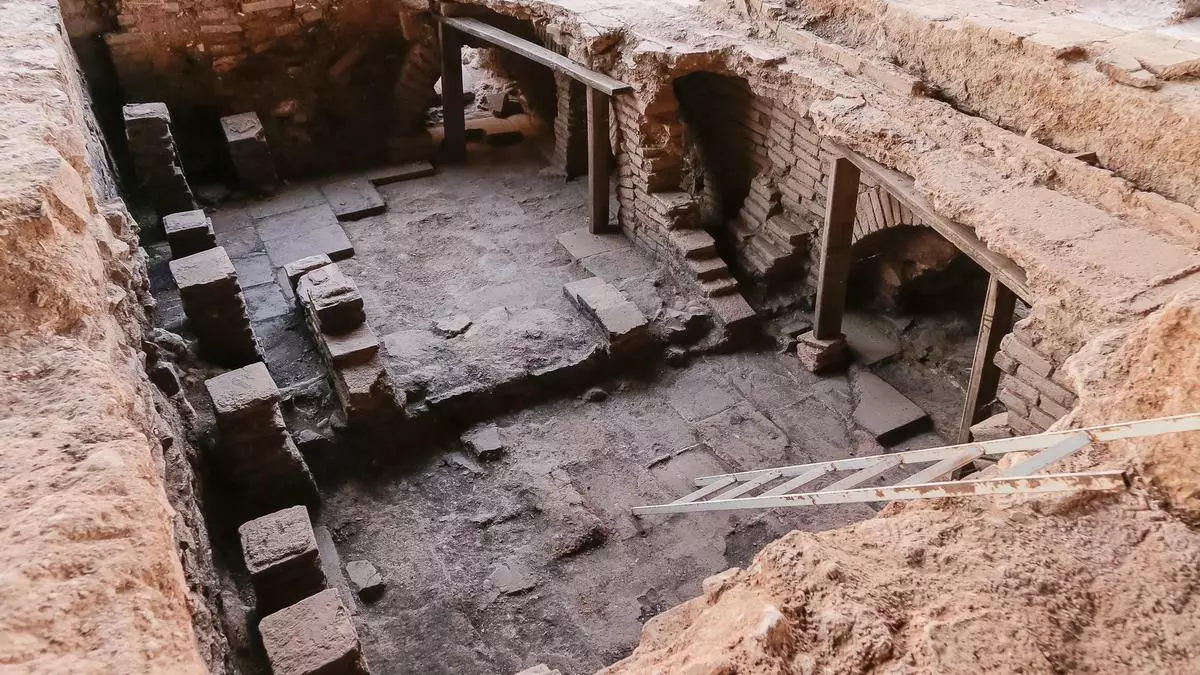
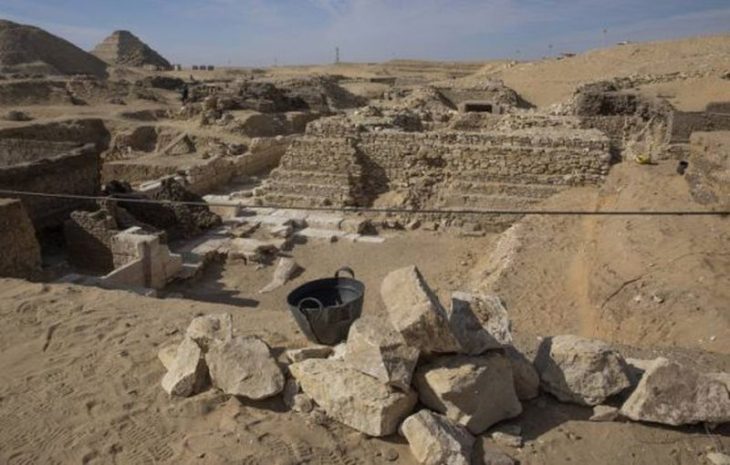
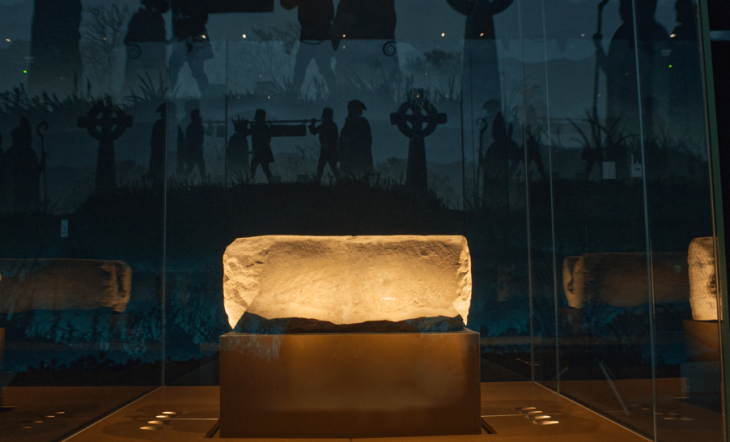
In Mérida, Spain, archaeologists have discovered a “massive” Roman bathing site in “excellent” condition. The discovery was found in the city of Mérida while excavating inside the famous 2,000-year-old Amphitheater House (Casa del Anfiteatro), built by the Romans in a colony they named Augusta Emerita.
Augustus founded Augusta Emerita, also known as Emerita Augusta, in 25 BC to resettle Emeriti soldiers from the veteran legions of the Cantabrian Wars. The city grew to become one of Hispania’s largest Roman centers and the capital of the province of Lusitania, covering an area of more than 20,000 square kilometers.
“The city was built as a model of Rome.”
“It is an excellent example of a provincial Roman capital during and after the Empire,” reads the UNESCO description.
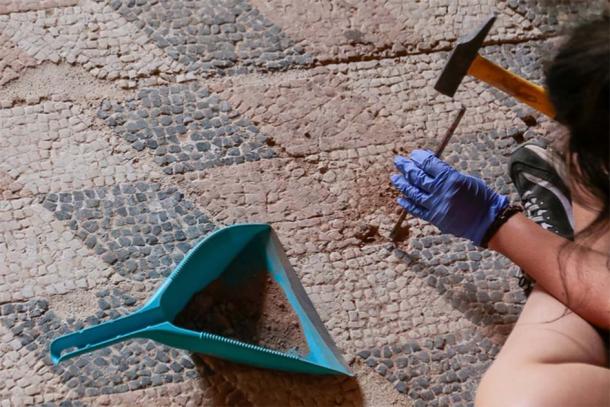

“Fantastic baths of an enormous size have been found for what is a standard Roman house,” stated Felix Palma, the director of the Consortium of the Monumental City of Mérida archaeological project, in a statement given to the Spanish publication El Diario. Palma said the baths would have belonged to a private residence or perhaps a set of private residences, although they would have been widely shared and therefore could still be labeled as “public” baths.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Anna Maria Bejarano, the Consortium archaeologist leading excavations at the site, said the baths are “perfectly preserved”—complete with decorations such as marble slabs, moldings on cornices, paintings on walls, and all of their underground structures.
The pool typically associated with these kinds of sites has not yet been uncovered in the excavation area, but archaeologists are not discounting the possibility that one will.
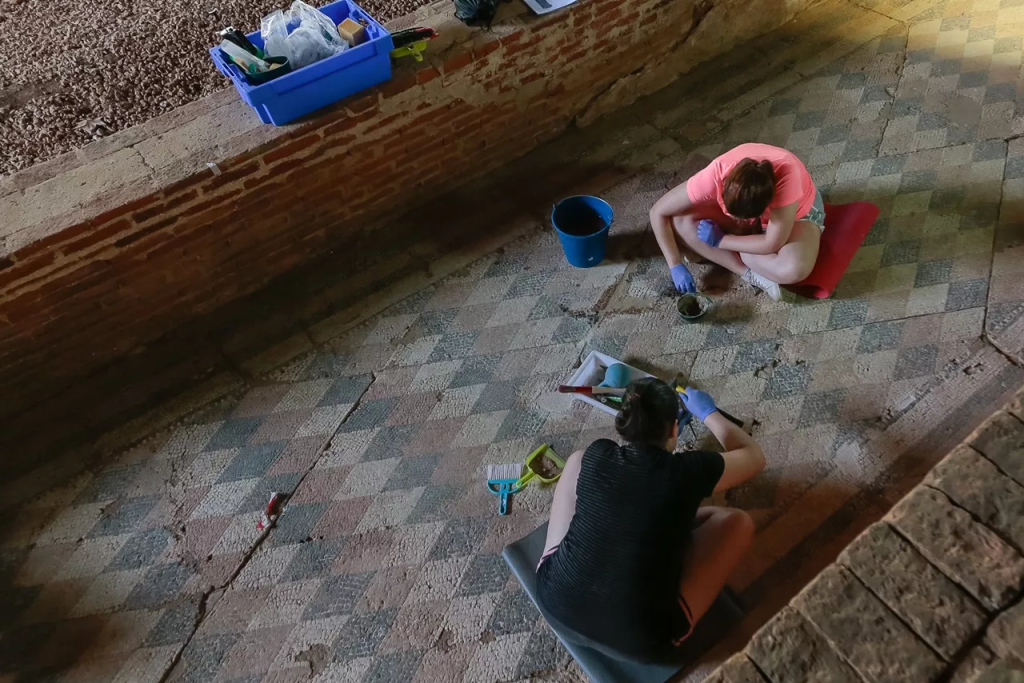

In an area first investigated during the 1940s at the Casa del Amphitheatre, a sizable domus constructed around a porticoed, trapezoidal courtyard with a garden in the middle, excavations carried out by the Emeritense Consortium and students from the University of Granada, the remains of a bathing complex were discovered.
According to Ana María Bejarano, an archaeologist from the Consortium responsible for the excavations, the team uncovered preserved public baths in the excavation area, suggesting that the Casa del Amphitheatre was not a typical domus, but a public complex linked to the shows of the Meritense amphitheater.
Cover Photo: Baths in the Casa del Amphitheatre, in Mérida Photo: Mérida City Council