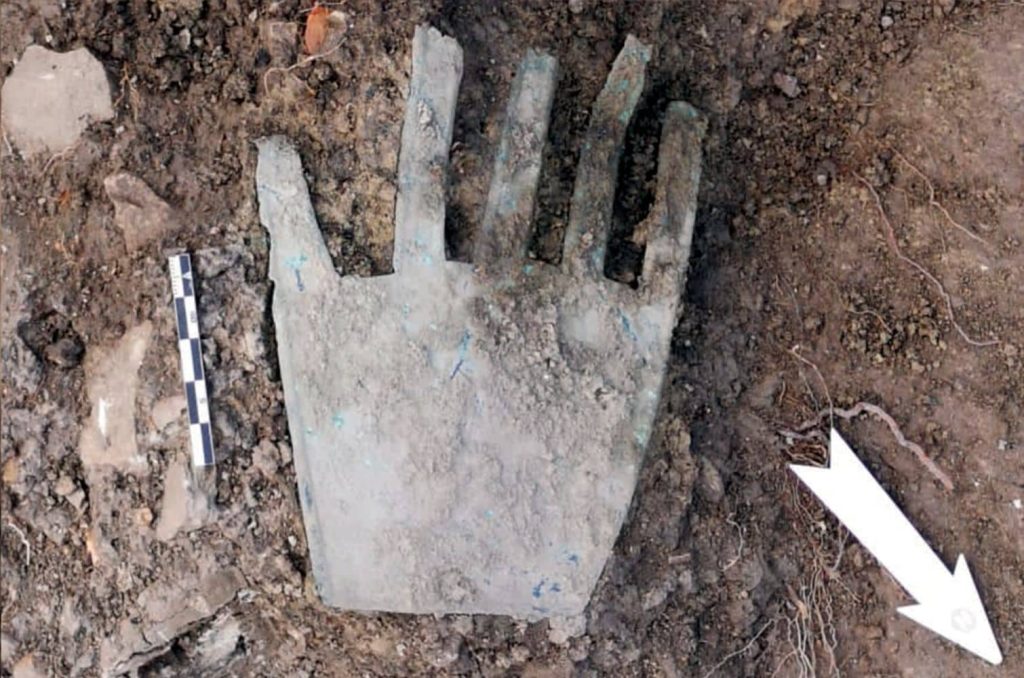

Researchers analyzed the artifact, northern Spain, for a newly published study in the journal Antiquity—and also suggested the words written on it could be linked to modern-day Basque. This connection is supported by the identification of the Basque term for ‘good fortune’ on the artifact.
Vasconic was spoken by the Vascones, a pre-Roman people who lived in the western Pyrenees, primarily in what is now Navarre, as well as parts of the Spanish regions of La Rioja and Aragon.
Due to the comparatively small number of pre-Roman writing samples found in the areas the Vascones once called home, it was previously believed that these people lived in a preliterate society. However, the most recent study’s findings support a developing body of evidence suggesting that the ancient Vascones were at least somewhat familiar with and used writing, undermining this theory.
One word is sufficiently similar to Basque to be considered a “cognate,” a term that suggests a possible connection, even though it is the only lengthy Vasconic text that has been found to date.
“The discovery of the Hand of Irulegi has opened a new horizon to unravel the history behind the most enigmatic language still alive in Europe: the Basque language,” Mikel Edeso Egia from the Aranzadi Science Society—a non-profit organization based in Spain’s Basque region that coordinated the research team—said in a press release.
“The Irulegi hand must be considered as a well-integrated element within the cultural context of the settlement,” the study’s lead author, Mattin Aiestaran with the University of the Basque Country, said. “The hand would have had a ritual function, either to attract good luck or as an offering to an indigenous god or goddess of fortune.” However, “the lack of other comparative texts makes it difficult to prove a direct link between the Vasconic language spoken at Irulegi and the present-day Basque language.”