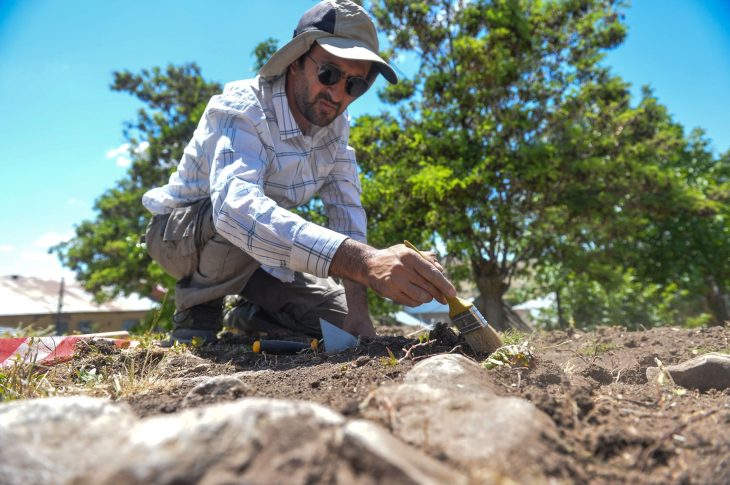
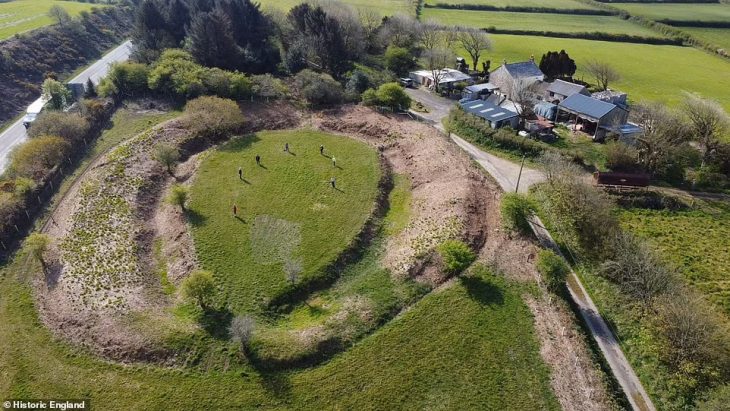
Archaeologists report discovering an “incredibly rare” and featured preserved floors and walls Roman mausoleum near London Bridge Station, UK.
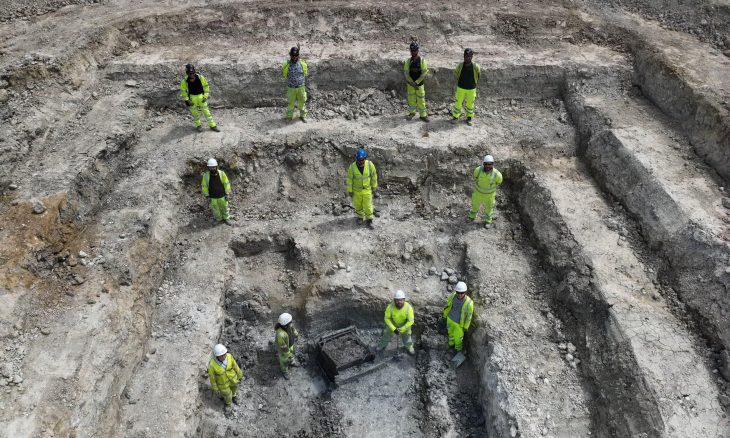
Archaeologists discovered big Roman mosaics at the same location last year, which led scientists to believe something much larger might be buried beneath the surface. Excavations conducted by MOLA archaeologists on behalf of Landsec, Transport for London (TfL), which owns the site, and Southwark Council have yielded extraordinary results.
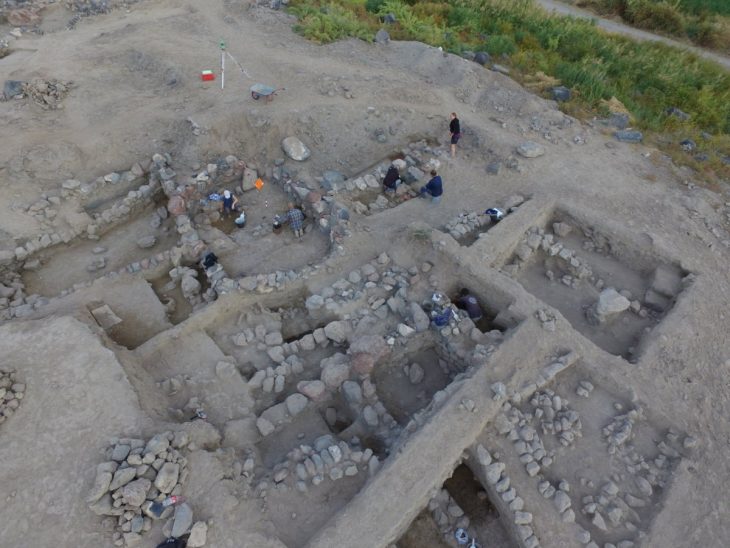
Archaeologists say they have unearthed the remains of a Roman mausoleum “with an astonishing level of preservation.”
The Museum of London Archaeology(MOLA) believes the quality of preservation makes it the most intact Roman mausoleum ever to be discovered in Britain.
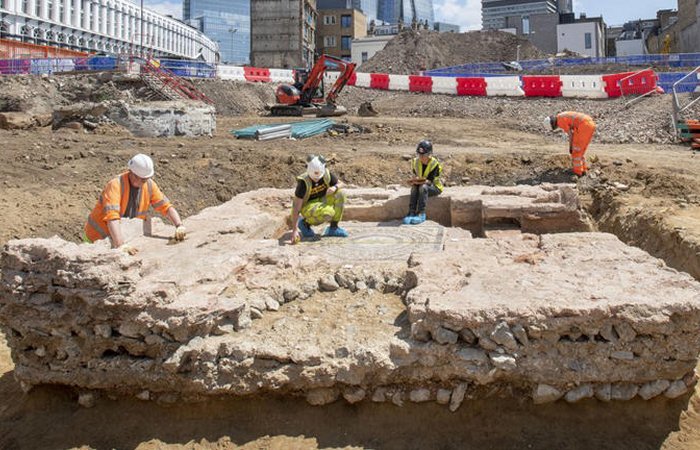

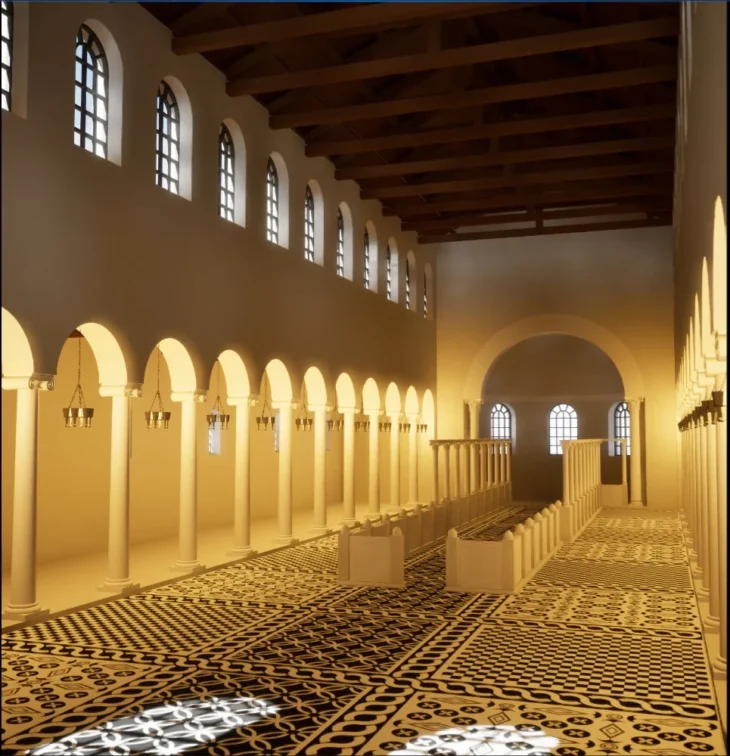
Scientists have “unearthed the walls, entrance steps and interior floors of the tomb. The mosaic at the center is surrounded by a raised platform on which the burials were placed.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
There’s evidence of a second mosaic directly beneath the first, indicating that it was raised during its lifetime. The two mosaics are similar, with a central flower surrounded by concentric circles.
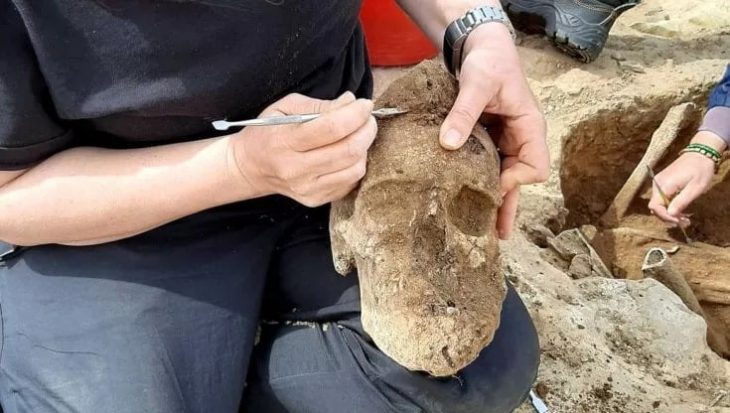
The tomb itself was a two-storey building likely to have been used by a wealthy Roman family. It doesn’t now contain any coffins or burial remains, with MOLA suggesting that these were likely removed in medieval times. However, the surrounding area is rich in traces of its ancient inhabitants, with over 80 burial sites and artifacts such as pottery, jewelry, coins, and glass beads.

Antonietta Lerz, senior archaeologist at MOLA, says the site is a “microcosm for the changing fortunes of Roman London” and provides “a fascinating window” into the life of its settlers.
Antonietta Lerz, senior archaeologist at MOLA, says the site is a “microcosm for the changing fortunes of Roman London” and provides “a fascinating window” into the life of its settlers.
Archaeologists from MOLA hope to pinpoint the age of the mausoleum and have provided a three-dimensional model of the site. There are plans for the future public display of the mausoleum.
Cover Photo: MOLA