5,000-year-old bread found in Küllüoba Höyük, Turkey reveals ancient baking methods and fertility rituals. Unique archaeological discovery with rich nutritional insights.
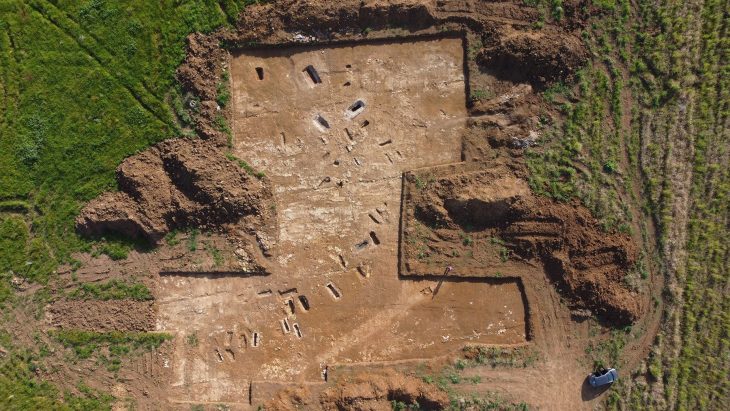
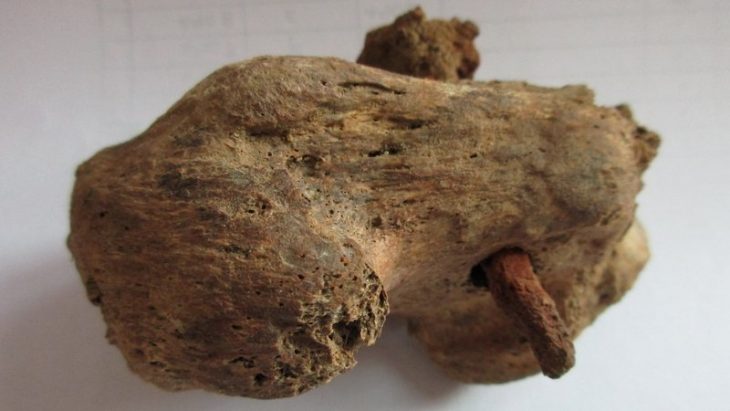
Archaeologists at the Küllüoba Höyük excavation site in Seyitgazi, Eskişehir, have uncovered an extraordinary 5,000-year-old ancient bread, providing unique insights into early Neolithic baking methods and ritual practices. The rare discovery reveals that the bread was intentionally burned and buried as part of a fertility ritual, a practice unseen in many ancient settlements.
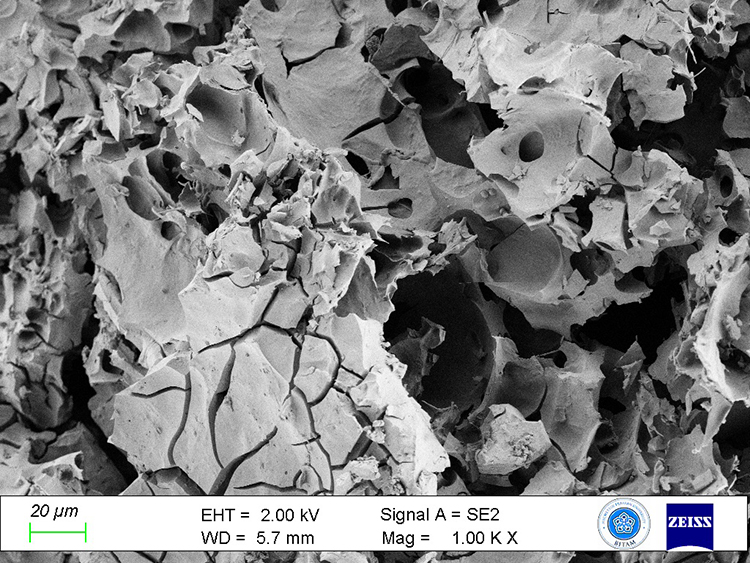
Conducted under official permits from the General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums, the excavation revealed the carbonized “Küllüoba bread” buried at the threshold of a dwelling’s rear chamber. Advanced electron microscopy analysis identified the bread’s composition: primarily emmer wheat (locally called gernik or kavılca) combined with lentils.
Ancient Baking Techniques and Nutritional Profile
Led by Prof. Dr. Murat Türkteki of Bilecik Şeyh Edebali University, the research showed the dough was fermented and baked at around 150°C, with a well-cooked crust and a softer interior. In a statement to Anadolu Agency (AA), Prof. Türkteki explained that emmer wheat, notable for its high protein and low gluten content, forms the bread’s main ingredient. The bread is also rich in B vitamins, antioxidants, dietary fiber, and resistant starch, which helps regulate blood sugar.

This nutritious, low-gluten bread likely had practical dietary benefits but also carried symbolic significance due to its unique preparation.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Ritual Significance: A Fertility Offering
Remarkably, the bread’s fragment was deliberately broken, burned, and buried beneath red-colored soil in the house’s threshold, indicating its use as a ritualistic object to invoke fertility or blessing. This discovery provides rare evidence of Neolithic spiritual practices linked to food.
Prof. Türkteki emphasized, “The bread’s carbonization and burial demonstrate ritual use, possibly related to prosperity and protection.”
Rare Archaeological Find in Anatolia
Organic materials like bread rarely survive millennia, making this find invaluable. It is only the second well-preserved baked bread unearthed in Anatolia, after an unbaked example found at Çatalhöyük. This discovery marks a crucial milestone in understanding ancient Anatolian culinary traditions and cultural rituals.
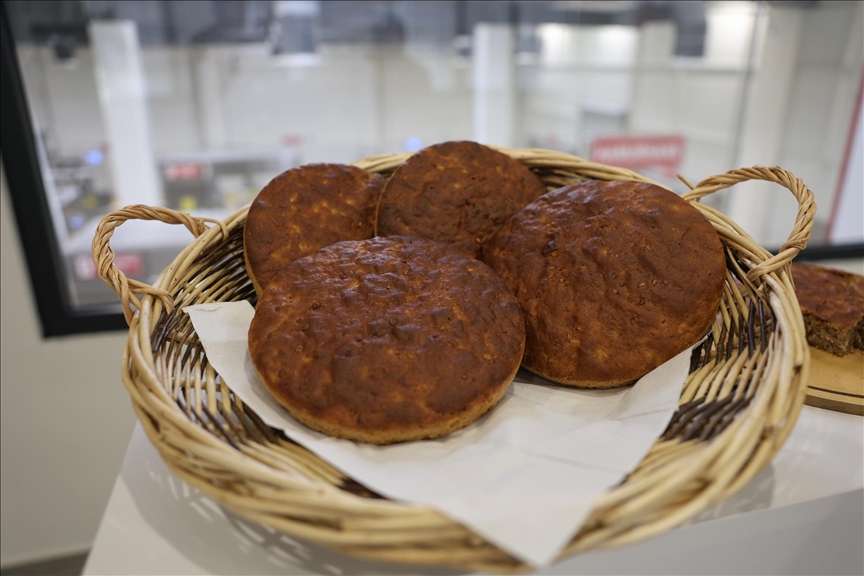
Modern Revival of the Küllüoba Bread
In homage to this historic find, Eskişehir Metropolitan Municipality’s Halk Ekmek Factory has begun producing the “Küllüoba Bread,” available in local markets for 50 Turkish Lira, bridging past and present culinary heritage.
Cover Image Credit: Küllüoba Excavation Directorate