In the Dorset Downs, a significant landscaping project has revealed a plethora of intriguing findings on a grand scale.
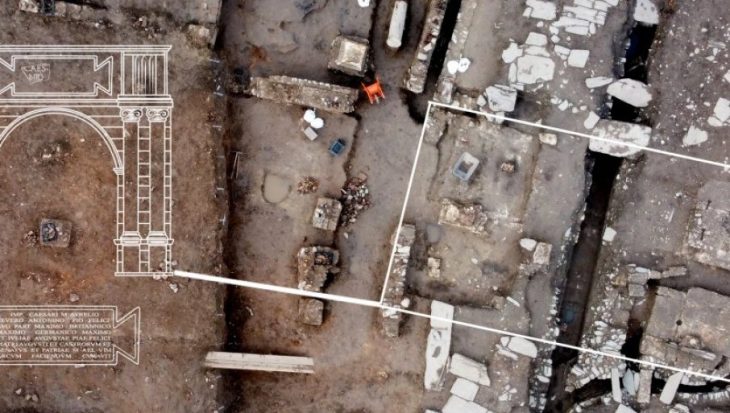
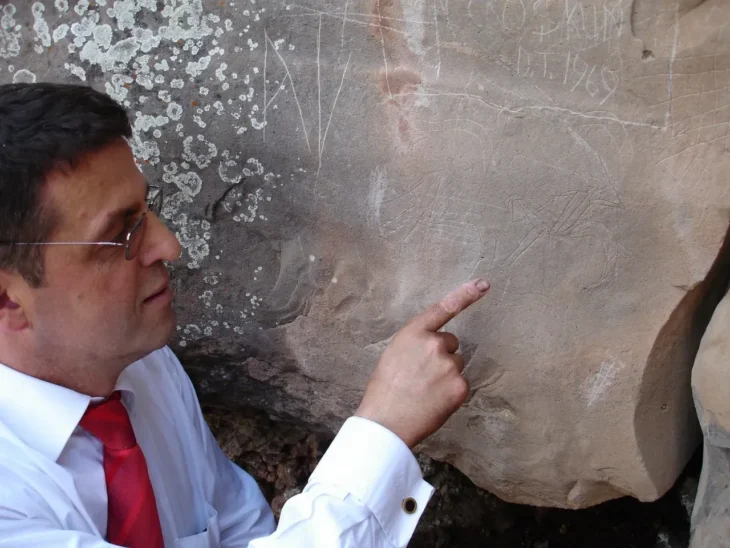
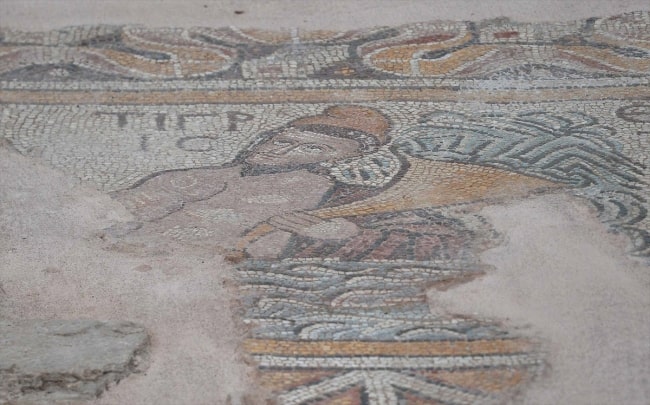
Excavations ahead of the works revealed a Roman settlement, as well as Neolithic and Bronze Age, finds. The oldest artifacts were flint tools and pottery from about 4,000 BC.
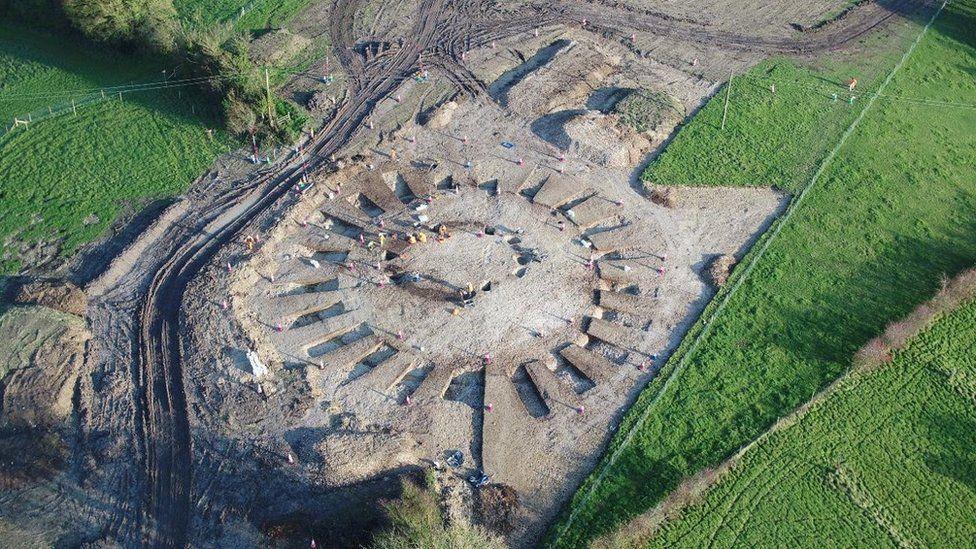
More than 25 archaeologists have unearthed convincing evidence of human activity in the region stretching back 6,000 years, barely 20 months after National Grid began work on its Dorset Visual Impact Provision (VIP) project just outside Dorchester in 2018.
By dismantling 22 pylons and replacing an 8.8km length of overhead line with subterranean cables in the villages of Winterbourne Abbas, Winterbourne Steepleton, Martinstown, and Friar Waddon, National Grid’s VIP project will enhance vistas of the Dorset Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB). It’s one of the first projects in the world to remove existing high-voltage electricity transmission infrastructure solely to enhance the landscape.
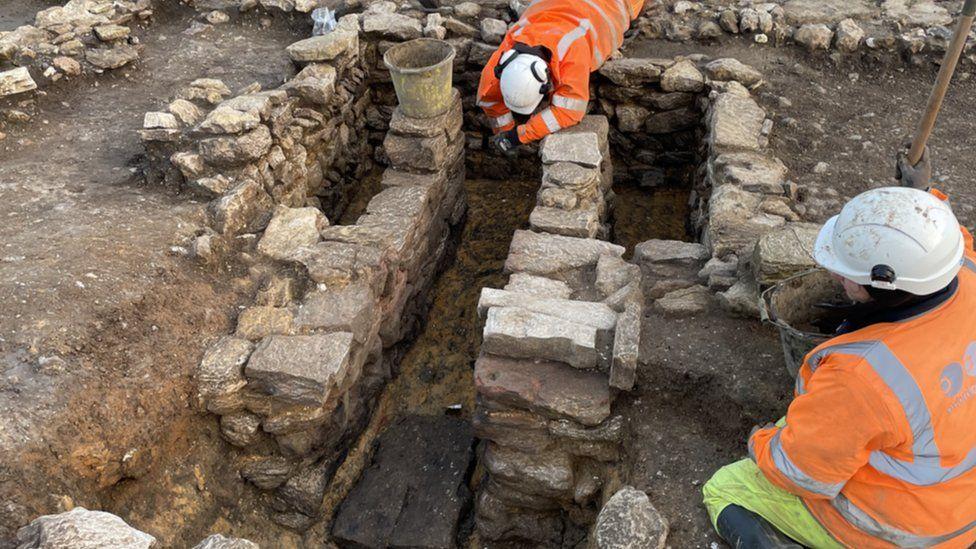

Work concluded last month and initial results are being revealed in a series of webinars hosted by the National Grid.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
At one of the sites, they discovered eight late Roman eight stone buildings, as well as a corn dryer, two enormous malting ovens, and several millstones that would have required livestock, water, or slave labor to operate.
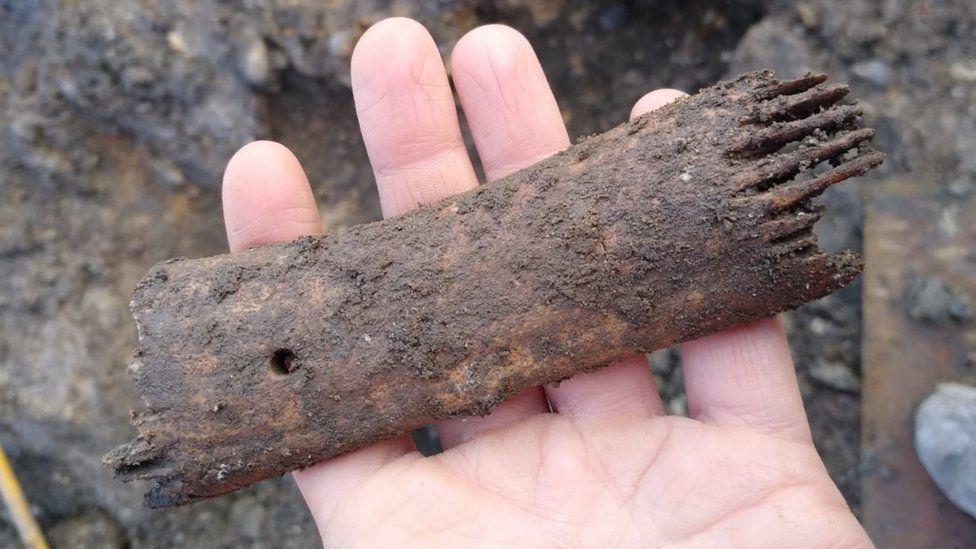

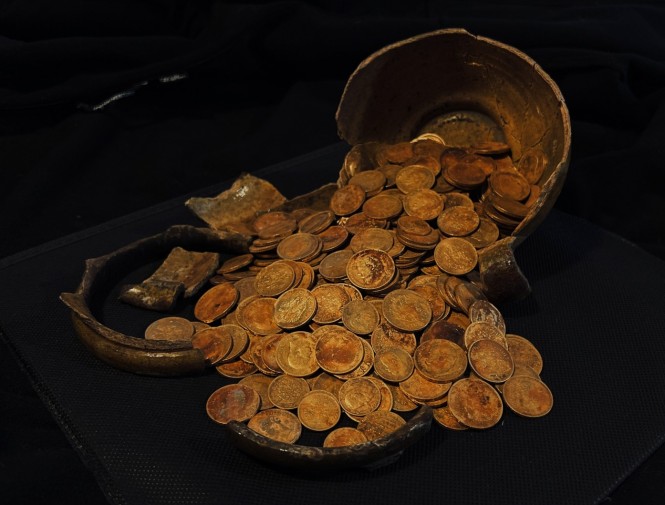
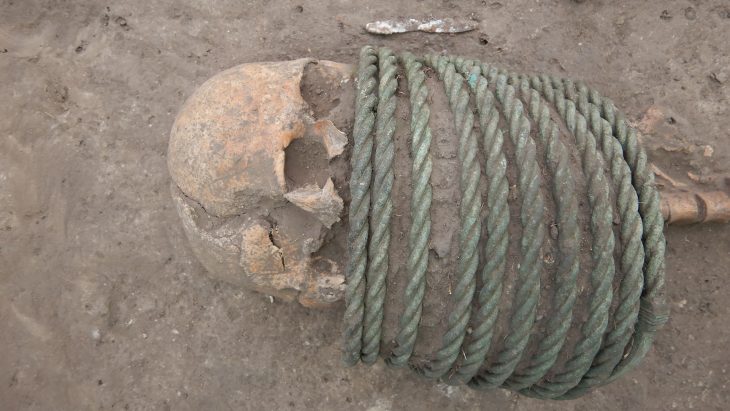
Archaeologists also found 34 burials accompanied by Iron Age pottery, suggesting the site was occupied for about 500 years.
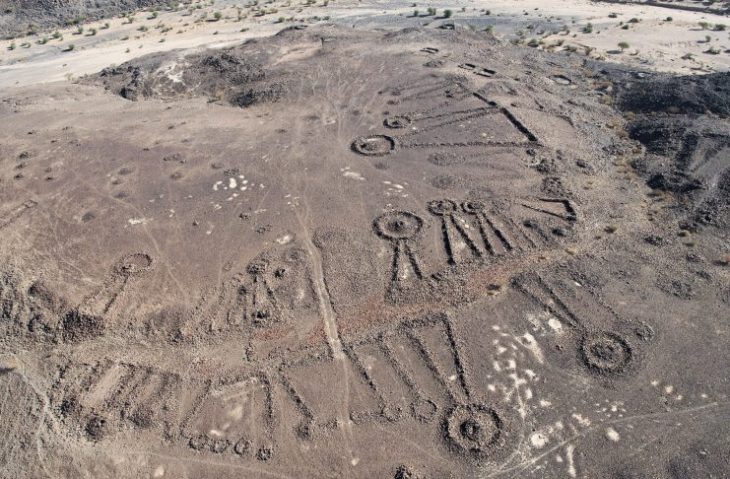
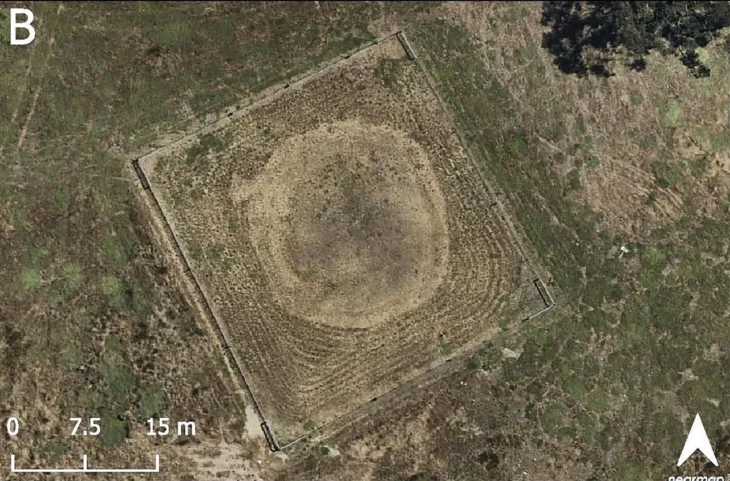
The investigations, which involved Historic England, the Dorset AONB Partnership and the Dorset county archaeologist, also revealed a cremation cemetery, believed to be Bronze Age, and 11 barrows – or burial mounds.
Oxford Archaeology senior project manager John Boothroyd said, although the archaeological potential of the sites had been assessed during pre-construction works, “it didn’t stop the scale of the archaeological remains identified far exceeding our expectations”.
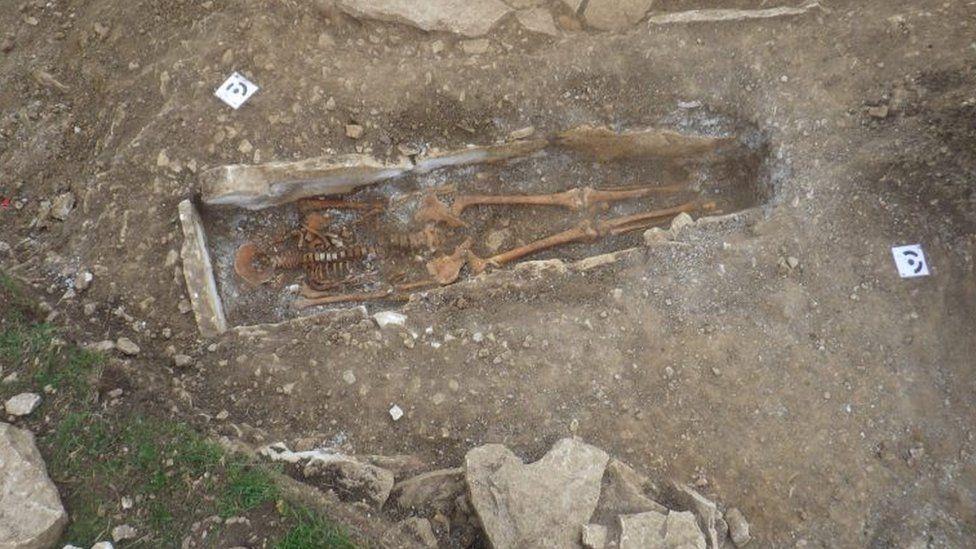

Analysing and recording the thousands of finds is expected to take up to two years.
National Grid lead project manager Paul Hamnett said: “The scale of the archaeology work is incredible. This is a scheme designed to enhance the landscape and enrich local experience. We are looking forward to sharing what we’ve discovered.”
The Dorset Visual Impact Provision project involves the removal of 22 pylons from the area which is designated as a landscape of national importance.
Dorset AONB is the fifth largest in the UK. It stretches from Lyme Regis to Poole Harbour and inland to Blandford.
Cover Photo: NATIONAL GRID
Source: Dorsetecho