An 8,500-year-old obsidian mirror has been unearthed at Canhasan in central Türkiye, revealing new insights into early Neolithic craftsmanship and urban planning.
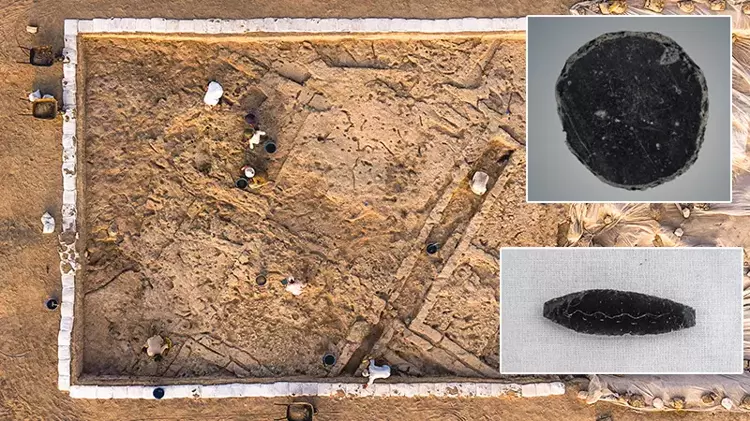
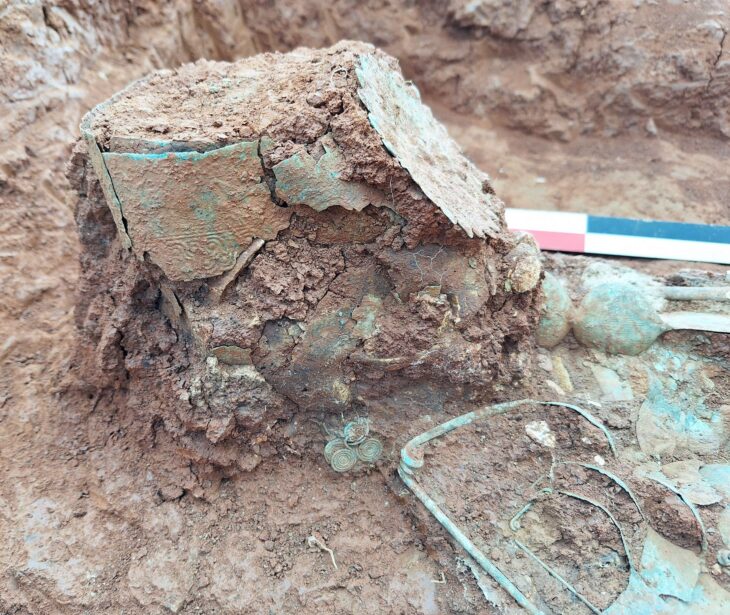
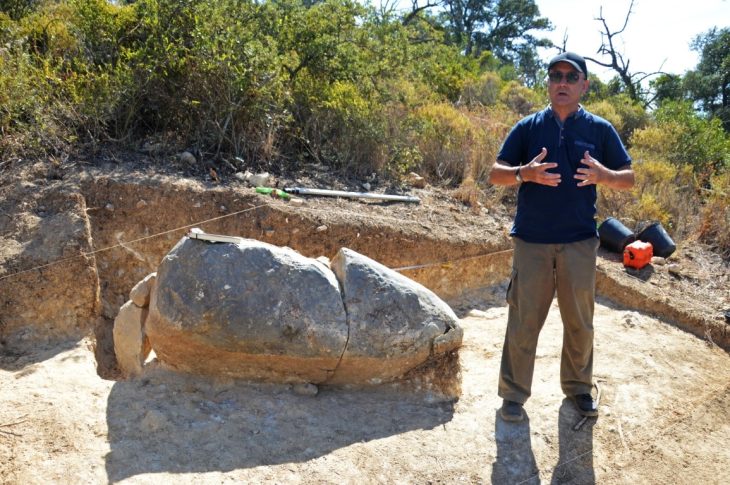
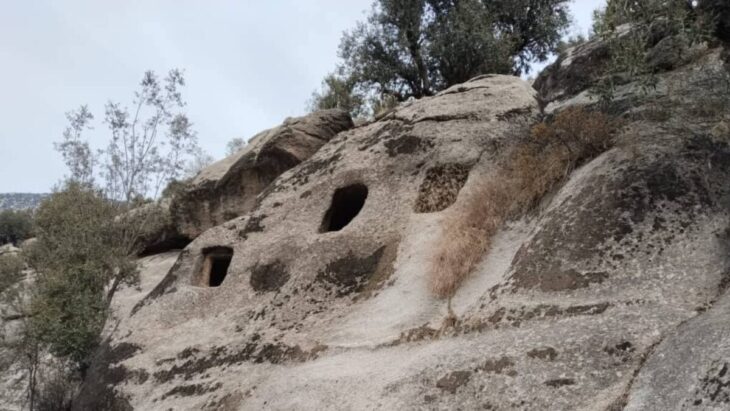
Archaeologists in central Türkiye have announced a remarkable discovery at Canhasan—one of the oldest known settlement areas in Anatolia, home to what is believed to be a 10,000-year-old street system. Recent excavations have revealed an 8,500-year-old obsidian mirror and a collection of finely incised obsidian tools, offering rare insight into early Neolithic craftsmanship and symbolic culture.
The findings were uncovered during the second phase of excavations at the Canhasan mounds in Karaman’s Alaçatı village, carried out under the Turkish Ministry of Culture and Tourism’s Heritage for the Future Project. Led by Associate Professor Adnan Baysal from Ankara University, the research team has been exploring the region’s deep-rooted Neolithic heritage—one that predates or parallels iconic sites like Çatalhöyük.
An Early Glimpse of Urban Planning
One of the most striking outcomes of this excavation season is the identification of the earliest known street layout from the Pre-Pottery Neolithic period. This discovery suggests that Canhasan may have played a pioneering role in the emergence of planned settlement structures—perhaps one of the earliest examples of an urban mindset in human history.
“This street concept from the aceramic Neolithic points to the very first steps of urbanization in Anatolia,” explains Baysal. “It suggests an organized community structure that valued accessibility, shared spaces, and architectural planning.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
These discoveries align Canhasan with other early Neolithic centers like Aşıklı Höyük, Boncuklu Höyük, and Pınarbaşı, which collectively map out the cultural transformation that climaxed at Çatalhöyük, one of the world’s best-preserved Neolithic megasites.
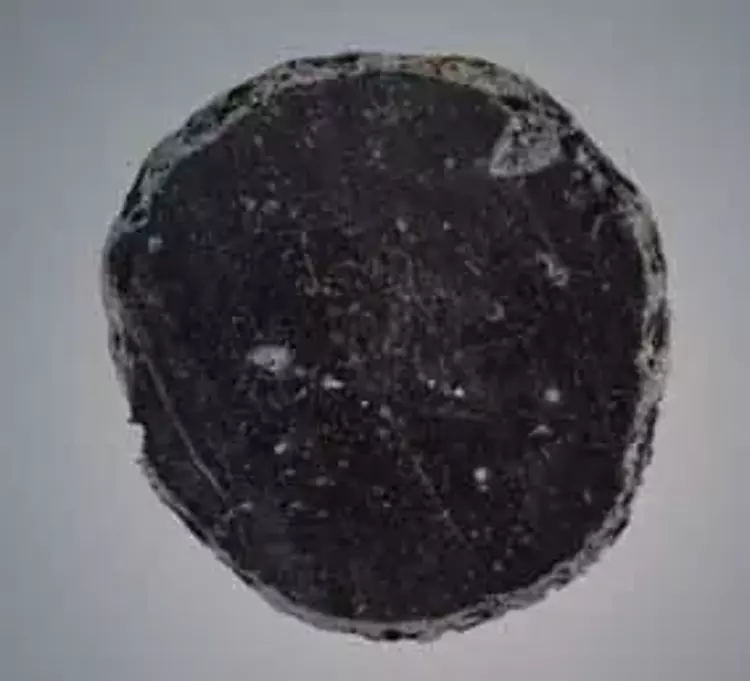

A Masterpiece in Obsidian: The 8,500-Year-Old Mirror
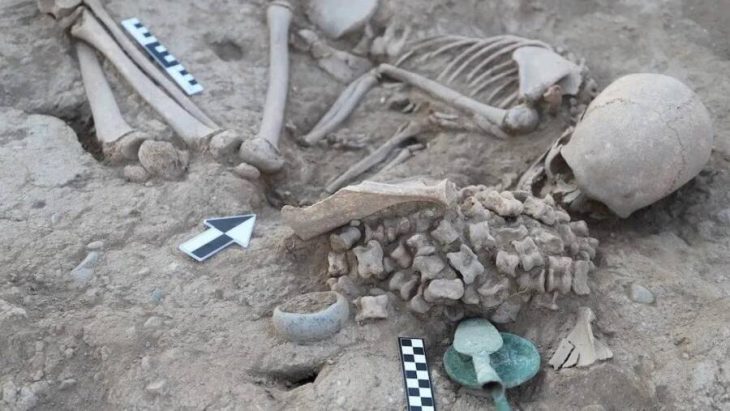
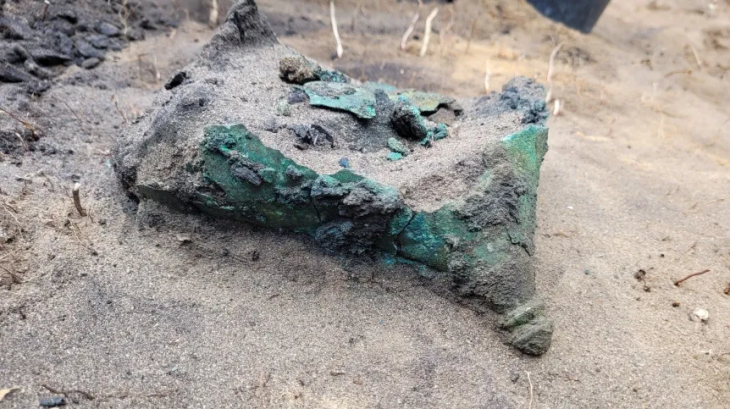
Among the season’s standout discoveries is a highly polished obsidian mirror, dated to approximately 6,500 BCE. Mirrors made from volcanic glass are rare, technically demanding to produce, and culturally significant.
According to Baysal, the Canhasan specimen is contemporary with those found in Çatalhöyük, and all known examples come from within modern Türkiye’s borders. This strengthens the view that obsidian mirror-making was a distinctly Anatolian innovation, rooted in local craftsmanship and technological expertise.
“These mirrors require an exceptional level of skill,” Baysal notes. “The production process is incredibly challenging—obsidian must be carefully shaped and polished using abrasive materials. This was not a casual craft; it was a specialized technology.”
Obsidian, valued for its sharp edges and glasslike sheen, was widely used across the ancient Near East for toolmaking, ritual objects, and long-distance trade. The presence of a mirror suggests both symbolic and possibly ritual significance—perhaps tied to personal identity, status, or spirituality.
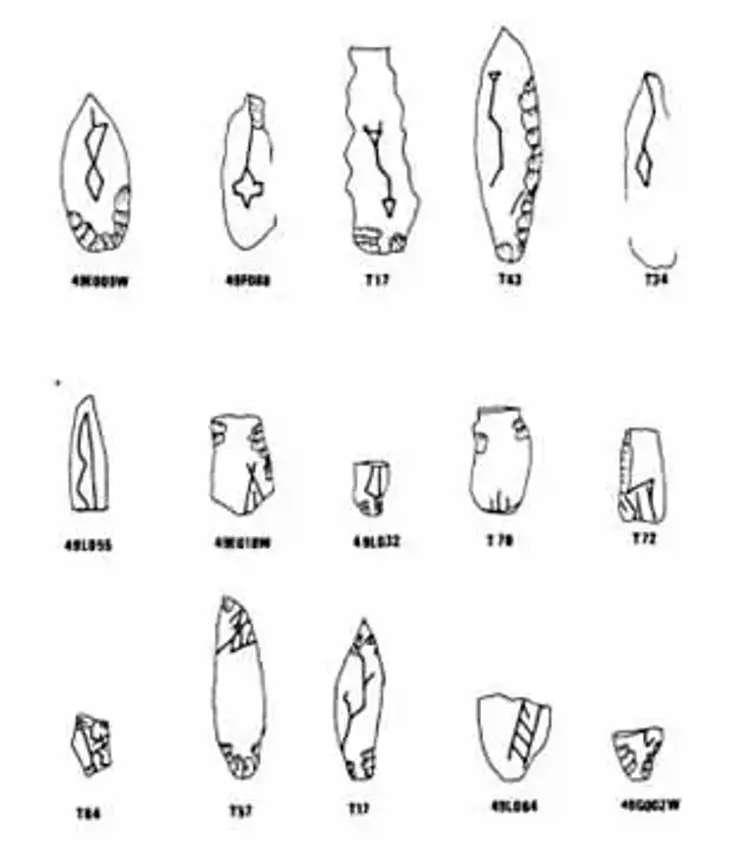
Incised Arrowheads Reveal a Local Symbolic Tradition
The team also uncovered a number of obsidian arrowheads decorated with fine linear incisions—patterns that appear to be unique to the Canhasan region.
“These engraved pieces indicate a long-standing local tradition,” says Baysal. “While obsidian is found in many Neolithic sites, this specific incised style seems so far to be exclusive to Canhasan.”
Archaeologists believe the engraved motifs may have held symbolic meaning—possibly related to social identity, ownership, or ritual practices. Such symbolic expression is a defining trait of Neolithic communities transitioning from nomadic life to permanent agricultural settlements.
Rewriting the Story of Central Anatolia’s Neolithic Culture
For decades, Çatalhöyük has dominated academic and public attention as the heart of Central Anatolia’s Neolithic world. Its murals, figurines, and complex architecture have shaped global narratives about early farming societies.
But Baysal emphasizes that this story is incomplete. “Up until now, we have learned only the Çatalhöyük chapter of this cultural evolution,” he states.
“Canhasan helps us uncover the earlier chapters—ones that began in sites like Aşıklı Höyük and Boncuklu Höyük, evolved through Canhasan, and eventually culminated in Çatalhöyük.”
This positions Canhasan as a crucial link in understanding how early communities developed symbolic systems, artistic traditions, and advanced craft technologies long before proto-urban megasites emerged.
A Broader Archaeological Context
Located strategically near volcanic obsidian sources in central Türkiye, Canhasan served as a hub for early tool production and innovation. The region’s obsidian was traded widely across the Near East, reaching as far as the Levant.
Archaeologists highlight several reasons why Canhasan is so important:
Continuity of occupation: The site was inhabited from the Pre-Pottery Neolithic through the Chalcolithic period.
Craft specialization: The mirror and incised tools demonstrate advanced craftsmanship far earlier than once assumed.
Symbolic culture: Engraved tools suggest complex social practices.
Urban precursors: The 10,000-year-old street supports emerging theories about early settlement planning.
Together, these insights challenge long-held assumptions that symbolic and technological sophistication emerged suddenly in large Neolithic towns. Instead, sites like Canhasan show a gradual, interconnected cultural evolution across Central Anatolia.

A New Chapter for Anatolia’s Deep Past
As excavations continue, researchers hope to uncover additional evidence that will illuminate the daily lives, rituals, and technological capabilities of Canhasan’s earliest inhabitants. Each new discovery adds depth to the story of how the world’s first settled societies organized themselves, shaped their tools, and expressed their identities.
For now, the obsidian mirror stands as a brilliant reminder—both literally and metaphorically—of the ingenuity and creativity of the Neolithic peoples who once lived in the high plains of Central Anatolia.
Cover Image Credit: The Canhasan Archaeological Excavation Team
















